12.2.4 POJA-L2610+2611
Title: Otic vesicle in future ear
Description:
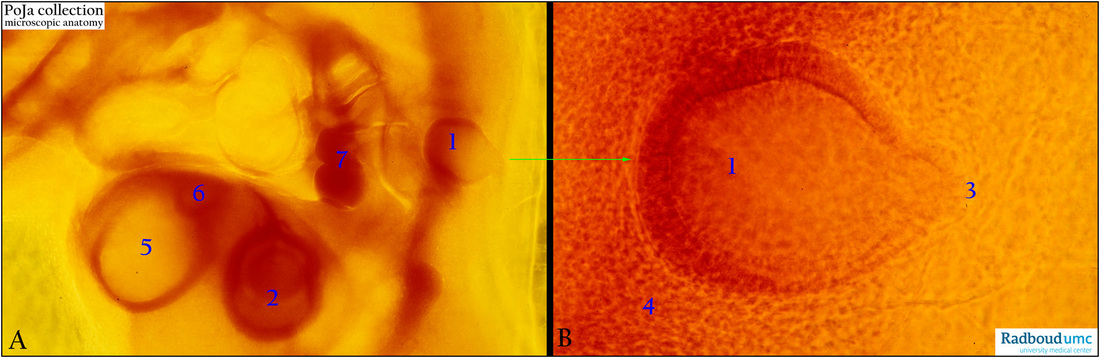
(A, B): Chicken embryo (72 h), in toto stained with eosin. Survey (embryo upside down) and detail. (A, 2) Optic cup with lens vesicle. (A, 5) Telencephalon.
(A, 6) Nasal placode plus nasal pit. (A, 7) Heart region. (A, 1 and B, 1) Otic vesicle (or otocyst).
- The otic vesicle is formed by fusion of the two edges of the otic pit (4th week) and the vesicle is the primordium of the future
membranous labyrinth (cochlear duct, utricle, saccule and semicircular ducts).
- The otic vesicle loses quite soon connection with the surface ectoderm.
- Out from the vesicle a diverticulum (B, 3) is growing, elongates and form the endolymphatic duct and sac.
- The surrounding mesenchyme (B, 4) forms the otic capsule that later develops into the osseus labyrinth (cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals).
Keyword/Mesh: ear, otic vesicle, otocyst, embryo, histology, POJA collection
Title: Otic vesicle in future ear
Description:
(A, B): Chicken embryo (72 h), in toto stained with eosin. Survey (embryo upside down) and detail. (A, 2) Optic cup with lens vesicle. (A, 5) Telencephalon.
(A, 6) Nasal placode plus nasal pit. (A, 7) Heart region. (A, 1 and B, 1) Otic vesicle (or otocyst).
- The otic vesicle is formed by fusion of the two edges of the otic pit (4th week) and the vesicle is the primordium of the future
membranous labyrinth (cochlear duct, utricle, saccule and semicircular ducts).
- The otic vesicle loses quite soon connection with the surface ectoderm.
- Out from the vesicle a diverticulum (B, 3) is growing, elongates and form the endolymphatic duct and sac.
- The surrounding mesenchyme (B, 4) forms the otic capsule that later develops into the osseus labyrinth (cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals).
Keyword/Mesh: ear, otic vesicle, otocyst, embryo, histology, POJA collection