2.4 POJA-L1098
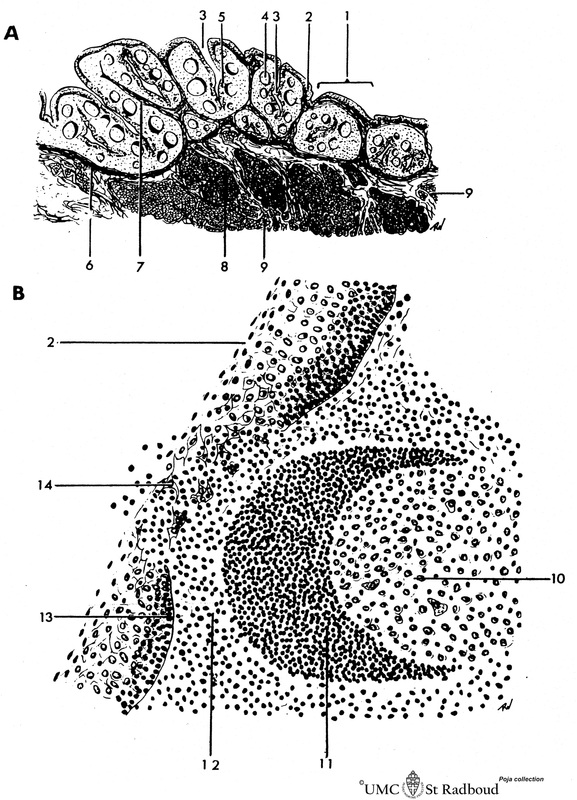
Title: Scheme of lingual tonsil (‘lymphoepithelial tissue’)
Description: Lingual tonsil (consisting of the accumulation of folliculi linguales).
The root of the tongue contains invaginations or crypts or narrow caverns (3). In these crypts the ducts of the mucous glands (8) end up. The crypts are lined by multilayered nonkeratinizing squamous epithelium (2) and are surrounded by lymphatic tissue. The lymphoid follicles are capped by a corona (11) or mantle layer of small dark lymphocytes (B cells) with the cap towards the lumen of the crypts. Depending on the activation status the lymphocytes can migrate from the follicle inwards between the squamous epithelial cells (14, infiltration). The Waldeyer’s tonsillar ring is a ring of lymphoid tissue located around the nasopharynx and oropharynx. It comprises the (naso-) pharyngeal tonsils or adenoids, the tubal tonsils, the palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils.
(A): Survey. (B): Detail crescent and diapedesis of free cells.
Keywords/Mesh: lymphatic tissue, lingual tonsil, lymphoepithelial tissue, reticular tissue, histology, POJA collection
Title: Scheme of lingual tonsil (‘lymphoepithelial tissue’)
Description: Lingual tonsil (consisting of the accumulation of folliculi linguales).
The root of the tongue contains invaginations or crypts or narrow caverns (3). In these crypts the ducts of the mucous glands (8) end up. The crypts are lined by multilayered nonkeratinizing squamous epithelium (2) and are surrounded by lymphatic tissue. The lymphoid follicles are capped by a corona (11) or mantle layer of small dark lymphocytes (B cells) with the cap towards the lumen of the crypts. Depending on the activation status the lymphocytes can migrate from the follicle inwards between the squamous epithelial cells (14, infiltration). The Waldeyer’s tonsillar ring is a ring of lymphoid tissue located around the nasopharynx and oropharynx. It comprises the (naso-) pharyngeal tonsils or adenoids, the tubal tonsils, the palatine tonsils and the lingual tonsils.
(A): Survey. (B): Detail crescent and diapedesis of free cells.
- folliculus lingualis (bulging subepithelial accumulations of lymphatic noduli)
- non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
- deep invagination of epithelial lining (so-called crypt)
- lymphatic nodulus with crescent (mantle zone)
- area of diapedesis of free cells through the epithelium
- fascia linguae between the mucosa and the underlying glands and muscle tissue
- connective tissue septa from the fascia delimiting the folliculi linguales
- mucous gland (posterior lingual gland)
- muscle tissue (palatoglossal muscle)
- germinal centre
- crescent (mantle zone) (always directed towards the free surface)
- small lymphocytes
- basement membrane
- isolated squamous epithelial cells due to heavy infiltration by lymphocytes (diapedesis) resulting in the disappearance or disintegration of the epithelial-connective tissue boundary (basement membrane)
Keywords/Mesh: lymphatic tissue, lingual tonsil, lymphoepithelial tissue, reticular tissue, histology, POJA collection