2.3 POJA-L1027-1028
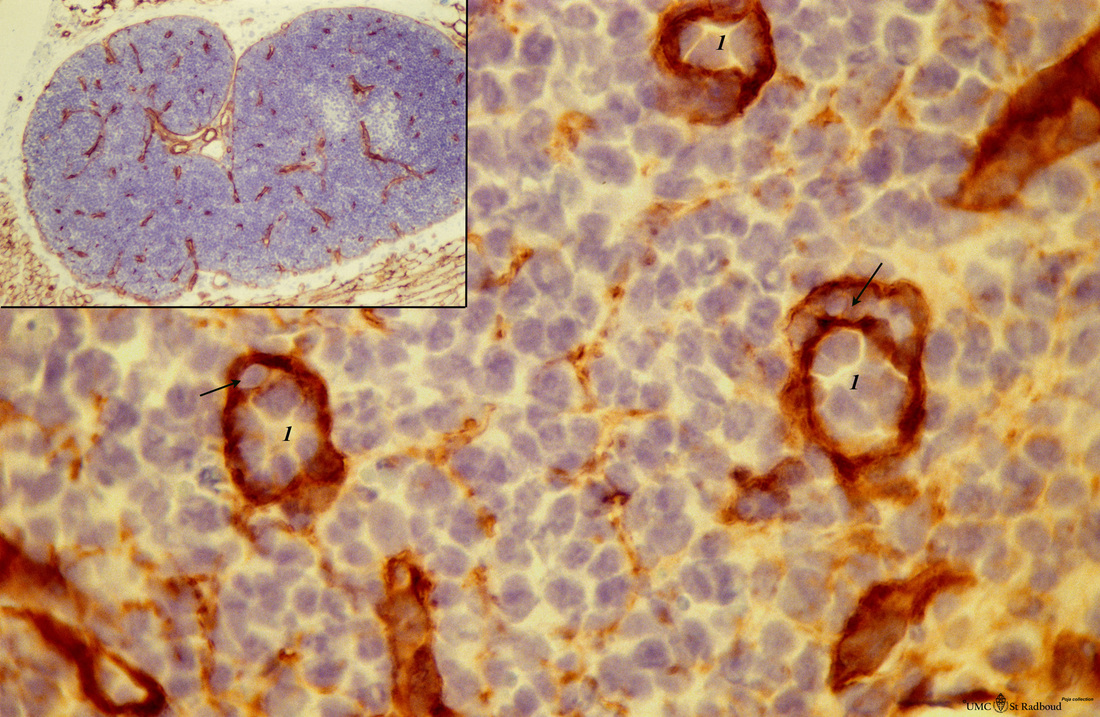
Title: Anti-laminin staining in cortex lymph node (rat)
Description: Stain: anti-laminin - antibody and immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and haematoxylin counter stained on frozen section.
Using an antibody against laminin brown-stained basement membranes (BM) are outlined demonstrating post capillary venules (1) in the paracortical areas.
In between the blue-stained nuclei of different types of cells faintly brown-stained threads indicate patches of basement membrane-material produced by reticular cells are visible.
The inset shows the survey of tangentional sectioned cortical area of the lymph node. Note that the BM of surrounding fat cells (3) is also slightly stained positive. Arrows (→) indicate lymphocytes in diapedesis.
Background: These specialized venules or so-called high endothelial venules (HEV) are lined by cuboidal or columnar endothelial cells that possess specific receptors for antigen-primed lymphocytes. B- and T lymphocytes. These are the sites of entry of these lymphocytes into the lymph node (lymphocyte homing mechanism) where they leave the blood stream through these HEV and subsequently by diapedesis between the endothelial cells B lymphocytes migrate to the lymphatic follicles in the cortex but T lymphocytes remain in the thymus-dependent area of the paracortex.
Keywords/Mesh: lymphatic tissue, lymph node, paracortex, reticular tissue, postcapillary venule, high endothelial venule, histology, POJA collection
Title: Anti-laminin staining in cortex lymph node (rat)
Description: Stain: anti-laminin - antibody and immunoperoxidase staining with diaminobenzidin (DAB) and haematoxylin counter stained on frozen section.
Using an antibody against laminin brown-stained basement membranes (BM) are outlined demonstrating post capillary venules (1) in the paracortical areas.
In between the blue-stained nuclei of different types of cells faintly brown-stained threads indicate patches of basement membrane-material produced by reticular cells are visible.
The inset shows the survey of tangentional sectioned cortical area of the lymph node. Note that the BM of surrounding fat cells (3) is also slightly stained positive. Arrows (→) indicate lymphocytes in diapedesis.
Background: These specialized venules or so-called high endothelial venules (HEV) are lined by cuboidal or columnar endothelial cells that possess specific receptors for antigen-primed lymphocytes. B- and T lymphocytes. These are the sites of entry of these lymphocytes into the lymph node (lymphocyte homing mechanism) where they leave the blood stream through these HEV and subsequently by diapedesis between the endothelial cells B lymphocytes migrate to the lymphatic follicles in the cortex but T lymphocytes remain in the thymus-dependent area of the paracortex.
Keywords/Mesh: lymphatic tissue, lymph node, paracortex, reticular tissue, postcapillary venule, high endothelial venule, histology, POJA collection