5.8 POJA-L2312+3878+3879
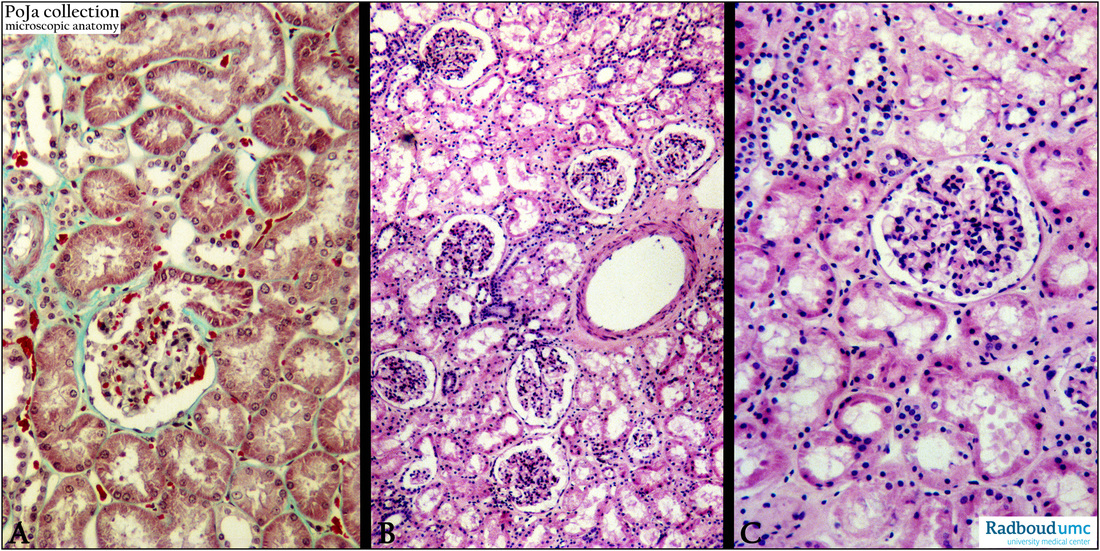
Title: Acute tubular necrosis in kidney
Description:
(A): Normal renal cortex, stain trichrome Goldner, human.
(B, C): Renal cortex with acute tubular necrosis (ATN), stain hematoxylin-eosin, human. The necrosis tends to be focal and involves segments of the proximal (PCT/PST) and distal convoluted tubules (DCT) and ascending limbs of Henle (TAL).
TALs and the straight proximal tubule (PST) are the most vulnerable. Apoptosis as well as tubulorrhexis (rupture of basement membranes) occurs. Note the degeneration and dilation of the necrotic tubules with some interstitial infiltrates in (C).
Although the glomeruli in (B, C) do have a reasonable normal appearance, they show an increased cellularity.
Background: Common causes of ATN include o.a. septicaemie, hypotension and the use of nephrotoxic drugs
(e.g. overdoses paracetamol, aminoglycosides).
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, acute tubular necrosis (ATN), necrosis, histology, pathology, POJA collection
Title: Acute tubular necrosis in kidney
Description:
(A): Normal renal cortex, stain trichrome Goldner, human.
(B, C): Renal cortex with acute tubular necrosis (ATN), stain hematoxylin-eosin, human. The necrosis tends to be focal and involves segments of the proximal (PCT/PST) and distal convoluted tubules (DCT) and ascending limbs of Henle (TAL).
TALs and the straight proximal tubule (PST) are the most vulnerable. Apoptosis as well as tubulorrhexis (rupture of basement membranes) occurs. Note the degeneration and dilation of the necrotic tubules with some interstitial infiltrates in (C).
Although the glomeruli in (B, C) do have a reasonable normal appearance, they show an increased cellularity.
Background: Common causes of ATN include o.a. septicaemie, hypotension and the use of nephrotoxic drugs
(e.g. overdoses paracetamol, aminoglycosides).
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, acute tubular necrosis (ATN), necrosis, histology, pathology, POJA collection