5.4.3 POJA-L2451+2432+4271+2520+2519+2518
Title: Collecting ducts (CDs) (XVII) in the human kidney
Description:
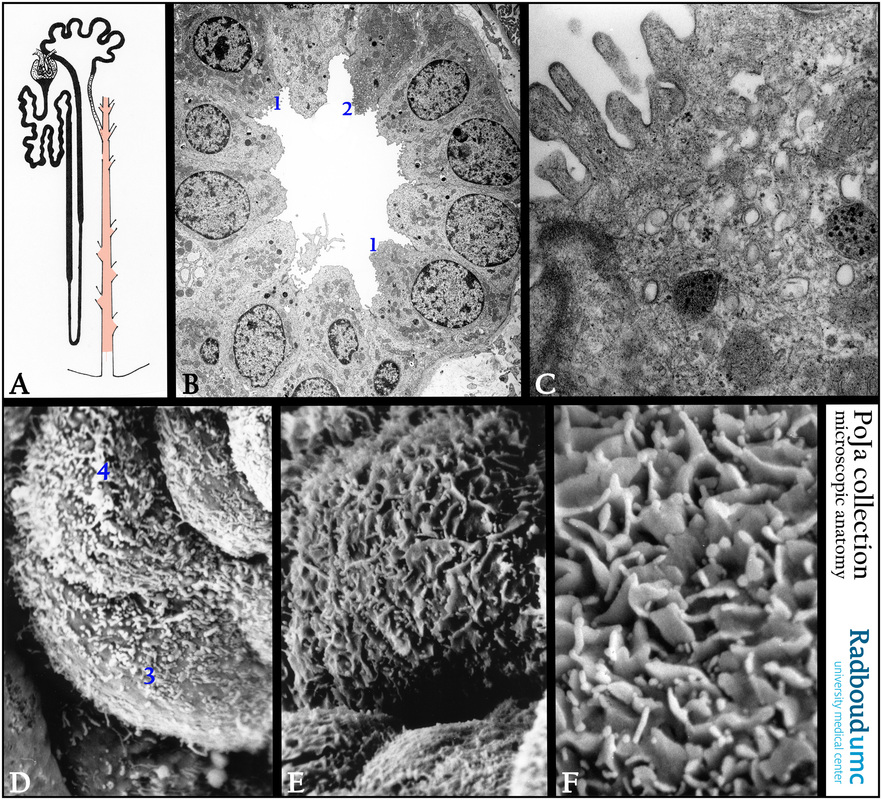
(A): Scheme nephron focused to the orange painted collecting duct.
(B): Electron micrograph of a cross-section of a collecting duct in the cortex (CCD), with two light ICs (intercalated cells, 1)
and one dark IC (2).
(C): Electron microscopy, detail of a dark IC with numerous apical vesicles and short stubby microvilli (= microplicae).
(D): Scanning electron micrograph of the inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD) showing the apex of a large principal cell with
microvilli (3, 4).
(E, detailed in F): Scanning electron micrograph of IMCD with the apex of an IC type cell with microplicae.
Background: The principal cell type is involved in the Na/K balance regulated via Na-channels and K-channels, under influence
of aldosterone. Vasopressin affects the aquaporin channels. The intercalated cells (α- and β-variants) are involved in H+/K+ exchange
and Cl-/HCO3- respectively and thus contribute to the acid-base balance (acidosis and alkalosis).
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, collecting duct, CCD, light intercalated cell, dark intercalated cell, principal cell, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Collecting ducts (CDs) (XVII) in the human kidney
Description:
(A): Scheme nephron focused to the orange painted collecting duct.
(B): Electron micrograph of a cross-section of a collecting duct in the cortex (CCD), with two light ICs (intercalated cells, 1)
and one dark IC (2).
(C): Electron microscopy, detail of a dark IC with numerous apical vesicles and short stubby microvilli (= microplicae).
(D): Scanning electron micrograph of the inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD) showing the apex of a large principal cell with
microvilli (3, 4).
(E, detailed in F): Scanning electron micrograph of IMCD with the apex of an IC type cell with microplicae.
Background: The principal cell type is involved in the Na/K balance regulated via Na-channels and K-channels, under influence
of aldosterone. Vasopressin affects the aquaporin channels. The intercalated cells (α- and β-variants) are involved in H+/K+ exchange
and Cl-/HCO3- respectively and thus contribute to the acid-base balance (acidosis and alkalosis).
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, collecting duct, CCD, light intercalated cell, dark intercalated cell, principal cell, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection