10.2 POJA-L2128+2061+2130+2005
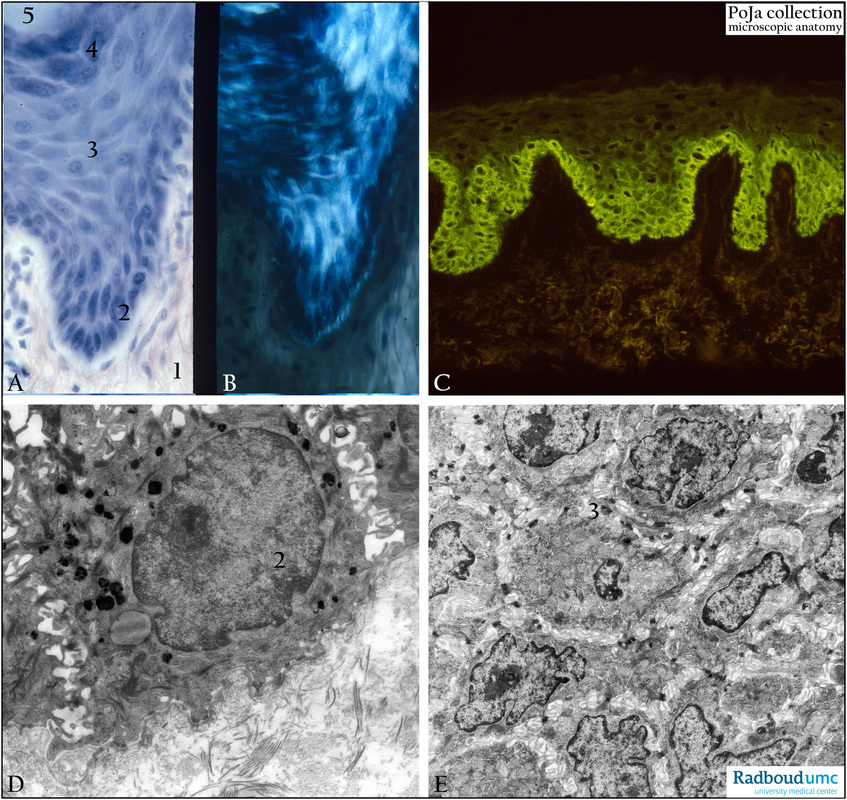
Title: Stratum germinativum (stratum basale) of the epidermis
Description:
(A, B): Foot sole, stain hematoxylin-eosin (left) and polarization microscopy (right), human.
(1) Dermis, connective tissue.
(2) Stratum basale (stratum germinativum) or basal layer (germinal layer).
(3) Stratum spinosum (spinous layer).
(4) Stratum granulosum (granular layer).
(5) Stratum lucidum (translucent layer).
Background:
Stratum malpighi (Malpighian layer) is defined as both the basal layer and the spinous layer
(C): Back skin, FITC-immunofluorescence staining with monoclonal antibodies RCK102 against keratin 5+8, human.
These cytokeratins 5 and 8 are mostly expressed in the basal layer (or stratum germinativum).
(D): Back skin, electron micrograph of a basal cell, human.
The basal cell (2) is connected to neighboring cells with desmosomal junctions who are enforced by cytokeratin filaments
as shown by immunofluorescence in (C).
The basal cell can also contain dark aggregates of melanin derived from melanosomes produced by melanocytes and passed
by to basal cells. The basal cell is also anchored to the basal lamina by hemidesmosomes. Hemidesmosomes use desmopenetrin
as cell adhesion proteins.
(E): Back skin, electron micrograph of stratum spinosum, human.
(3) Stratum spinosum (spinous layer) with cells that are bridged together by numerous stellate-like desmosomal junctions.
Keywords/Mesh: skin, epidermis, stratum basale (germinativum), stratum spinosum, cytokeratin, desmosome, histology,
electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Stratum germinativum (stratum basale) of the epidermis
Description:
(A, B): Foot sole, stain hematoxylin-eosin (left) and polarization microscopy (right), human.
(1) Dermis, connective tissue.
(2) Stratum basale (stratum germinativum) or basal layer (germinal layer).
(3) Stratum spinosum (spinous layer).
(4) Stratum granulosum (granular layer).
(5) Stratum lucidum (translucent layer).
Background:
Stratum malpighi (Malpighian layer) is defined as both the basal layer and the spinous layer
(C): Back skin, FITC-immunofluorescence staining with monoclonal antibodies RCK102 against keratin 5+8, human.
These cytokeratins 5 and 8 are mostly expressed in the basal layer (or stratum germinativum).
(D): Back skin, electron micrograph of a basal cell, human.
The basal cell (2) is connected to neighboring cells with desmosomal junctions who are enforced by cytokeratin filaments
as shown by immunofluorescence in (C).
The basal cell can also contain dark aggregates of melanin derived from melanosomes produced by melanocytes and passed
by to basal cells. The basal cell is also anchored to the basal lamina by hemidesmosomes. Hemidesmosomes use desmopenetrin
as cell adhesion proteins.
(E): Back skin, electron micrograph of stratum spinosum, human.
(3) Stratum spinosum (spinous layer) with cells that are bridged together by numerous stellate-like desmosomal junctions.
Keywords/Mesh: skin, epidermis, stratum basale (germinativum), stratum spinosum, cytokeratin, desmosome, histology,
electron microscopy, POJA collection