12.1.5 POJA-L2594+4408+3375+3891
Title: Eye lens fibres
Description:
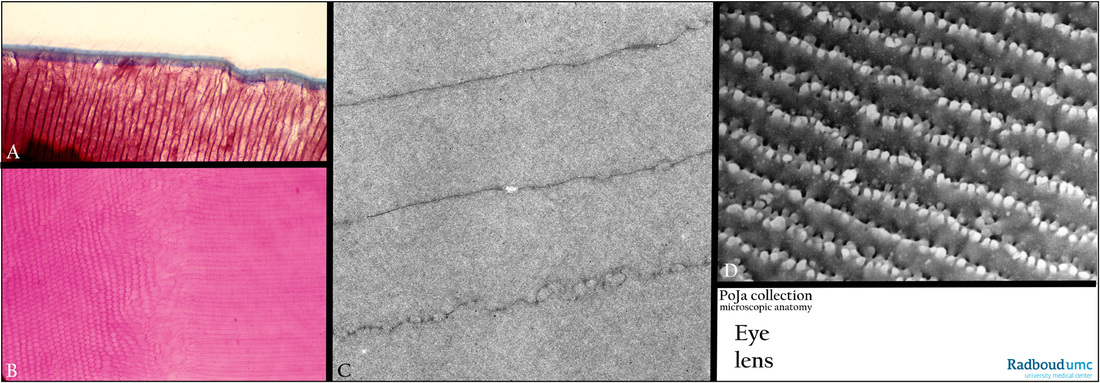
The hexagonal lens fibres (A – D) arise from the lens epithelium and contain several lens-specific proteins especially α-, β-
and γ-crystallins.
(A): Posterior side of lens, stain Azan, monkey. The blue band represents the capsule of the lens.
(B): Part of a suture (centrally), stain Haematoxylin-eosin, pig. The fibres are arranged in a three dimensional interlocking structures. i.e. concentric layers of radial lamellae.
(C): Electron micrograph bovine lens fibres. These fibres lose their nuclei. The fibres are connected to each other via focal junctional complexes and interdigitations.
(D): Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) lens fibres, rat. The long and thin lens cells have complex interdigitations
(also called ‘knobs and sockets’) that firmly interlock these cells.
Keywords/Mesh: eye, lens, lens fibre, crystallin, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Eye lens fibres
Description:
The hexagonal lens fibres (A – D) arise from the lens epithelium and contain several lens-specific proteins especially α-, β-
and γ-crystallins.
(A): Posterior side of lens, stain Azan, monkey. The blue band represents the capsule of the lens.
(B): Part of a suture (centrally), stain Haematoxylin-eosin, pig. The fibres are arranged in a three dimensional interlocking structures. i.e. concentric layers of radial lamellae.
(C): Electron micrograph bovine lens fibres. These fibres lose their nuclei. The fibres are connected to each other via focal junctional complexes and interdigitations.
(D): Scanning electron micrograph (SEM) lens fibres, rat. The long and thin lens cells have complex interdigitations
(also called ‘knobs and sockets’) that firmly interlock these cells.
Keywords/Mesh: eye, lens, lens fibre, crystallin, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection