13.1 POJA-L4670+La0293+La0295+L4599
Title: Muscular artery: light and electron microscopy
Description:
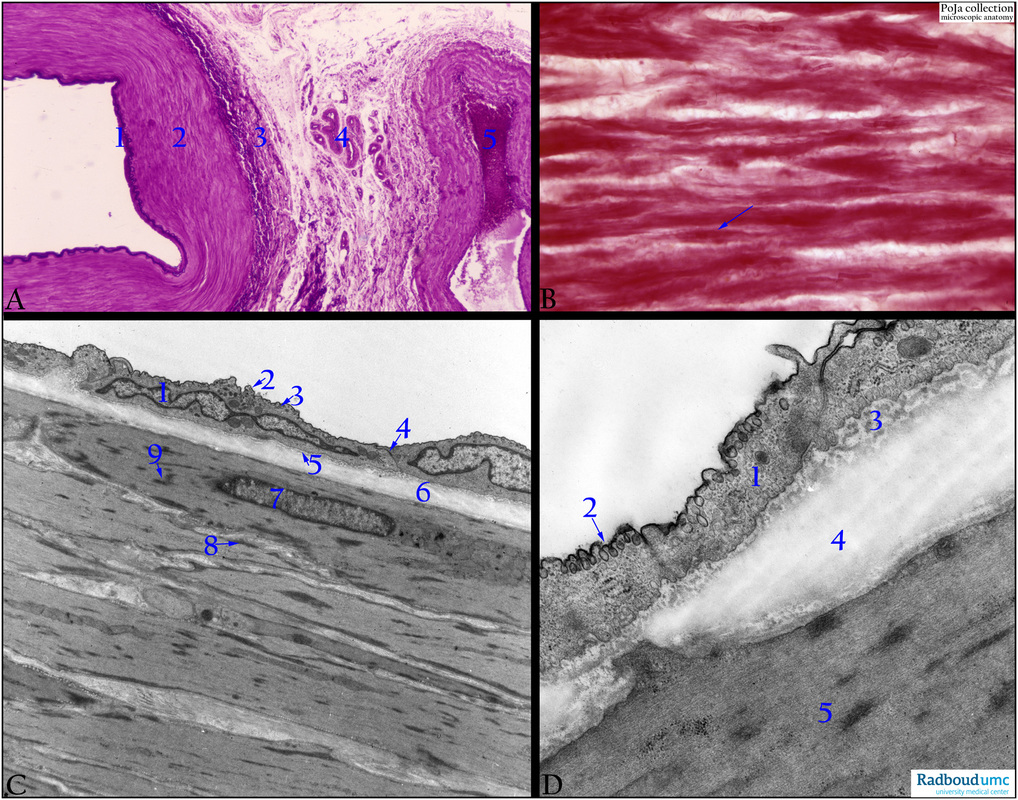
(A): Mid-sized muscular artery/vein (cubital artery/vein), Haematoxylin-elastica (Weigert), human. Muscular artery with intima with IEL (1). Media (2). Adventitia (3) with vasa vasorum (4). Vein (concomittant vein) with circular arranged smooth muscle cells (SMC) in the media-adventitia. (5) Lumen vein.
(B): Circular arranged SMC in media (femoral artery), Azan, human. Some SMC (arrow) show slender nuclei.
(C): Mid-sized muscular artery (branch of bronchial artery), EM, golden hamster. The intima is lined by endothelial cells (1), provided with caveolae (2) and pinocytotic vesicles (3). The two endothelial cells are firmly attached to each other by junctions (4). A thin basal lamina (5) separates the cell from scarcely distributed subendothelial tissue with thin collagen fibrils followed by (6) the distinct internal elastic lamina (IEL). The media consists of smooth muscle cells (SMC) or myocytes (7) with their characteristic filamentous sarcoplasm, focal attachment densities (8) and dense bodies (9).
(D): Muscular artery (femoral artery), EM, golden hamster. (1) Endothelium with caveolae (2). (3) Subendothelial collagen fibrils. (4) IEL with gap of myocyte-endothelial contact. (5) Myocyte with densities.
Background: A muscular artery (or distributing artery) contains a fenestrated internal elastic lamina (IEL) 2-3 micrometers between the intima and media. Endothelial processes through the pores of the IEL contact by gap junctions the smooth muscle cells (SMC) of the adjacent media with its finely distributed elastic fibers between the SMCs. In small arteries (8-10 layers of SMCs) and larger arteries (3- 30 layers of SMCs) mutual nexus contacts of SMCs are present. The boundary line with the surrounding adventitia is marked by an external elastic lamina (EEL) that sometimes appear discontinuous. It is followed by numerous elastic fibres in the collagenous adventitia where SMCs might be present especially in larger muscular arteries. Different muscular arteries show a distinct variation in the muscular building of their wall dependent on the physiological factors in relation to the blood pressure.
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, vascularisation, blood vessel, arteriole , muscular artery, smooth muscle, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Muscular artery: light and electron microscopy
Description:
(A): Mid-sized muscular artery/vein (cubital artery/vein), Haematoxylin-elastica (Weigert), human. Muscular artery with intima with IEL (1). Media (2). Adventitia (3) with vasa vasorum (4). Vein (concomittant vein) with circular arranged smooth muscle cells (SMC) in the media-adventitia. (5) Lumen vein.
(B): Circular arranged SMC in media (femoral artery), Azan, human. Some SMC (arrow) show slender nuclei.
(C): Mid-sized muscular artery (branch of bronchial artery), EM, golden hamster. The intima is lined by endothelial cells (1), provided with caveolae (2) and pinocytotic vesicles (3). The two endothelial cells are firmly attached to each other by junctions (4). A thin basal lamina (5) separates the cell from scarcely distributed subendothelial tissue with thin collagen fibrils followed by (6) the distinct internal elastic lamina (IEL). The media consists of smooth muscle cells (SMC) or myocytes (7) with their characteristic filamentous sarcoplasm, focal attachment densities (8) and dense bodies (9).
(D): Muscular artery (femoral artery), EM, golden hamster. (1) Endothelium with caveolae (2). (3) Subendothelial collagen fibrils. (4) IEL with gap of myocyte-endothelial contact. (5) Myocyte with densities.
Background: A muscular artery (or distributing artery) contains a fenestrated internal elastic lamina (IEL) 2-3 micrometers between the intima and media. Endothelial processes through the pores of the IEL contact by gap junctions the smooth muscle cells (SMC) of the adjacent media with its finely distributed elastic fibers between the SMCs. In small arteries (8-10 layers of SMCs) and larger arteries (3- 30 layers of SMCs) mutual nexus contacts of SMCs are present. The boundary line with the surrounding adventitia is marked by an external elastic lamina (EEL) that sometimes appear discontinuous. It is followed by numerous elastic fibres in the collagenous adventitia where SMCs might be present especially in larger muscular arteries. Different muscular arteries show a distinct variation in the muscular building of their wall dependent on the physiological factors in relation to the blood pressure.
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, vascularisation, blood vessel, arteriole , muscular artery, smooth muscle, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection