2.1 POJA-L900
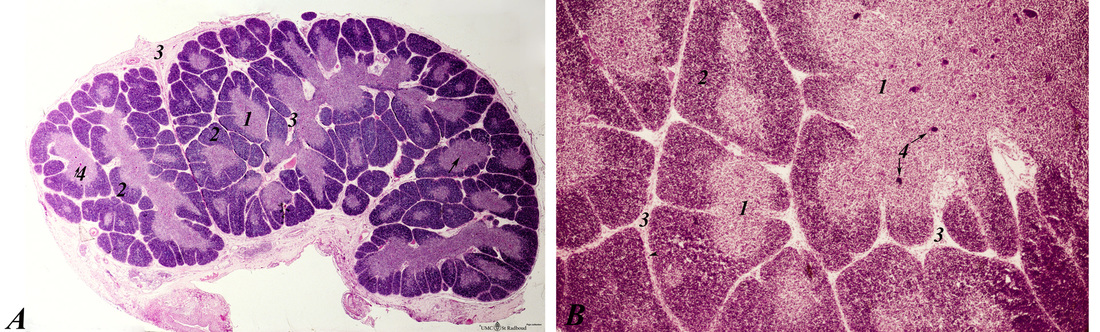
Title: Thymus (human, newborn, lower and higher magnification)
Description: Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin.
The infantile thymus is surrounded by connective tissue capsule (3) from where vascularized interlobular septa (or trabculae, 3) penetrate into the lobulated organ. Each lobule consists of a darker stained cortex (2) and a lighter stained medulla (1). The medulla has a lower cell density than the cortex.
Meshwork of epithelial reticulum cells forms the supportive structures for cortex and medulla. These reticulum cells are derived from entodermal epithelium. In the medulla, the epithelial cell types can aggregate to so-called Hassall corpuscles (4), which show sometimes signs of light keratinization.
Bone marrow stem cells (pre-T cells) arrive in the outer cortex, divide and maturate to T-cells while migrating to the medulla. They leave the medulla as mature, immunocompetent T cells.
The thymus contains also macrophages and various types of interdigitating dendritic cells, i.e. cells that contribute to the maturation and selection process of T cells. The capsule also contains a few mast cells. However, B cells as well as follicles do not exist in the thymus.
Keywords/Mesh: lymphatic tissue, thymus, cortex, medulla, Hassall corpuscle (bodies), histology, POJA collection
Title: Thymus (human, newborn, lower and higher magnification)
Description: Stain: Hematoxylin & eosin.
The infantile thymus is surrounded by connective tissue capsule (3) from where vascularized interlobular septa (or trabculae, 3) penetrate into the lobulated organ. Each lobule consists of a darker stained cortex (2) and a lighter stained medulla (1). The medulla has a lower cell density than the cortex.
Meshwork of epithelial reticulum cells forms the supportive structures for cortex and medulla. These reticulum cells are derived from entodermal epithelium. In the medulla, the epithelial cell types can aggregate to so-called Hassall corpuscles (4), which show sometimes signs of light keratinization.
Bone marrow stem cells (pre-T cells) arrive in the outer cortex, divide and maturate to T-cells while migrating to the medulla. They leave the medulla as mature, immunocompetent T cells.
The thymus contains also macrophages and various types of interdigitating dendritic cells, i.e. cells that contribute to the maturation and selection process of T cells. The capsule also contains a few mast cells. However, B cells as well as follicles do not exist in the thymus.
Keywords/Mesh: lymphatic tissue, thymus, cortex, medulla, Hassall corpuscle (bodies), histology, POJA collection