16.1.3 POJA-L7055+7056+7057+7058 Osteoclast 1
16.1.3 POJA-L7055+7056+7057+7058 Osteoclast 1
Title: Osteoclast 1
Description:
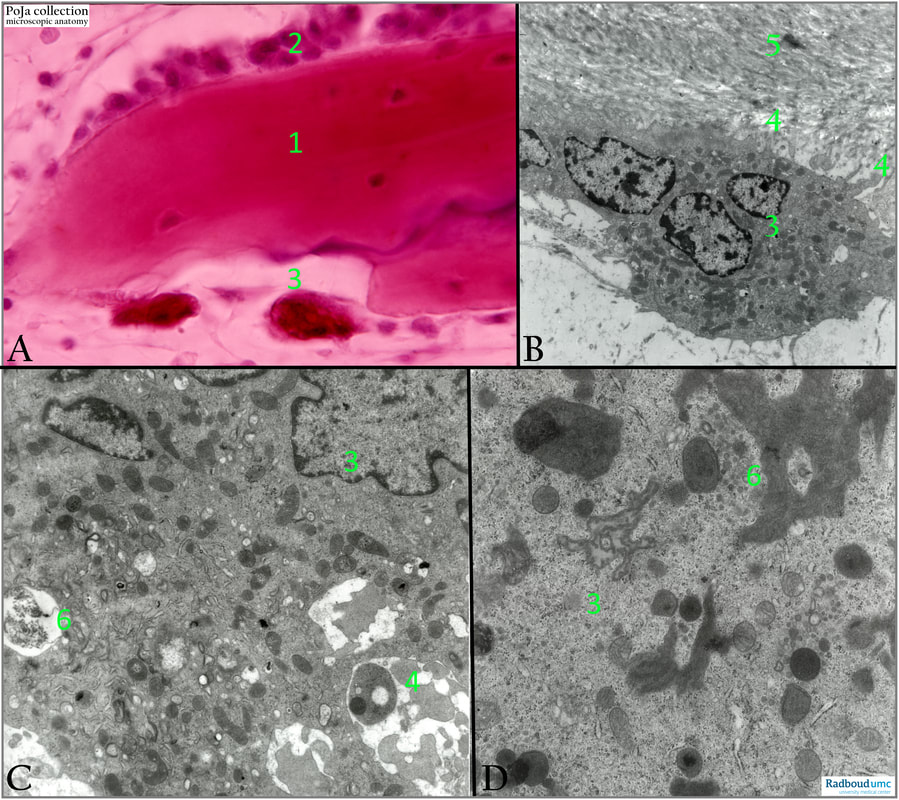
(A): Human foetus, desmal ossification, Haematoxylin-eosin stain.
(1): Osteoid or non-mineralised bone matrix.
(2): Osteoblasts in a row along the osteoid (predominantly type I collagen masked by groundsubstance).
(3): Osteoclast.
(B+C+D): Electron micrographs of osteoclast in woven bone, rabbit.
(3): Osteoclast apposed to the matrix of woven bone.
(4): Note the numerous cytoplasmic processes.
(5):Bone matrix.
(6): Lysosome.
Background:
Before osteoclasts start bone degradation, they have to be activated and will become highly polarised. Active osteoclasts show the following specialised three regions:
1.The ruffled border: contact zone of osteoclast with bone tissue.
2. The clear zone (sealing zone): peripheral cytoplasm bordering the area of the ruffled border.
3. The basolateral region of the cytoplasm: exocytosis of digested material (opposite side of the ruffled border).
General physiological activities:
See also:
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, bone, foetus, desmal ossification, osteoblast, osteoid, osteoclast, lysosome, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection
Title: Osteoclast 1
Description:
(A): Human foetus, desmal ossification, Haematoxylin-eosin stain.
(1): Osteoid or non-mineralised bone matrix.
(2): Osteoblasts in a row along the osteoid (predominantly type I collagen masked by groundsubstance).
(3): Osteoclast.
(B+C+D): Electron micrographs of osteoclast in woven bone, rabbit.
(3): Osteoclast apposed to the matrix of woven bone.
(4): Note the numerous cytoplasmic processes.
(5):Bone matrix.
(6): Lysosome.
Background:
Before osteoclasts start bone degradation, they have to be activated and will become highly polarised. Active osteoclasts show the following specialised three regions:
1.The ruffled border: contact zone of osteoclast with bone tissue.
2. The clear zone (sealing zone): peripheral cytoplasm bordering the area of the ruffled border.
3. The basolateral region of the cytoplasm: exocytosis of digested material (opposite side of the ruffled border).
General physiological activities:
- Lysosomes ares striking in the osteoclast, their contents are released between the processes of the ruffled border;
- After acidification of the resorption groove microenvironment the degradation of bone matrix collagen, proteins starts by secreted cathepsin and matrix metalloproteinases;
- After resorption of bone tissue the osteoclasts undergo apoptosis. It is known that normal and dying osteocytes communicate with osteoclasts to engage them for remodelling processes;
- At sites of bone damage apoptotic osteocytes produce apoptotic bodies that re-express RANKL molecules resulting in increased osteoclastic activities.
See also:
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, bone, foetus, desmal ossification, osteoblast, osteoid, osteoclast, lysosome, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection