4.1.1 POJA-L-2922
Title: Brunner glands in duodenum (gerbil)
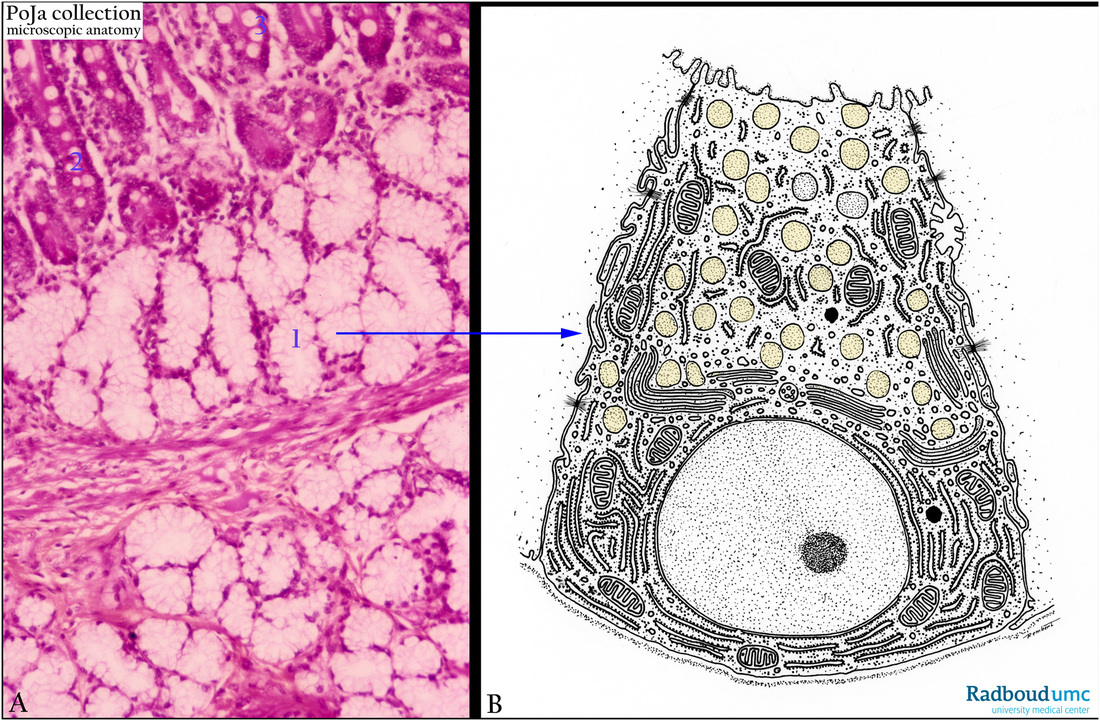
Description: Stain: (A) Hematoxylin-eosin. (B) Scheme electron microscopy.
(A): The lightly stained Brunner glands (1) end up in the bottom of the crypts (2). The crypts also contain many goblet cells (3). The gland cells (B) do have a vast RER for the generation of the secretory granules (yellowish stained).
The Brunner glands produce alkaline mucus with bicarbonate to neutralize the acidic chyme of the stomach, and to optimize the further enzymatic degradation of food. They also secrete urogastrone which inhibits chief cells and parietal cells in the stomach.
Keywords/Mesh: duodenum, Brunner glands. goblet cell, crypts, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection
Title: Brunner glands in duodenum (gerbil)
Description: Stain: (A) Hematoxylin-eosin. (B) Scheme electron microscopy.
(A): The lightly stained Brunner glands (1) end up in the bottom of the crypts (2). The crypts also contain many goblet cells (3). The gland cells (B) do have a vast RER for the generation of the secretory granules (yellowish stained).
The Brunner glands produce alkaline mucus with bicarbonate to neutralize the acidic chyme of the stomach, and to optimize the further enzymatic degradation of food. They also secrete urogastrone which inhibits chief cells and parietal cells in the stomach.
Keywords/Mesh: duodenum, Brunner glands. goblet cell, crypts, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection