12.2.4.2 POJA-L3401+3616+3611+3625+3447+3439
Title: Otoconia in the macula of the saccule in the inner ear
Description:
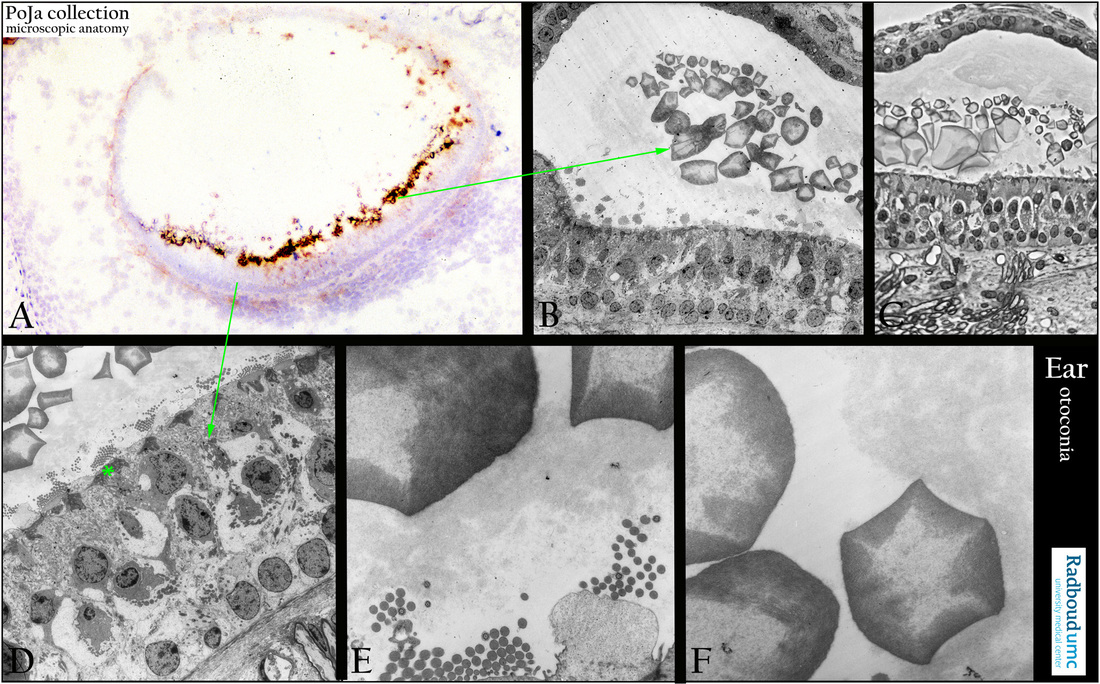
(A): Macula with otoconia (statoconia), immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and antibodies against keratan sulfate show immunoreactivity around the otoconia, 1 day postnatal rat.
Keratan sulfate proteoglycan (KSPG) is the predominant proteoglycan in the inner ear and shows strong staining in murine otoconia. KSPG may participate in sequestering and retaining Ca2+ for crystal formation because of its strong negative charges.
Background:
Otoconia contain otoconin-90 (Oc90) as the major core matrix protein that accounts for more than 90% of the organic phase.
Otolin is a secreted glycoprotein present in both otoconial crystals and otolithic membranes, it may function similarly to collagen X.
Co-expressing of Oc90 with otolin leads to increased extracellular matrix calcification.
It is assumed that KSPG may interact with Oc90 and otolin to form the matrix framework for depositions of calcite crystals.
Some disorders involving keratin sulfate metabolism might result in deficit otoconia formation.
(B, D): Macula with otoconia, low survey electron micrograph of macula epithelium with otoconia, rat. A macula consists of a small sensory receptor area with type I/type II hair cells and supporting cells covered by a gelatinous glycoprotein layer. (*) Cuticular area of sensory cell, with above cross sectioned stereocilia. Each hair cell has about 40-70 stereocilia fixed in the apical cuticular plate as well as one long free flexible kinocilium and a basal body within the apical cytoplasm. Within a bundle of stereocilia shorter stereocilia are connected to their taller neighbours by protein fibres called tip-links an important component of the mechanotransduction apparatus.
The stereociliary tips are embedded in the so-called otolithic membrane, a jelly-like otoconia-containing substance that contains glycoproteins (otolin) and a.o. alpha- and beta-tectorin proteins. Otogelin is a specific protein that is synthesised by nonsensory cells located underneath the acellular membranes. It is found in otolithic and accessory membranes of utricle and saccule.
(C): Macula with otoconia, toluidine-blue stain (phase contrast, black-white), one micron plastic section, similar as in (B), rat.
Pseudostratified layering of supporting cells and receptor cells with apical cross-sectioned ciliary bundles. Basally myelinated nerve fibres.
(E, F): Otoconia, electron micrographs (higher magnification); statoconia decalcified due to the procedure technique, rat.
The inner core of the otoconia exhibits a fibrillar meshwork continuous with the adjacent outer zone. Notice cross-sections of single kinocilia amid those of numerous stereocilia. Otoconia contain an inner core made of otoconins (glycoproteins, Oc90) and proteoglycans while the outer surface consists mostly of precipitated CaCO3 (dissolved in these pictures). They add to the density of the membrane contributing in sensing motion and gravity. Otogelin is also present as the acellular material covering the otoconia.
Keywords/Mesh: inner ear, macula, saccule, otoconium, statoconium, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Otoconia in the macula of the saccule in the inner ear
Description:
(A): Macula with otoconia (statoconia), immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and antibodies against keratan sulfate show immunoreactivity around the otoconia, 1 day postnatal rat.
Keratan sulfate proteoglycan (KSPG) is the predominant proteoglycan in the inner ear and shows strong staining in murine otoconia. KSPG may participate in sequestering and retaining Ca2+ for crystal formation because of its strong negative charges.
Background:
Otoconia contain otoconin-90 (Oc90) as the major core matrix protein that accounts for more than 90% of the organic phase.
Otolin is a secreted glycoprotein present in both otoconial crystals and otolithic membranes, it may function similarly to collagen X.
Co-expressing of Oc90 with otolin leads to increased extracellular matrix calcification.
It is assumed that KSPG may interact with Oc90 and otolin to form the matrix framework for depositions of calcite crystals.
Some disorders involving keratin sulfate metabolism might result in deficit otoconia formation.
(B, D): Macula with otoconia, low survey electron micrograph of macula epithelium with otoconia, rat. A macula consists of a small sensory receptor area with type I/type II hair cells and supporting cells covered by a gelatinous glycoprotein layer. (*) Cuticular area of sensory cell, with above cross sectioned stereocilia. Each hair cell has about 40-70 stereocilia fixed in the apical cuticular plate as well as one long free flexible kinocilium and a basal body within the apical cytoplasm. Within a bundle of stereocilia shorter stereocilia are connected to their taller neighbours by protein fibres called tip-links an important component of the mechanotransduction apparatus.
The stereociliary tips are embedded in the so-called otolithic membrane, a jelly-like otoconia-containing substance that contains glycoproteins (otolin) and a.o. alpha- and beta-tectorin proteins. Otogelin is a specific protein that is synthesised by nonsensory cells located underneath the acellular membranes. It is found in otolithic and accessory membranes of utricle and saccule.
(C): Macula with otoconia, toluidine-blue stain (phase contrast, black-white), one micron plastic section, similar as in (B), rat.
Pseudostratified layering of supporting cells and receptor cells with apical cross-sectioned ciliary bundles. Basally myelinated nerve fibres.
(E, F): Otoconia, electron micrographs (higher magnification); statoconia decalcified due to the procedure technique, rat.
The inner core of the otoconia exhibits a fibrillar meshwork continuous with the adjacent outer zone. Notice cross-sections of single kinocilia amid those of numerous stereocilia. Otoconia contain an inner core made of otoconins (glycoproteins, Oc90) and proteoglycans while the outer surface consists mostly of precipitated CaCO3 (dissolved in these pictures). They add to the density of the membrane contributing in sensing motion and gravity. Otogelin is also present as the acellular material covering the otoconia.
Keywords/Mesh: inner ear, macula, saccule, otoconium, statoconium, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection