12.2.4.1 POJA-La0115+La0132+L2963+La0117+2622
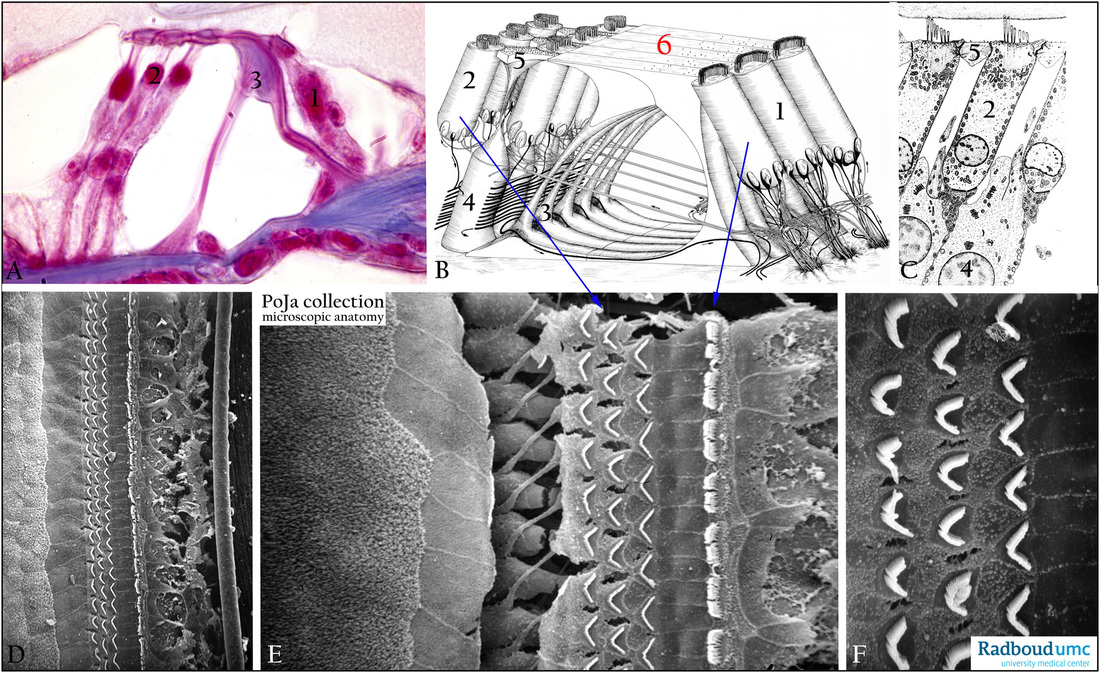
Title: Hair cells in the organ of Corti in the inner ear
Description:
(A): Stain Azan, organ of Corti, human. (1) Row of inner hair cells and at right side the inner spiral sulcus (2) Rows of outer hair cells and at left side the outer tunnel. (3) Pillar cells enclosing the inner tunnel (of Corti).
(B, C): Show schemes electron microscopy of organ of Corti and the structure of the outer hair cells, human.
Each auditory or cochlear nerve (8th cranial nerve) contains both afferent and efferent fibres. 95% of the afferent fibres of the
cochlear nerve runs to the bases of the inner hair cells (IHCs) and only 5 % goes to the outer hair cells (OHCs).
The nerve fibres to the OHCs partly run below the tunnel of Corti and subsequently between the Deiters cells upwards to synapse
on the hair cells. Synaptic ribbons in the cytoplasm are shown in (C).
Note the small black arrows in (B) indicating the afferent direction of pulse conduction.
"Crossing fibres" are efferent axons from neurons in the superior olivary complex (brainstem) and traverse through the tunnel of
Corti to the OHCs. Efferent fibres synapse directly on the OHCs but on the IHCs the efferent fibres synapse on the afferent fibres.
In (C) the phalangeal processes (5) of the supporting Deiters cells (4) composed the reticular membrane (or reticular lamina) that
enclosed the OHCs. (6) Indicates the reticular membrane formed by the phalangeal processes of the outer pillar cells and outer
phalangeal cells. The reticular membrane seal off the apicis of the OHCs and only their stereocilia pop out above the surface.
(D - F): show the scanning electron micrographs after removal of the tectorial membrane from the organ of Corti, rat.
The surface of the organ of Corti with three rows of stereocilia in a wide V-like conformation of the outer hair cells and one row of
the inner hair cells in a slightly curved conformation. Between the groups of cilia the reticular membrane (B, red 6) is present.
(D): Low magnification shows from the left to the right the area of the outer spiral sulcus with the cells of Hensen
from left to right with woolly microvilli and subsequently flat lining till the reticular membrane composed of flattened semi-rigid phalangeal processes of the supporting Deiters cells.
Between the three ciliary rows of OHCs and one ciliary row of IHCs a flattened dour plate is formed by plate-like processes of
the inner pillar cells layered on top of the outer pillar cells.
At the right side of the ciliary IHCs remnants of damaged border cells of internal spiral sulcus.
(E): Higher magnification reveals from the left to the right the same structures. Additionally an artificial induced large crack
demonstrated distinctly the rows of the cell bodies of the OHCs as well as thinner phalangeal processes (5) running from down
under the base of the OHCs upwards to form the reticular membrane (reticular lamina).
(F): Characteristic formation of stereocilia on the bare apex of the OHC, note that the enclosing phalangeal processes areas are
well delimited and provided with stubby microvilli.
Keywords/Mesh: inner ear, cochlear duct, organ of Corti, cochlear nerve, hair cell, stereocilium, phalangeal cell,
basilar membrane, efferent nerve, afferent nerve, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Hair cells in the organ of Corti in the inner ear
Description:
(A): Stain Azan, organ of Corti, human. (1) Row of inner hair cells and at right side the inner spiral sulcus (2) Rows of outer hair cells and at left side the outer tunnel. (3) Pillar cells enclosing the inner tunnel (of Corti).
(B, C): Show schemes electron microscopy of organ of Corti and the structure of the outer hair cells, human.
Each auditory or cochlear nerve (8th cranial nerve) contains both afferent and efferent fibres. 95% of the afferent fibres of the
cochlear nerve runs to the bases of the inner hair cells (IHCs) and only 5 % goes to the outer hair cells (OHCs).
The nerve fibres to the OHCs partly run below the tunnel of Corti and subsequently between the Deiters cells upwards to synapse
on the hair cells. Synaptic ribbons in the cytoplasm are shown in (C).
Note the small black arrows in (B) indicating the afferent direction of pulse conduction.
"Crossing fibres" are efferent axons from neurons in the superior olivary complex (brainstem) and traverse through the tunnel of
Corti to the OHCs. Efferent fibres synapse directly on the OHCs but on the IHCs the efferent fibres synapse on the afferent fibres.
In (C) the phalangeal processes (5) of the supporting Deiters cells (4) composed the reticular membrane (or reticular lamina) that
enclosed the OHCs. (6) Indicates the reticular membrane formed by the phalangeal processes of the outer pillar cells and outer
phalangeal cells. The reticular membrane seal off the apicis of the OHCs and only their stereocilia pop out above the surface.
(D - F): show the scanning electron micrographs after removal of the tectorial membrane from the organ of Corti, rat.
The surface of the organ of Corti with three rows of stereocilia in a wide V-like conformation of the outer hair cells and one row of
the inner hair cells in a slightly curved conformation. Between the groups of cilia the reticular membrane (B, red 6) is present.
(D): Low magnification shows from the left to the right the area of the outer spiral sulcus with the cells of Hensen
from left to right with woolly microvilli and subsequently flat lining till the reticular membrane composed of flattened semi-rigid phalangeal processes of the supporting Deiters cells.
Between the three ciliary rows of OHCs and one ciliary row of IHCs a flattened dour plate is formed by plate-like processes of
the inner pillar cells layered on top of the outer pillar cells.
At the right side of the ciliary IHCs remnants of damaged border cells of internal spiral sulcus.
(E): Higher magnification reveals from the left to the right the same structures. Additionally an artificial induced large crack
demonstrated distinctly the rows of the cell bodies of the OHCs as well as thinner phalangeal processes (5) running from down
under the base of the OHCs upwards to form the reticular membrane (reticular lamina).
(F): Characteristic formation of stereocilia on the bare apex of the OHC, note that the enclosing phalangeal processes areas are
well delimited and provided with stubby microvilli.
Keywords/Mesh: inner ear, cochlear duct, organ of Corti, cochlear nerve, hair cell, stereocilium, phalangeal cell,
basilar membrane, efferent nerve, afferent nerve, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection