5.4.1 POJA-L2355+2311+4292+2510+2512+2508+2516
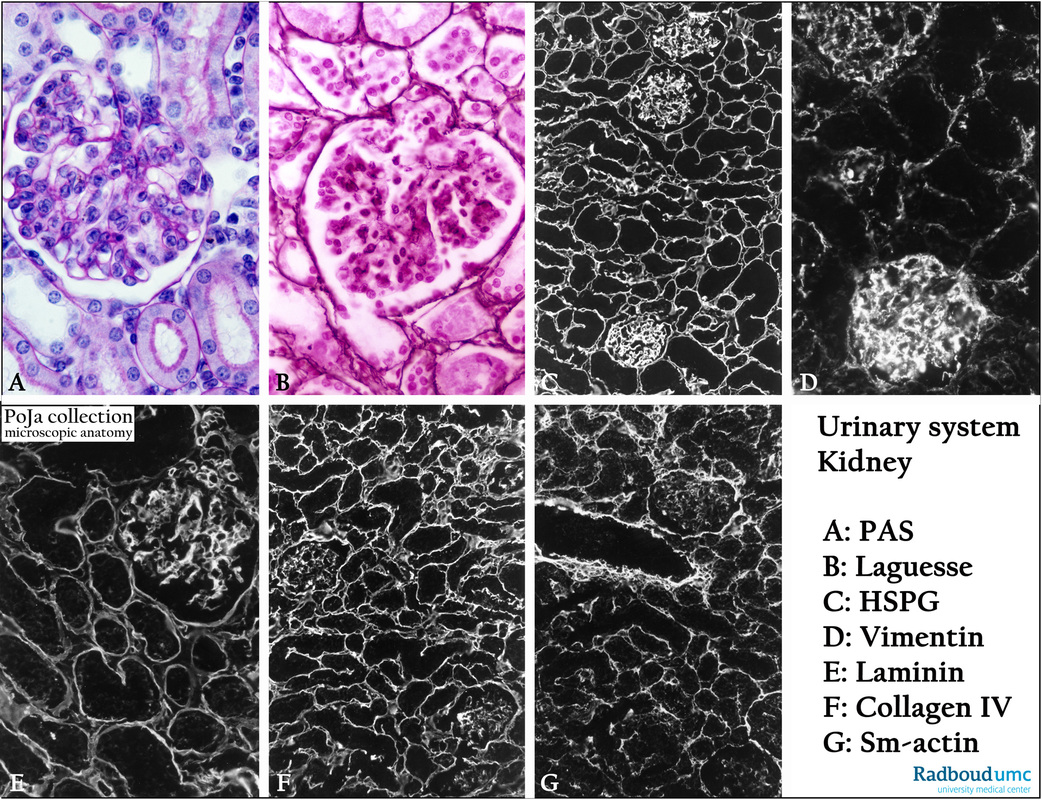
Title: Basement membrane components in glomeruli (III) of kidney
Description:
Glomeruli, (A): Stain PAS, mouse. (B): Silver stain (Laguesse), human. Silver staining for reticulin and PAS staining for glycosaminoglycans reveal mainly the basement membranes around the tubules, glomerular capsule and intraglomerular mesangium. Additionally PAS also stains the lumenal brush borders of the proximal tubules.
(C): Glomeruli, immunofluorescence staining with antibodies, human.
Against heparan sulfate proteoglycans which are elements of the basal membranes around renal tubules and blood vessels in glomeruli.
(D): Ditto, against vimentin found in mesenchymal-derived non-epithelial cell types.
(E): Ditto, against laminin present in basal lamina or cell-associated extracellular matrices.
(F): Ditto, against collagen IV, found primarily in the basal lamina.
(G): Ditto, against smooth muscle actin (vascular smooth muscle cells and myofibroblasts).
Background: With concern to basement membranes laminin and collagen IV show an equally reaction pattern as HSPG, however the latter stains more strongly the mesangial components within the glomerulus.
Vimentin staining differs between the several glomeruli dependent on the influx of circulating cells (e.g. macrophages, white blood cells). Compared to inflamed interstitia normal interstitium with little loose connective tissue with fibroblasts and capillaries is weakly positive. Smooth muscle actin is well presented in the media of blood vessels as well as in its surroundings, and in peritubular myofibroblasts. Contractile mesangial cells within the glomerulus are weakly positive, too.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, glomerulus, basement membrane, basal lamina, mesangium, histology, POJA collection
Title: Basement membrane components in glomeruli (III) of kidney
Description:
Glomeruli, (A): Stain PAS, mouse. (B): Silver stain (Laguesse), human. Silver staining for reticulin and PAS staining for glycosaminoglycans reveal mainly the basement membranes around the tubules, glomerular capsule and intraglomerular mesangium. Additionally PAS also stains the lumenal brush borders of the proximal tubules.
(C): Glomeruli, immunofluorescence staining with antibodies, human.
Against heparan sulfate proteoglycans which are elements of the basal membranes around renal tubules and blood vessels in glomeruli.
(D): Ditto, against vimentin found in mesenchymal-derived non-epithelial cell types.
(E): Ditto, against laminin present in basal lamina or cell-associated extracellular matrices.
(F): Ditto, against collagen IV, found primarily in the basal lamina.
(G): Ditto, against smooth muscle actin (vascular smooth muscle cells and myofibroblasts).
Background: With concern to basement membranes laminin and collagen IV show an equally reaction pattern as HSPG, however the latter stains more strongly the mesangial components within the glomerulus.
Vimentin staining differs between the several glomeruli dependent on the influx of circulating cells (e.g. macrophages, white blood cells). Compared to inflamed interstitia normal interstitium with little loose connective tissue with fibroblasts and capillaries is weakly positive. Smooth muscle actin is well presented in the media of blood vessels as well as in its surroundings, and in peritubular myofibroblasts. Contractile mesangial cells within the glomerulus are weakly positive, too.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, glomerulus, basement membrane, basal lamina, mesangium, histology, POJA collection