11.5 POJA-L3363+4454+3002+3018
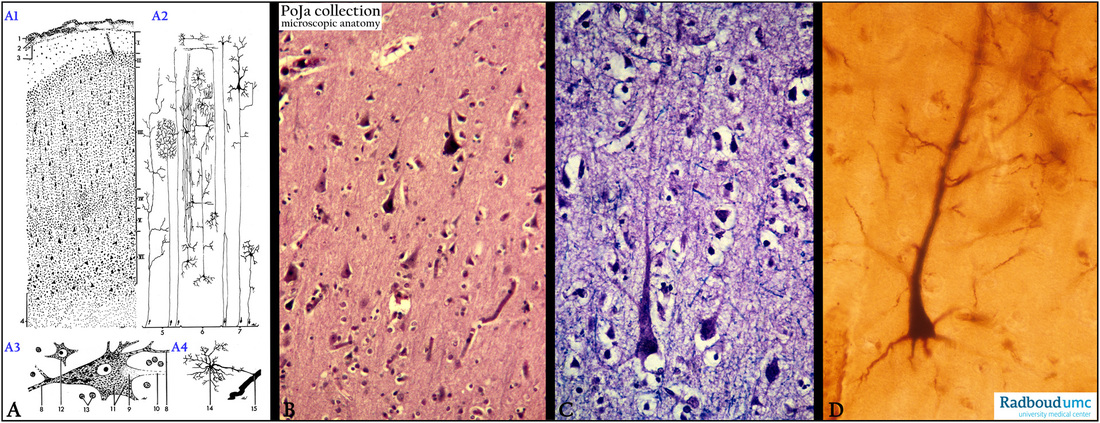
Title: Pyramidal cell types and shapes in cerebrum
Description:
(A1-A4): Scheme cerebral cortex (calcarine region), human (zoom in).
Referred to Section 11.1.
(1) Arachnoidea.
(2) Subarachnoideal space.
(3) Pia mater, followed by the cortex layers:
I. lamina zonalis or molecularis
II. Lamina granularis externa
III. Lamina pyramidalis externa
IV. Lamina granularis interna
V. Lamina ganglionaris (pyramidalis interna)
VI. Lamina multiformis
(4) Medulla.
(A2): Signal scheme of the cerebrum: (5) Input signaling of the cerebrum. (6) Interneurons. (7) Output signaling.
(A3): Pyramid cells in motor cortex (stained for Nissl bodies). (8) Dendrites. (9) Axon hillock. (10) Axon. (11) Nissl body
(RER and free ribosomes). (12) Perikaryon of an interneuron. (13) Nuclei of glial cells.
(A4): Glial cell such as (14) astrocyte with perivascular endfeet. (15) Capillary.
(B): Stain hematoxylin-eosin, human, associative cortex with lamina pyramidalis externa (layer III).
Generally between layers III and IV one finds also the outer band of Baillarger.
(C): Stain Kluver-Barrera, human. Detail of large pyramidal cell and apical dendrite, thin nerve fibers are blue .
(D): Golgi staining shows large pyramidal cell and it’s ascending apical branched dendrite and basally smaller-sized axon and
collaterals, human.
Background: Interneurons (A2, 6) also called relay neurons or associative neurons are found exclusively in
the central nervous system. Generally they are small locally projecting neurons that include 1) inhibitory neurons with
neurotransmitters as GABA or glycine; 2) excitatory neurons using glutamate as neurotransmitter; 3) neurons that release neuromodulators as acetylcholine.
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, cerebrum, associative cortex, pyramid cell, neuron, interneuron, glia cell, axon, dendrite, histology, POJA collection
Title: Pyramidal cell types and shapes in cerebrum
Description:
(A1-A4): Scheme cerebral cortex (calcarine region), human (zoom in).
Referred to Section 11.1.
(1) Arachnoidea.
(2) Subarachnoideal space.
(3) Pia mater, followed by the cortex layers:
I. lamina zonalis or molecularis
II. Lamina granularis externa
III. Lamina pyramidalis externa
IV. Lamina granularis interna
V. Lamina ganglionaris (pyramidalis interna)
VI. Lamina multiformis
(4) Medulla.
(A2): Signal scheme of the cerebrum: (5) Input signaling of the cerebrum. (6) Interneurons. (7) Output signaling.
(A3): Pyramid cells in motor cortex (stained for Nissl bodies). (8) Dendrites. (9) Axon hillock. (10) Axon. (11) Nissl body
(RER and free ribosomes). (12) Perikaryon of an interneuron. (13) Nuclei of glial cells.
(A4): Glial cell such as (14) astrocyte with perivascular endfeet. (15) Capillary.
(B): Stain hematoxylin-eosin, human, associative cortex with lamina pyramidalis externa (layer III).
Generally between layers III and IV one finds also the outer band of Baillarger.
(C): Stain Kluver-Barrera, human. Detail of large pyramidal cell and apical dendrite, thin nerve fibers are blue .
(D): Golgi staining shows large pyramidal cell and it’s ascending apical branched dendrite and basally smaller-sized axon and
collaterals, human.
Background: Interneurons (A2, 6) also called relay neurons or associative neurons are found exclusively in
the central nervous system. Generally they are small locally projecting neurons that include 1) inhibitory neurons with
neurotransmitters as GABA or glycine; 2) excitatory neurons using glutamate as neurotransmitter; 3) neurons that release neuromodulators as acetylcholine.
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, cerebrum, associative cortex, pyramid cell, neuron, interneuron, glia cell, axon, dendrite, histology, POJA collection