|
1.1 POJA-L773
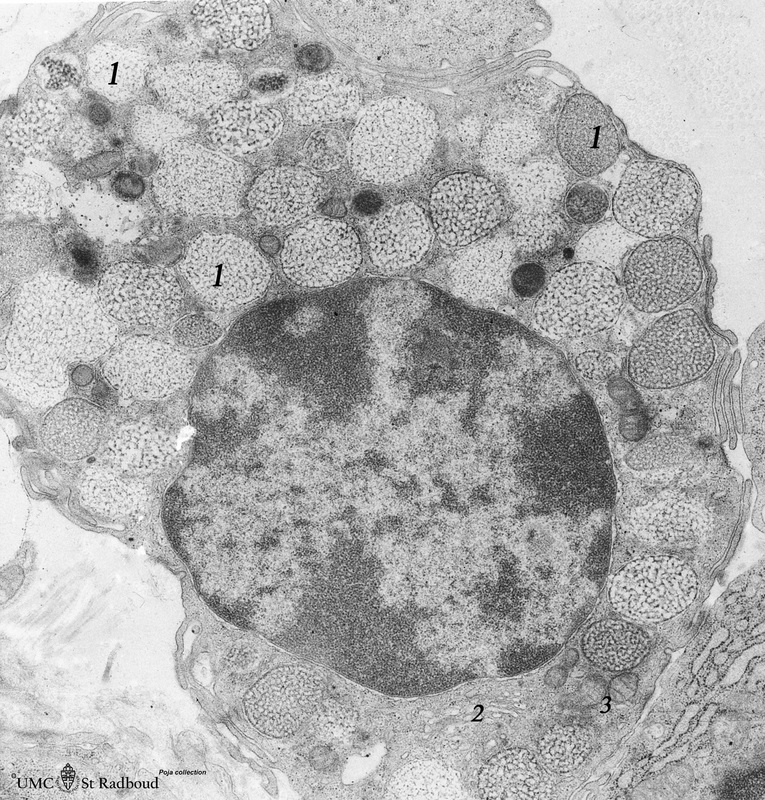
Title: Mast cell (lung, golden hamster) Description: Electron microscopy. Mucosa mast cells (mastocytes) are frequently found perivascularly or perineurally. The mast cell shows long thin microvilli at the surface and the cytoplasm is stuffed with granules (1) varying in shape and size. At (2) a Golgi area and at (3) small mitochondria and some electron-dense lysosomes. The larger membrane-bound vesicles (so-called compound granules) show a metachromatic reaction in light microscopy and ultrastructurally a granule exhibits a heterogeneous content (different with species) e.g. osmiophilic granular, filamentous, whorl-like substances. The younger granules are less dense and show a more loosened reticular internal structure. The granules contain among others heparin, histamine, enzymes such as superoxide dismutase, b-hexosaminidase, tryptase, factors such as neutrophil – and eosinophil-chemotactic factors, vasoactive mediators. |
Background:
Analogous to basophilic granulocytes mast cells possess specific membrane receptors for the Fc segment of IgE produced in response to allergens. Eventually the release of the granular content by exocytosis (leading to degranulation of the mast cell) occurs resulting in e.g. an immediate hypersensitivity (anaphylactoid) reaction. It is considered that the mast cells arise from the bone marrow, either of a different lineage than the basophilic granulocyte or that the latter on arrival in the extravascular environment matures into a mast cell. It is also possible that extravascularly wandering hematopoetic stem cells give rise to subclasses of mast cells.
Keywords/Mesh: blood, bone marrow, basophilic granulocyte, specific granule, mast cell, histamine, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Analogous to basophilic granulocytes mast cells possess specific membrane receptors for the Fc segment of IgE produced in response to allergens. Eventually the release of the granular content by exocytosis (leading to degranulation of the mast cell) occurs resulting in e.g. an immediate hypersensitivity (anaphylactoid) reaction. It is considered that the mast cells arise from the bone marrow, either of a different lineage than the basophilic granulocyte or that the latter on arrival in the extravascular environment matures into a mast cell. It is also possible that extravascularly wandering hematopoetic stem cells give rise to subclasses of mast cells.
Keywords/Mesh: blood, bone marrow, basophilic granulocyte, specific granule, mast cell, histamine, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection