5.4.2 POJA-La0054+La0087+L2340+2344+2346+La0088
Title: Juxtaglomerular apparatus in the kidney VII
Description:
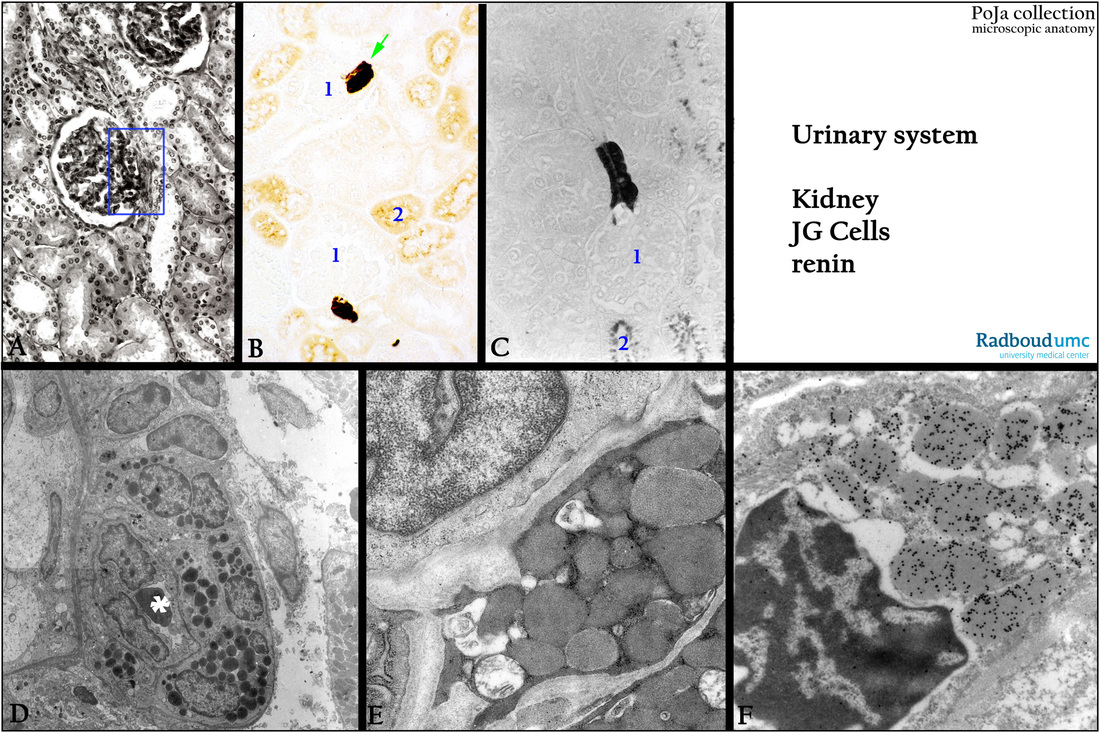
(A): Kidney cortex, stain Azan (black-white), human. The rectangle comprises all elements of the juxtaglomerular apparatus, i.e. macula densa, lacis cells (Goormaghtigh cells) and juxtaglomerular cells with renin in the afferent arteriole of the glomerulus.
(B): Immunoperoxidase staining with DAB and antibodies against renin, toad. The enzyme renin is produced in the JG cells of the glomerular afferent vessel (arrow) and converts the angiotensinogen (produced by the liver) into the peptide angiotensin I that is further processed by the lung endothelial cells.
(C): Immunoperoxidase staining with PAP and DAB with antibodies against renin, phase-contrast,mouse. Note that the glomeruli (1)
and tubuli (2) are negative except for the endogenous peroxidase in the tubular lysosomes.
(D): Electron microscopy, toad. Granulated JG cells in the afferent vessel of the glomerulus. (*) is the lumen of the arteriole.
(E): Electron microscopy showing details of the JG granules, mouse.
(F): Electron micrograph showing immunogold staining of the renin in the JG granules using antibodies against rennin, toad. The gold particles are selectively localized on the content of the granules.
(B, C, D and F by courtesy of A. Lamers PhD, Department Cell biology and Histology, Radboud university medical center, Nijmegen, The Netherlands).
Background: The renin-angiotensin-system (RAS): The mature enzyme renin (37 kDa, 340 amino acids) is secreted by the JG cells in
the vas afferens in response to several stimuli such as decreased arterial blood pressure, decreased NaCl level in the ultrafiltrate of the nephron as monitored by the macula densa cells that are closely apposed to the JG cells.
The sympathetic nervous system also affects the RAS system. Renin hydrolyzes the angiotensinogen (liver) into angiotensin I that is further converted into angiotensin II by the angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) at the lung endothelial cells.
Angiotensin II acts on the smooth muscle cells of the blood vessels organizing vasoconstriction, eliciting subsequently an increase in
blood pressure by the heart.
Angiotensin II also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal gland. The aldosterone stimulates the reabsorption of Na and H2O in the distal tubules and collecting ducts.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, glomerulus, macula densa, vas afferens, juxtaglomerular apparatus, JG cell, renin, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Juxtaglomerular apparatus in the kidney VII
Description:
(A): Kidney cortex, stain Azan (black-white), human. The rectangle comprises all elements of the juxtaglomerular apparatus, i.e. macula densa, lacis cells (Goormaghtigh cells) and juxtaglomerular cells with renin in the afferent arteriole of the glomerulus.
(B): Immunoperoxidase staining with DAB and antibodies against renin, toad. The enzyme renin is produced in the JG cells of the glomerular afferent vessel (arrow) and converts the angiotensinogen (produced by the liver) into the peptide angiotensin I that is further processed by the lung endothelial cells.
(C): Immunoperoxidase staining with PAP and DAB with antibodies against renin, phase-contrast,mouse. Note that the glomeruli (1)
and tubuli (2) are negative except for the endogenous peroxidase in the tubular lysosomes.
(D): Electron microscopy, toad. Granulated JG cells in the afferent vessel of the glomerulus. (*) is the lumen of the arteriole.
(E): Electron microscopy showing details of the JG granules, mouse.
(F): Electron micrograph showing immunogold staining of the renin in the JG granules using antibodies against rennin, toad. The gold particles are selectively localized on the content of the granules.
(B, C, D and F by courtesy of A. Lamers PhD, Department Cell biology and Histology, Radboud university medical center, Nijmegen, The Netherlands).
Background: The renin-angiotensin-system (RAS): The mature enzyme renin (37 kDa, 340 amino acids) is secreted by the JG cells in
the vas afferens in response to several stimuli such as decreased arterial blood pressure, decreased NaCl level in the ultrafiltrate of the nephron as monitored by the macula densa cells that are closely apposed to the JG cells.
The sympathetic nervous system also affects the RAS system. Renin hydrolyzes the angiotensinogen (liver) into angiotensin I that is further converted into angiotensin II by the angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) at the lung endothelial cells.
Angiotensin II acts on the smooth muscle cells of the blood vessels organizing vasoconstriction, eliciting subsequently an increase in
blood pressure by the heart.
Angiotensin II also stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal gland. The aldosterone stimulates the reabsorption of Na and H2O in the distal tubules and collecting ducts.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, glomerulus, macula densa, vas afferens, juxtaglomerular apparatus, JG cell, renin, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection