14.6 POJA-L6175+6176+6177 Cellular infiltrate in skeletal muscle (human)
14.6 POJA-L6175+6176+6177 Cellular infiltrate in skeletal muscle (human)
(By courtesy of H. ter Laak PhD Section Neuropathology, retired staff member Department of Pathology, Radboud university medical centre, Nijmegen, The Netherlands)
Title: Cellular infiltrate in skeletal muscle (human)
Description:
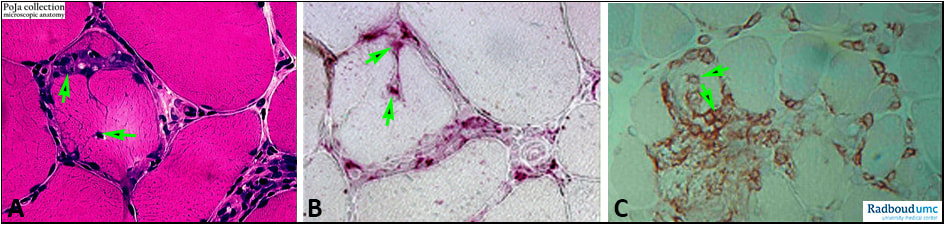
(A): Haematoxylin-eosin staining of skeletal muscle cells. The arrows point to invading leucocytes mixed with macrophages as in the case of polymyositis and inclusion body myositis.
(B): Acid phosphatase staining visualising the infiltrating cells (arrows) in non-necrotic muscle fibers. This hydrolytic enzyme is used as a marker and is abundantly present in leucocytes, macrophages, is therefore indicative for processes of breakdown and digestion.
(C): (Arrows). CD8 immunostaining of infiltrating CD8 positive T cells or cytotoxic lymphocytes.
Cellular infiltrate in non-necrotic muscle fibres usually occurs in inflammatory muscle diseases e.g. polymyositis with locations also in perivascular, perimysial and endomysial regions.
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, skeletal muscle, striated muscle, neuromuscular disease, myopathy, inflammation, CD8, acid phosphatase, pathology, POJA collection
Title: Cellular infiltrate in skeletal muscle (human)
Description:
(A): Haematoxylin-eosin staining of skeletal muscle cells. The arrows point to invading leucocytes mixed with macrophages as in the case of polymyositis and inclusion body myositis.
(B): Acid phosphatase staining visualising the infiltrating cells (arrows) in non-necrotic muscle fibers. This hydrolytic enzyme is used as a marker and is abundantly present in leucocytes, macrophages, is therefore indicative for processes of breakdown and digestion.
(C): (Arrows). CD8 immunostaining of infiltrating CD8 positive T cells or cytotoxic lymphocytes.
Cellular infiltrate in non-necrotic muscle fibres usually occurs in inflammatory muscle diseases e.g. polymyositis with locations also in perivascular, perimysial and endomysial regions.
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, skeletal muscle, striated muscle, neuromuscular disease, myopathy, inflammation, CD8, acid phosphatase, pathology, POJA collection