13.1 POJA-L2982+4584+4588+4590+4603+4316
Title: Muscular arteries (human)
Description:
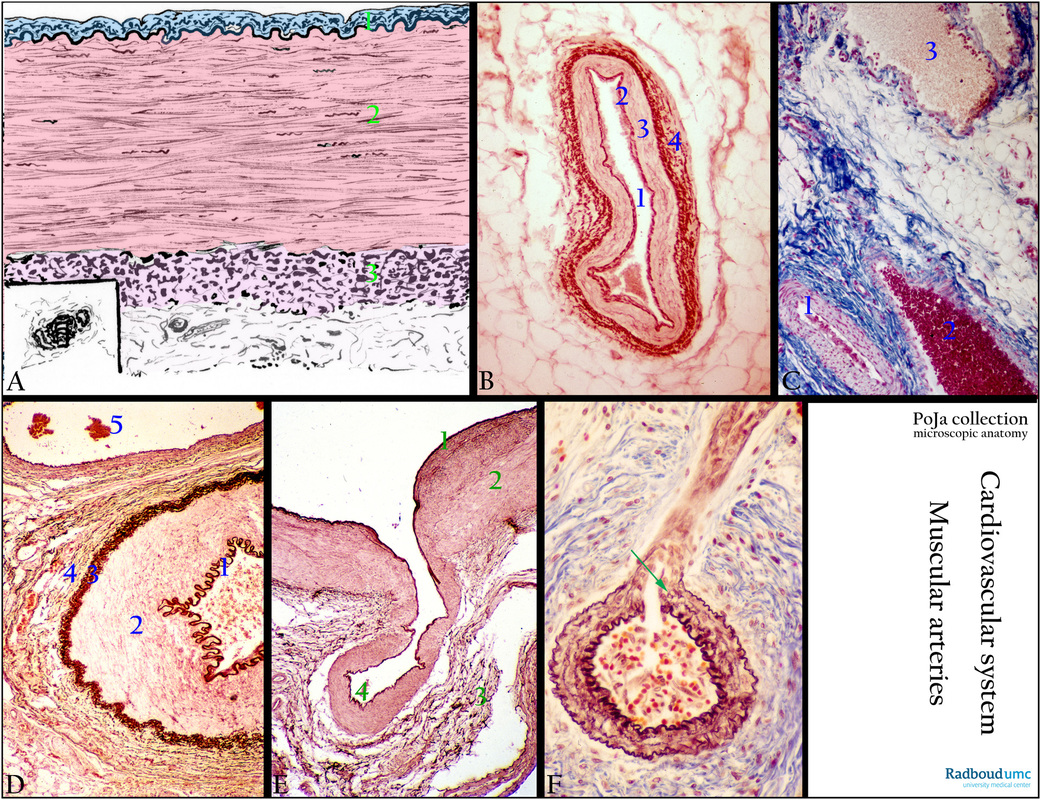
(A): Scheme muscular artery (dorsal pedis artery). (1) Intima. (2) Tunica media with smooth muscle cells (SMC). (3) Tunica adventitia.
(B): Orcein staining for elastic fibres of a muscular artery (mesentery). (1) Lumen lined by endothelial cells. (2) IEL, dense stained internal elastic lamina. (3) Tunica media with smooth muscle cells. (4) Adventitia with coarse dense stained elastic fibres.
(C): Azan staining of artery and vein, subcutis. (1) Muscular artery. (2) Vein. (3) Lymph vessel.
(D): Orcein staining for elastic fibres of a muscular artery and a vein (mesentery). (1) dense stained IEL of the muscular artery. (2) Tunica media with smooth muscle cells. Followed by packed shorter elastic fibres (3) at the transition of tunica media to tunica adventitia. (4) Tunica adventitia. (5) Vein. Vasa vasorum are present in the adventitia. The wall of the vein contains brown spots/lines of elastic fibres.
(E): Orcein-haematoxylin staining of the muscular cubital artery with a fold (elbow region). (1) Intima with dark-brown reddish stained internal elastic membrane (IEL). (2) Media. (3) Adventitia with fine elastic fibres. At (4) invagination of the vessel with a continuity of the IEL.
(F): Elastica stain, Mallory, branching bronchial, muscular artery (infant). The larger artery branches into a small arteriole. Note abrupt ending of internal and external elastic membranes at the branching point (arrow). In lumen of the artery desquamated endothelial cells and erythrocytes.
Background: There are two main types of arteries: elastic arteries, and muscular arteries. A third type of artery is the so-called transitional or hybrid artery. Characteristic examples of muscular arteries are the femoral and cubital arteries. Their walls contain numerous smooth muscle cells (SMC). By contraction and dilation, they regulate the amount of blood flow needed in the organs. The internal elastic layer (IEL) is reduced to a small single, fenestrated membrane at the border between the tunica intima and tunica media (a well-developed muscular layer), while the external elastic layer (EEL) between media and adventitia is less defined.
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, vascularisation, blood vessel, muscular artery, hybrid artery, vasa vasorum, smooth muscle, elastic fibre, endothelium, histology, POJA collection
Title: Muscular arteries (human)
Description:
(A): Scheme muscular artery (dorsal pedis artery). (1) Intima. (2) Tunica media with smooth muscle cells (SMC). (3) Tunica adventitia.
(B): Orcein staining for elastic fibres of a muscular artery (mesentery). (1) Lumen lined by endothelial cells. (2) IEL, dense stained internal elastic lamina. (3) Tunica media with smooth muscle cells. (4) Adventitia with coarse dense stained elastic fibres.
(C): Azan staining of artery and vein, subcutis. (1) Muscular artery. (2) Vein. (3) Lymph vessel.
(D): Orcein staining for elastic fibres of a muscular artery and a vein (mesentery). (1) dense stained IEL of the muscular artery. (2) Tunica media with smooth muscle cells. Followed by packed shorter elastic fibres (3) at the transition of tunica media to tunica adventitia. (4) Tunica adventitia. (5) Vein. Vasa vasorum are present in the adventitia. The wall of the vein contains brown spots/lines of elastic fibres.
(E): Orcein-haematoxylin staining of the muscular cubital artery with a fold (elbow region). (1) Intima with dark-brown reddish stained internal elastic membrane (IEL). (2) Media. (3) Adventitia with fine elastic fibres. At (4) invagination of the vessel with a continuity of the IEL.
(F): Elastica stain, Mallory, branching bronchial, muscular artery (infant). The larger artery branches into a small arteriole. Note abrupt ending of internal and external elastic membranes at the branching point (arrow). In lumen of the artery desquamated endothelial cells and erythrocytes.
Background: There are two main types of arteries: elastic arteries, and muscular arteries. A third type of artery is the so-called transitional or hybrid artery. Characteristic examples of muscular arteries are the femoral and cubital arteries. Their walls contain numerous smooth muscle cells (SMC). By contraction and dilation, they regulate the amount of blood flow needed in the organs. The internal elastic layer (IEL) is reduced to a small single, fenestrated membrane at the border between the tunica intima and tunica media (a well-developed muscular layer), while the external elastic layer (EEL) between media and adventitia is less defined.
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, vascularisation, blood vessel, muscular artery, hybrid artery, vasa vasorum, smooth muscle, elastic fibre, endothelium, histology, POJA collection