11.5 POJA-L3062+3034+3063+3064
Title: Blood vessels in cerebrum
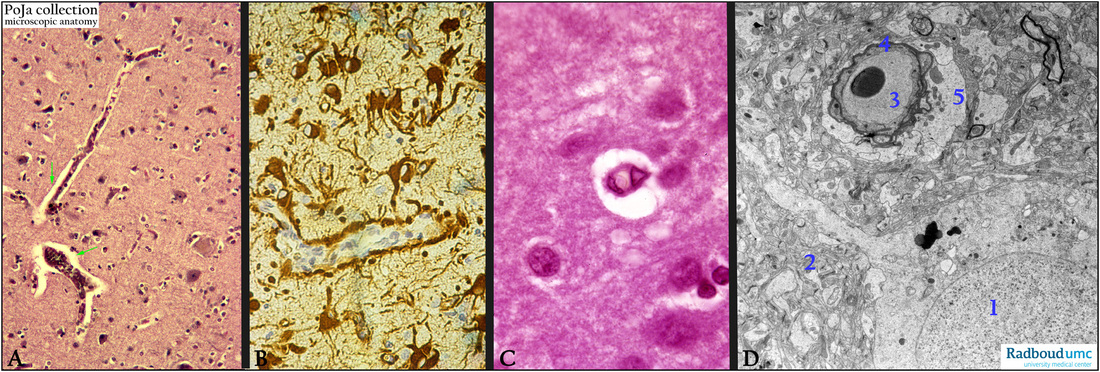
Description:
(A): Stain hematoxylin-eosin, human. Cortex cerebrum with Virchow-Robin spaces (VRS) (arrows), i.e. interstitial perivascular (or paravascular) canals that surround perforating arteries and veins in the parenchym of the brain. These paravascular spaces or channels filled with cerebrospinal fluid are formed between the brain blood vessels and the leptomeningeal sheathes. The VRS drain fluid from the central nervous system to the cervical lymph nodes (sponge-like function).
(See: Glymphatic System in 13.1 POJA-L4750)
(B): Immunoperoxidase staining with DAB and antibodies against GFAP, human. Glial fibrillary acidic protein
is an intermediate filament that is found in glia cells and NOT in ependym.
Here in the cortex they stain the astrocytes up to their endfeet (terminals) that envelop the capillaries.
(By courtesy of H. ter Laak PhD, Department of Pathology, University Medical Centre Radboud University,
Nijmegen, The Netherlands).
(C): Stain hematoxylin-eosin, cortex, human. Detail of the VRS around the blood vessel which is embedded in
surrounding neuropil and myelinated fibers. The larger nuclei are astrocytes, the smaller denser ones are oligodendrocytes.
(D): Electron micrograph of a postoperative biopsy of the cortex (human) showing a neuron (1) embedded in the neuropil (2) in which
the capillary and an erythrocyte in its lumen (3) is surrounded by a pericyte (4) and swollen astrocytic endfeet (5).
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, cerebrum, glymphatic system, neuron, neuropil, Virchow-Robin space, blood-brain-barrier, astrocyte, capillary, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Blood vessels in cerebrum
Description:
(A): Stain hematoxylin-eosin, human. Cortex cerebrum with Virchow-Robin spaces (VRS) (arrows), i.e. interstitial perivascular (or paravascular) canals that surround perforating arteries and veins in the parenchym of the brain. These paravascular spaces or channels filled with cerebrospinal fluid are formed between the brain blood vessels and the leptomeningeal sheathes. The VRS drain fluid from the central nervous system to the cervical lymph nodes (sponge-like function).
(See: Glymphatic System in 13.1 POJA-L4750)
(B): Immunoperoxidase staining with DAB and antibodies against GFAP, human. Glial fibrillary acidic protein
is an intermediate filament that is found in glia cells and NOT in ependym.
Here in the cortex they stain the astrocytes up to their endfeet (terminals) that envelop the capillaries.
(By courtesy of H. ter Laak PhD, Department of Pathology, University Medical Centre Radboud University,
Nijmegen, The Netherlands).
(C): Stain hematoxylin-eosin, cortex, human. Detail of the VRS around the blood vessel which is embedded in
surrounding neuropil and myelinated fibers. The larger nuclei are astrocytes, the smaller denser ones are oligodendrocytes.
(D): Electron micrograph of a postoperative biopsy of the cortex (human) showing a neuron (1) embedded in the neuropil (2) in which
the capillary and an erythrocyte in its lumen (3) is surrounded by a pericyte (4) and swollen astrocytic endfeet (5).
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, cerebrum, glymphatic system, neuron, neuropil, Virchow-Robin space, blood-brain-barrier, astrocyte, capillary, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection