1.1 POJA-L850
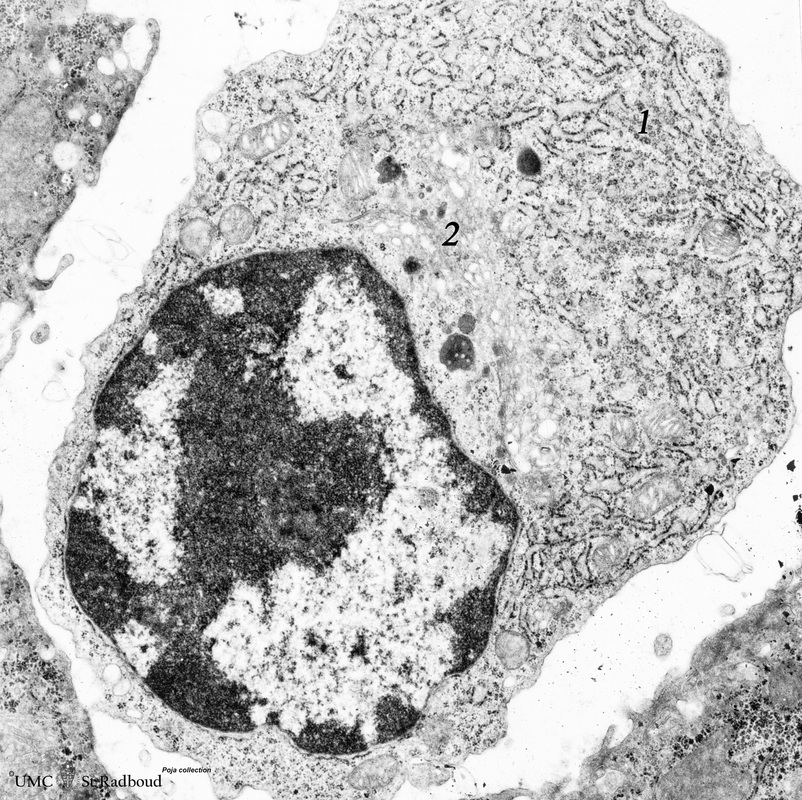
Title: Plasma cell (liver, rat)
Description: Electron microscopy.
The mature plasma cell or plasmacyte shows an eccentric nucleus with a characteristic chunky distribution of heterochromatin along the inner nuclear membrane (“spoke-wheel” effect in light microscopy).
Juxtanuclearly an elaborate Golgi area (2) (cytocentrum/centrosome).
The cytoplasma is packed with long dilated profiles (1) of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) filled with electron-grey material confirming the secretory activity. Dependent on the cellular activity the RER vary from distended up to dilated profiles.
Background: A pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell gives rise to a common lymphoid progenitor cell. The latter divides to produce two types of lymphoid stem cells. One type migrates to the thymus, proliferates and differentiates into T lymphocytes. The other type (pre-B cell) remains in the bone marrow or settles in the spleen, lymph nodes where it proliferates into lymphoblasts that in turn divide and eventually result in immunocompetent B lymphocytes. Dependent on the appropriate stimulation B lymphocytes can be activated to divide and differentiate via plasmablasts into antibody-secreting plasma cells (plasmacytes).
Keywords/Mesh: blood, bone marrow, plasma cell, B cell, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Plasma cell (liver, rat)
Description: Electron microscopy.
The mature plasma cell or plasmacyte shows an eccentric nucleus with a characteristic chunky distribution of heterochromatin along the inner nuclear membrane (“spoke-wheel” effect in light microscopy).
Juxtanuclearly an elaborate Golgi area (2) (cytocentrum/centrosome).
The cytoplasma is packed with long dilated profiles (1) of rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) filled with electron-grey material confirming the secretory activity. Dependent on the cellular activity the RER vary from distended up to dilated profiles.
Background: A pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell gives rise to a common lymphoid progenitor cell. The latter divides to produce two types of lymphoid stem cells. One type migrates to the thymus, proliferates and differentiates into T lymphocytes. The other type (pre-B cell) remains in the bone marrow or settles in the spleen, lymph nodes where it proliferates into lymphoblasts that in turn divide and eventually result in immunocompetent B lymphocytes. Dependent on the appropriate stimulation B lymphocytes can be activated to divide and differentiate via plasmablasts into antibody-secreting plasma cells (plasmacytes).
Keywords/Mesh: blood, bone marrow, plasma cell, B cell, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection