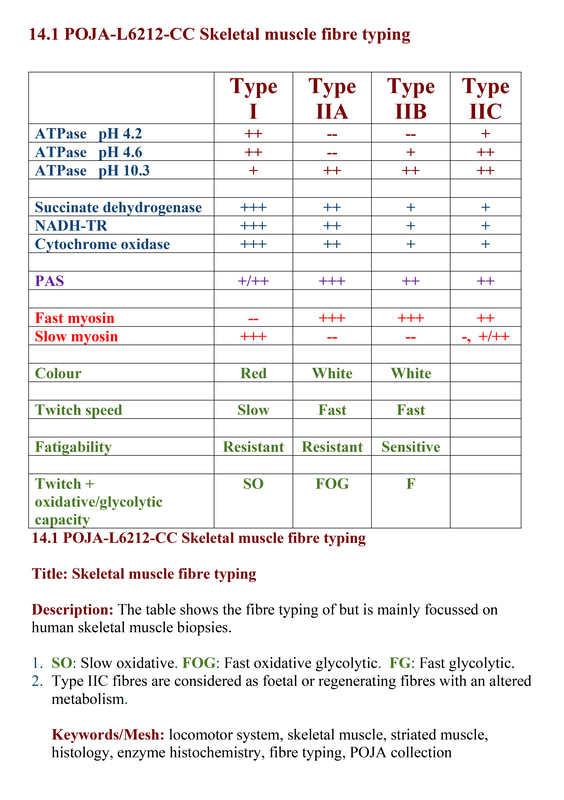
14.1 POJA-L6212-CC
Title: Skeletal muscle fibre typing
Description:
The table shows the fibre typing and is mainly focussed on human skeletal muscle biopsies.
See also:
Background
Type 1 myofibres are the slow-twitch fibres, slow-oxidative (SO) fibres. They have a slow contraction time, and generate less force than type 2 myofibres. They are used for sustained, low-level activity and are equipped with numerous large mitochondria and relatively abundant intracellular lipid for oxidative metabolism.
Type 2 myofibres are the fast-twitch fibres, fast-glycolytic (FG) fibres. They have a rapid contraction time, but they are recruited late and used for brief-duration intense activity and anaerobic metabolism. Their mitochondria are smaller and less numerous, less lipid. The glycogen stores are larger than in type 1 fibres.
Each muscle has its own characteristic composition of type 1 and type 2 fibres, which is determined by its innervation. Myosin-ATPase stain, performed at a pH of 4.3 demonstrates brown staining of the type 1 myofibres. Similar pattern is obtained with immunostaining with anti-myosin antibodies.
For extensive staining patterns of skeletal muscle fibres see: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1923188-overview#a3
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, skeletal muscle, striated muscle, histology, enzyme histochemistry, fibre typing, POJA collection
Title: Skeletal muscle fibre typing
Description:
The table shows the fibre typing and is mainly focussed on human skeletal muscle biopsies.
See also:
- 14.1 POJA-L6212-BB Typing of muscle fibres with ATPase histochemistry
Background
Type 1 myofibres are the slow-twitch fibres, slow-oxidative (SO) fibres. They have a slow contraction time, and generate less force than type 2 myofibres. They are used for sustained, low-level activity and are equipped with numerous large mitochondria and relatively abundant intracellular lipid for oxidative metabolism.
Type 2 myofibres are the fast-twitch fibres, fast-glycolytic (FG) fibres. They have a rapid contraction time, but they are recruited late and used for brief-duration intense activity and anaerobic metabolism. Their mitochondria are smaller and less numerous, less lipid. The glycogen stores are larger than in type 1 fibres.
Each muscle has its own characteristic composition of type 1 and type 2 fibres, which is determined by its innervation. Myosin-ATPase stain, performed at a pH of 4.3 demonstrates brown staining of the type 1 myofibres. Similar pattern is obtained with immunostaining with anti-myosin antibodies.
For extensive staining patterns of skeletal muscle fibres see: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1923188-overview#a3
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, skeletal muscle, striated muscle, histology, enzyme histochemistry, fibre typing, POJA collection
