5.3 POJA-L5006+2316+La0044+La0047+L2315
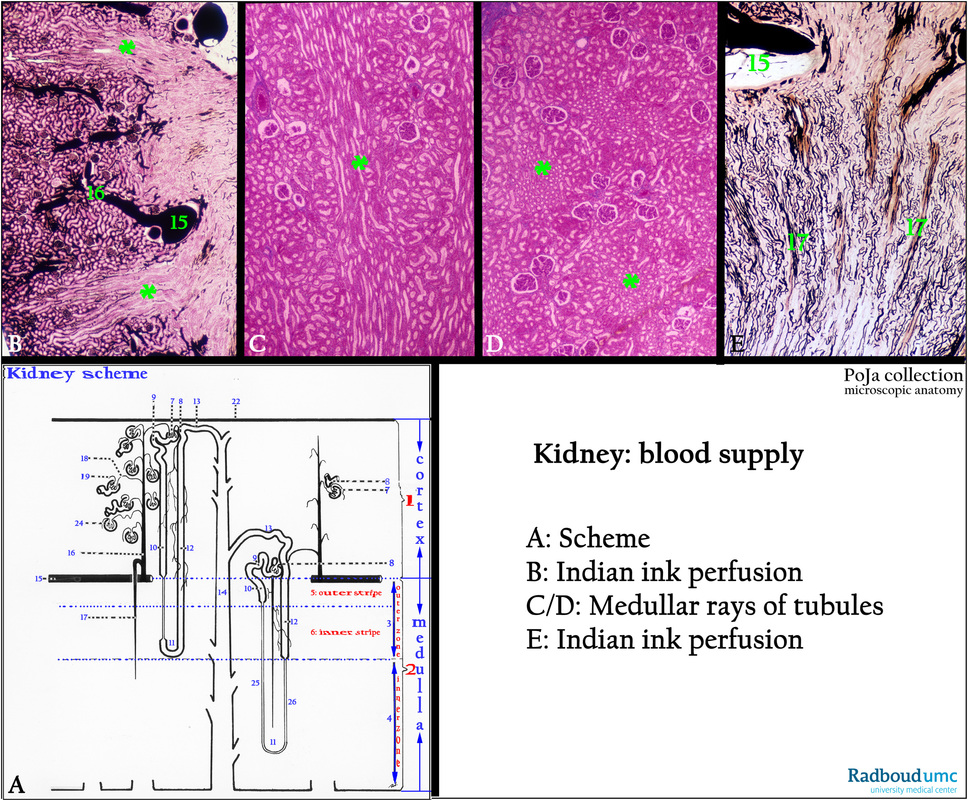
Title: Blood supply of the kidney
Description:
(A): Scheme kidney with nephrons, human.
(1) Cortex.
(2) Medulla, with the outer zone (3) and with the inner zone (4) of the medulla.
(5) Outer stripe of the outer zone.
(6) Inner stripe of the outer zone.
(7) Arteriola efferens leaving the glomerulus.
(8) Macula densa (MD).
(9) Pars contorta I or proximal convoluted tubule (PCT).
(10) Pars recta I or proximal straight tubule (PST).
(11) Henle’s loop (short-looped and long-looped nephrons) .
(12) Pars recta II or distal straight tubule (DST) or thick ascending limb (TAL) (13) Pars contorta II or distal convoluted tubule (DCT);
last part is connecting tubule (CNT) toward (14) Collecting duct divided in a cortical collecting duct (CCD), an outer medullary collecting duct (OMCD) and an inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD).
(15) Arteria arcuata.
(16) Arteria corticalis radiate (interlobular artery).
(17) Arteriola medullaris recta (vasa recta).
(18) Arteriola afferens.
(19) Arteriola efferens.
(22) Capsula fibrosa.
(24) Glomerulus (glomerular tuft).
(25) Thin ascending limb. (ATL) (long-looped nephron).
(26) Thin descending limb (DTL) (long-looped nephron). Note ATL + DTL = intermediate tubule (IT).
(B): Indian ink perfusion, mouse. (**) Medullary rays. Cross-sectioned arcuate artery (15) and (16) a branch (cortical radial artery).
The cortical vascular network including the glomeruli is black-stained.
(C, D): Stain Azan, human. Medullar rays (**) of tubules longitudinal and cross-sectioned respectively.
(E): Indian ink perfusion, mouse. Black-stained arteria arcuata (15) and (17) vasa recta consisting of descending arteriolae rectae and ascending venulae rectae.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, arcuate artery, cortical radial artery, interlobular artery, vasa recta, blood supply, histology, POJA collection
Title: Blood supply of the kidney
Description:
(A): Scheme kidney with nephrons, human.
(1) Cortex.
(2) Medulla, with the outer zone (3) and with the inner zone (4) of the medulla.
(5) Outer stripe of the outer zone.
(6) Inner stripe of the outer zone.
(7) Arteriola efferens leaving the glomerulus.
(8) Macula densa (MD).
(9) Pars contorta I or proximal convoluted tubule (PCT).
(10) Pars recta I or proximal straight tubule (PST).
(11) Henle’s loop (short-looped and long-looped nephrons) .
(12) Pars recta II or distal straight tubule (DST) or thick ascending limb (TAL) (13) Pars contorta II or distal convoluted tubule (DCT);
last part is connecting tubule (CNT) toward (14) Collecting duct divided in a cortical collecting duct (CCD), an outer medullary collecting duct (OMCD) and an inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD).
(15) Arteria arcuata.
(16) Arteria corticalis radiate (interlobular artery).
(17) Arteriola medullaris recta (vasa recta).
(18) Arteriola afferens.
(19) Arteriola efferens.
(22) Capsula fibrosa.
(24) Glomerulus (glomerular tuft).
(25) Thin ascending limb. (ATL) (long-looped nephron).
(26) Thin descending limb (DTL) (long-looped nephron). Note ATL + DTL = intermediate tubule (IT).
(B): Indian ink perfusion, mouse. (**) Medullary rays. Cross-sectioned arcuate artery (15) and (16) a branch (cortical radial artery).
The cortical vascular network including the glomeruli is black-stained.
(C, D): Stain Azan, human. Medullar rays (**) of tubules longitudinal and cross-sectioned respectively.
(E): Indian ink perfusion, mouse. Black-stained arteria arcuata (15) and (17) vasa recta consisting of descending arteriolae rectae and ascending venulae rectae.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, arcuate artery, cortical radial artery, interlobular artery, vasa recta, blood supply, histology, POJA collection