5.4.3 POJA-L4258+2436+La0058+2405+La0060+2411+2372+La0064
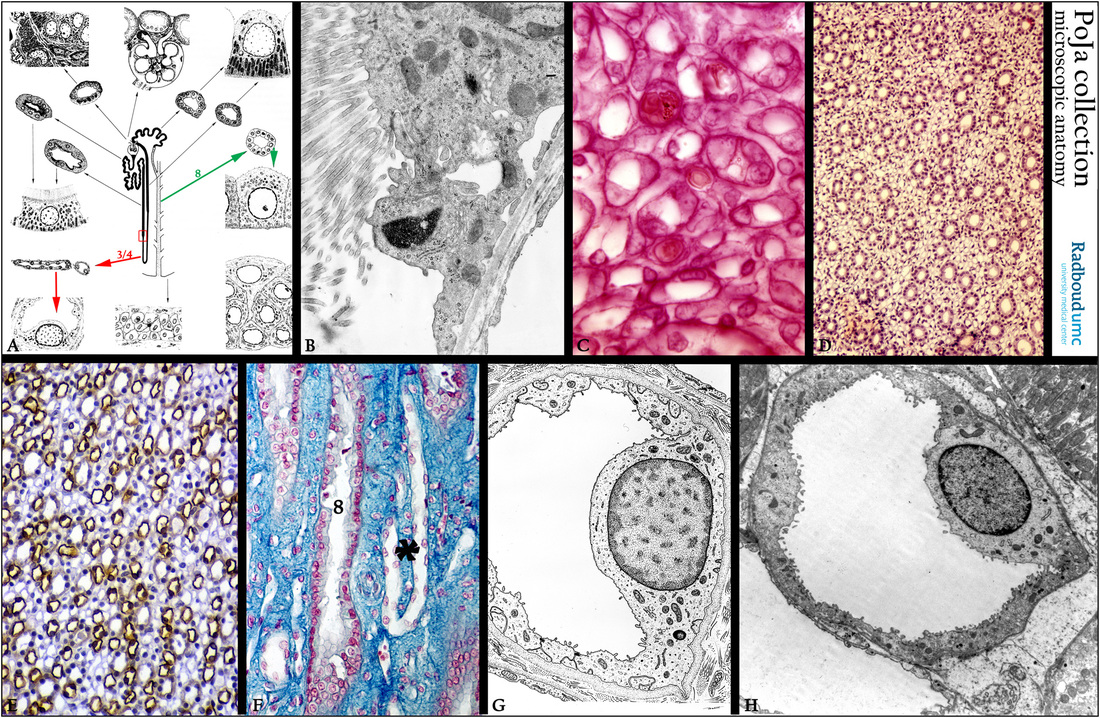
Title: Intermediate tubules (DTL and ATL) (III) in the kidney
Description:
(A): Scheme nephron, human. (Zoom in). The red frame and arrows (3/4) illustrate the descending thin limb (DTL), while the green
frame (8) points to collecting tubule.
(B): Electron microscopy, rat. Detail of the transition zone (red frame in A) from proximal straight tubule (PST) in a descending
thin limb (DTL): a lining cell studded with numerous long slender microvilli is abruptly followed by a flattened “bald” cell.
(C): Stain eosin, rat. Below part of an inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD), few capillaries with orange-like erythrocytes and intermediate tubules (or thin loops of Henle: descending thin limb (DTL) + ascending thin limb (ATL).
(D): Stain hematoxylin-eosin, rat. Cross sections through inner medulla collecting tubules (IMCD) and thin loops of Henle.
(E): Immunoperoxidase staining with DAB and antibodies against parvalbumin, rat. Inner medulla showing positive staining on thin loops
of Henle (DTL and ATL), but weakly in the inner medullary collecting ducts (IMCD) and capillaries are negative.
Parvalbumin, a calcium-binding protein, localizes in the thick ascending loop of Henle, the distal convoluted tubule, the connecting tubule and the intercalated cells of the collecting duct.
It is present in a thin cytosolic layer along the basolateral membrane and it is thought to be involved in the regulation of transport processes located in these membranes.
(F): Stain Azan, inner medulla, human. A longitudinal sectioned IMCD (8) next to the “hook” (*) of the intermediate tubule reversing upwards.
(G): Electron microscopy scheme of an intermediate tubule.
(H): Electron micrograph of an intermediate tubule in outer medulla, rat. DTL (type II epithelium) of a long-looped nephron.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, medulla, tubule,Henle, intermediate tubule, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Intermediate tubules (DTL and ATL) (III) in the kidney
Description:
(A): Scheme nephron, human. (Zoom in). The red frame and arrows (3/4) illustrate the descending thin limb (DTL), while the green
frame (8) points to collecting tubule.
(B): Electron microscopy, rat. Detail of the transition zone (red frame in A) from proximal straight tubule (PST) in a descending
thin limb (DTL): a lining cell studded with numerous long slender microvilli is abruptly followed by a flattened “bald” cell.
(C): Stain eosin, rat. Below part of an inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD), few capillaries with orange-like erythrocytes and intermediate tubules (or thin loops of Henle: descending thin limb (DTL) + ascending thin limb (ATL).
(D): Stain hematoxylin-eosin, rat. Cross sections through inner medulla collecting tubules (IMCD) and thin loops of Henle.
(E): Immunoperoxidase staining with DAB and antibodies against parvalbumin, rat. Inner medulla showing positive staining on thin loops
of Henle (DTL and ATL), but weakly in the inner medullary collecting ducts (IMCD) and capillaries are negative.
Parvalbumin, a calcium-binding protein, localizes in the thick ascending loop of Henle, the distal convoluted tubule, the connecting tubule and the intercalated cells of the collecting duct.
It is present in a thin cytosolic layer along the basolateral membrane and it is thought to be involved in the regulation of transport processes located in these membranes.
(F): Stain Azan, inner medulla, human. A longitudinal sectioned IMCD (8) next to the “hook” (*) of the intermediate tubule reversing upwards.
(G): Electron microscopy scheme of an intermediate tubule.
(H): Electron micrograph of an intermediate tubule in outer medulla, rat. DTL (type II epithelium) of a long-looped nephron.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, medulla, tubule,Henle, intermediate tubule, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection