15.2 POJA-L7026+7028+7027 Elastic cartilage
15.2 POJA-L7026+7028+7027 Elastic cartilage
Title: Elastic cartilage
Description:
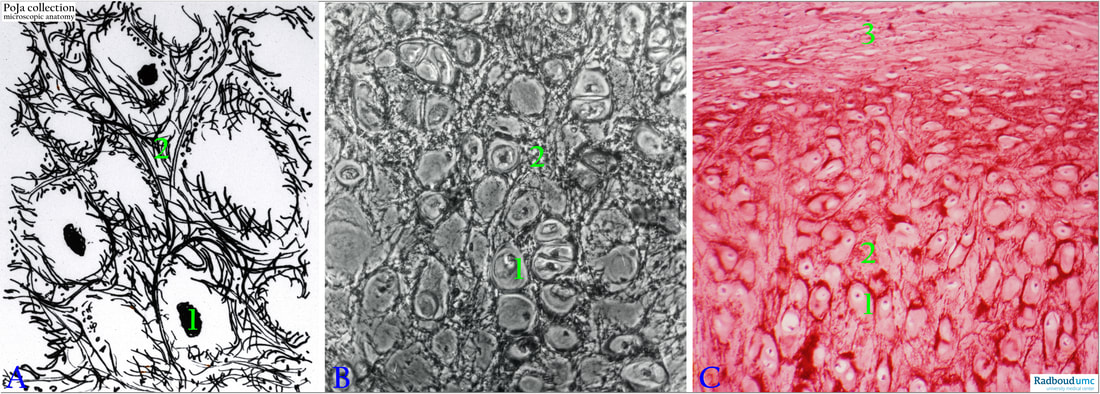
Scheme (A), Phase contrast (B) and orcein stained (C) elastic cartilage (human, epiglottis).
(1): Chondrocytes.
(2): Reddish stained elastic fibres.
(3): Perichondrium.
Background:
Elastic cartilage contains nonmasked elastic fibre network in the interterritorial matrix. Like hyaline cartilage the elastic cartilage also contains masked collagen fibres. The perichondrium with small spindle shaped chondroblasts runs parallel to the surface. Elastic cartilage occurs in the auricular cartilage, epiglottis, vocal processes and in part of the small bronchi.
The ECM of elastic cartilage is also produced by chondroblasts in the inner perichondrium and contains elastin, fibrillin, various collagen types (II, IX, X, XI) and proteoglycans (in majority aggrecan). The glycosaminoglycan chains in the aggrecan attract water and due to the osmotic effect the elastic cartilage has shock-absorbing and lubricating properties. The elastic fibres are composed of large amounts of elastin proteins that co-polymerise with fibrillin present in so-called microfibrils.
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, cartilage, elastic, matrix, chondrocyte, elastic fibre, orcein stain, histology, POJA collection
Title: Elastic cartilage
Description:
Scheme (A), Phase contrast (B) and orcein stained (C) elastic cartilage (human, epiglottis).
(1): Chondrocytes.
(2): Reddish stained elastic fibres.
(3): Perichondrium.
Background:
Elastic cartilage contains nonmasked elastic fibre network in the interterritorial matrix. Like hyaline cartilage the elastic cartilage also contains masked collagen fibres. The perichondrium with small spindle shaped chondroblasts runs parallel to the surface. Elastic cartilage occurs in the auricular cartilage, epiglottis, vocal processes and in part of the small bronchi.
The ECM of elastic cartilage is also produced by chondroblasts in the inner perichondrium and contains elastin, fibrillin, various collagen types (II, IX, X, XI) and proteoglycans (in majority aggrecan). The glycosaminoglycan chains in the aggrecan attract water and due to the osmotic effect the elastic cartilage has shock-absorbing and lubricating properties. The elastic fibres are composed of large amounts of elastin proteins that co-polymerise with fibrillin present in so-called microfibrils.
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, cartilage, elastic, matrix, chondrocyte, elastic fibre, orcein stain, histology, POJA collection