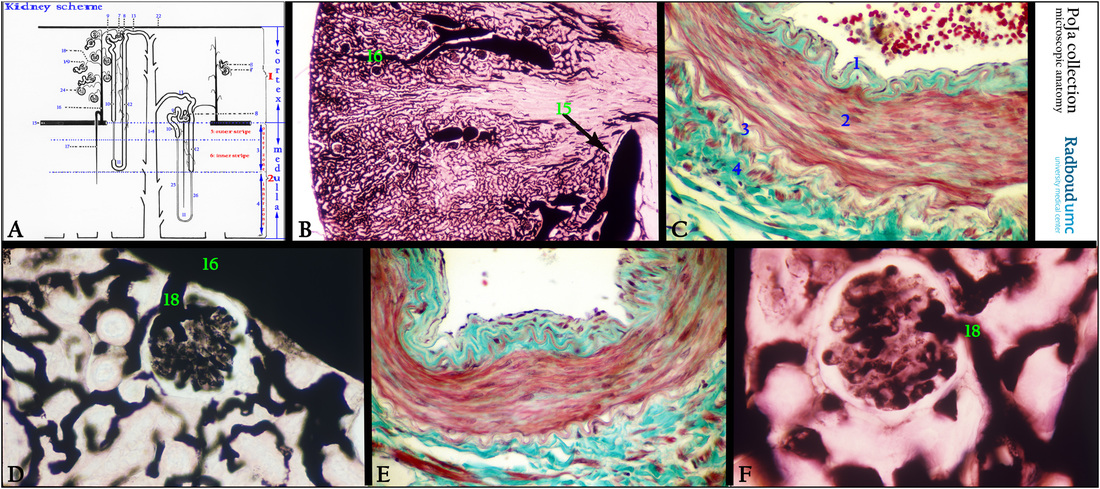
5.3 POJA-L2309+5006+2318+2354+2317+2310
Title: Blood vessel supply system in the kidney
Description:
(A): Kidney, scheme, human. (See also for better resolution 5.3 POJA-L5006B)
Right side vertical strip with blue/red characters: (1) Cortex.
(2) Medulla.
(3) Outer zone of the renal medulla.
(4) Inner zone of the renal medulla.
Left side with nephrons:
(1) Cortex.
(2) Medulla, with the outer zone (3) and with the inner zone (4) of the medulla.
(5) Outer stripe of the outer zone.
(6) Inner stripe of the outer zone.
(7) Arteriola efferens leaving the glomerulus.
(8) Macula densa (MD).
(9) Pars contorta I or proximal convoluted tubule (PCT).
(10) Pars recta I or proximal straight tubule (PST).
(11) Henle’s loop (short-looped and long-looped nephrons).
(12) Pars recta II or distal straight tubule (DST) or thick ascending limb (TAL)
(13) Pars contorta II or distal convoluted tubule (DCT); last part is connecting tubule (CNT) toward (14) Collecting duct divided in
cortical collecting duct (CCD), an outer medullary collecting duct (OMCD) and an inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD)
(15) Arteria arcuata.
(16) Arteria corticalis radiata (interlobular artery).
(17) Arteriola medullaris recta (vasa recta).
(18) Arteriola afferens.
(19) Arteriola efferens.
(22) Capsula fibrosa.
(24) Glomerulus (glomerular tuft).
(25) Thin ascending limb. (ATL) (long-looped nephron).
(26) Thin descending limb (DTL) (long-looped nephron). Note ATL + DTL = intermediate tubule (IT).
(B): Indian ink perfusion in order to visualize the blood vessel system, mouse. (15) Arteria arcuata. (16) Arteria corticalis radiata.
(C): Stain trichrome, human. Detail wall of a large arcuate artery (or arched artery) with lumen and erythrocytes. Note redly stained smooth muscular fibers of the tunica media (2) and a strong undulating (reddish) internal elastic lamina in the intima (1) with endothelial cells. Outside the tunica media the connective tissue of the adventitia (4) is shown with a likewise undulating external elastic lamina (3).
(D): Indian ink perfusion, mouse. (16) Cortical radial artery (or interlobular artery) in the cortex, and (18) vas afferens of a glomerulus.
(E): Stain trichrome, human. Detail of the wall of an interlobular artery (arteria corticalis radiata), structurally equal to the arcuate (or arched) artery (C).
(F): Indian ink perfusion, mouse. Detail of the inlet of a vas afferens (18) into the glomerulus.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, arcuate artery, arteria arcuata, cortical artery, arteria corticalis, interlobular artery, vas afferens, histology, POJA collection
Title: Blood vessel supply system in the kidney
Description:
(A): Kidney, scheme, human. (See also for better resolution 5.3 POJA-L5006B)
Right side vertical strip with blue/red characters: (1) Cortex.
(2) Medulla.
(3) Outer zone of the renal medulla.
(4) Inner zone of the renal medulla.
Left side with nephrons:
(1) Cortex.
(2) Medulla, with the outer zone (3) and with the inner zone (4) of the medulla.
(5) Outer stripe of the outer zone.
(6) Inner stripe of the outer zone.
(7) Arteriola efferens leaving the glomerulus.
(8) Macula densa (MD).
(9) Pars contorta I or proximal convoluted tubule (PCT).
(10) Pars recta I or proximal straight tubule (PST).
(11) Henle’s loop (short-looped and long-looped nephrons).
(12) Pars recta II or distal straight tubule (DST) or thick ascending limb (TAL)
(13) Pars contorta II or distal convoluted tubule (DCT); last part is connecting tubule (CNT) toward (14) Collecting duct divided in
cortical collecting duct (CCD), an outer medullary collecting duct (OMCD) and an inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD)
(15) Arteria arcuata.
(16) Arteria corticalis radiata (interlobular artery).
(17) Arteriola medullaris recta (vasa recta).
(18) Arteriola afferens.
(19) Arteriola efferens.
(22) Capsula fibrosa.
(24) Glomerulus (glomerular tuft).
(25) Thin ascending limb. (ATL) (long-looped nephron).
(26) Thin descending limb (DTL) (long-looped nephron). Note ATL + DTL = intermediate tubule (IT).
(B): Indian ink perfusion in order to visualize the blood vessel system, mouse. (15) Arteria arcuata. (16) Arteria corticalis radiata.
(C): Stain trichrome, human. Detail wall of a large arcuate artery (or arched artery) with lumen and erythrocytes. Note redly stained smooth muscular fibers of the tunica media (2) and a strong undulating (reddish) internal elastic lamina in the intima (1) with endothelial cells. Outside the tunica media the connective tissue of the adventitia (4) is shown with a likewise undulating external elastic lamina (3).
(D): Indian ink perfusion, mouse. (16) Cortical radial artery (or interlobular artery) in the cortex, and (18) vas afferens of a glomerulus.
(E): Stain trichrome, human. Detail of the wall of an interlobular artery (arteria corticalis radiata), structurally equal to the arcuate (or arched) artery (C).
(F): Indian ink perfusion, mouse. Detail of the inlet of a vas afferens (18) into the glomerulus.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, arcuate artery, arteria arcuata, cortical artery, arteria corticalis, interlobular artery, vas afferens, histology, POJA collection