16.1.3 POJA-L7095+7098+7096 Endochondral ossification in foetus 1
16.1.3 POJA-L7095+7098+7096 Endochondral ossification in foetus 1
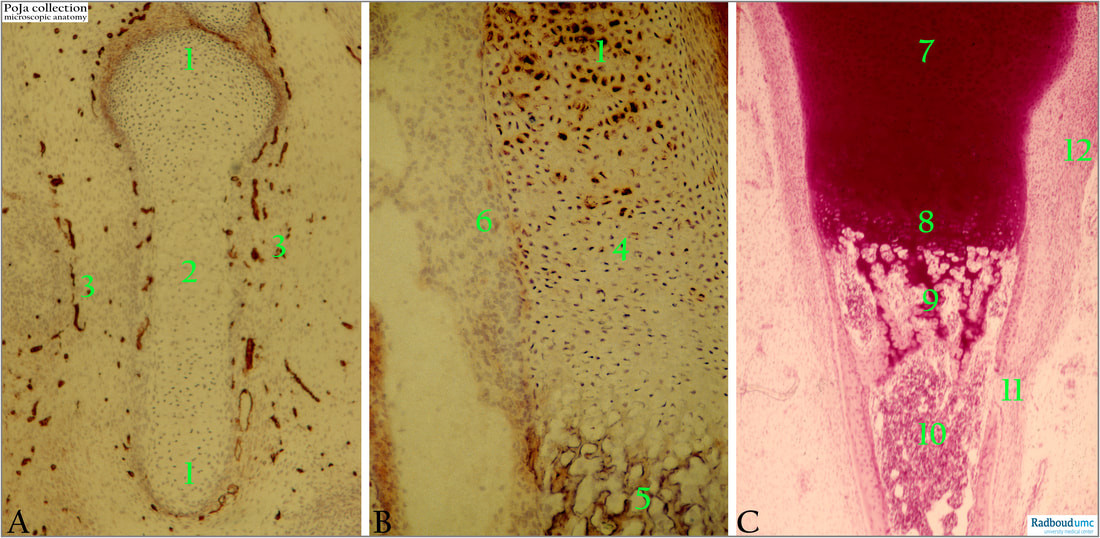
Title: Endochondral ossification in foetus 1
Description:
(A): Immunoperoxidase stain of collagen IV in rat (1 day postnatally).
(1): Epiphysis.
(2): Diaphysis.
(3): Connective tissue with positive basal membrane staining of blood vessels. Collagen IV is characteristic for basal membrane collagen.
(B): Immunoperoxidase stain of keratan sulphate in rat (1 day postnatally).
(1): Cartilage, epiphysis.
(4): Distended hypertrophied cartilage cells.
(5): Formation site of spiculae.
(6): Mesenchyme-fibroblast cells around the chondral bone shape. The unstained space (medullary cavities) between the future trabeculae is the site where bone marrow with haematopoietic cells is formed.
Keratan sulphate is part of the matrix in the cartilage and is produced by the chondrocytes.
(C): Human foetus.
(7): Cartilage epiphyse.
(8): Cartilage diaphyse, area of hypertrophic chondrocytes.
(9): Ossification zone, where cartilage is gradually replaced by bone represented as trabeculae.
(10): Bone marrow.
(11): Site where the periosteum is going to be formed from mesenchymal cells. There is a small opening where blood vessels (medullary or nutrient artery) can enter (future nutrient foramen).
(12): Thick perichondral layer of cells.
The endochondral ossification requires an existing scaffold of hyaline cartilage. The cartilage is degraded and replaced by bone tissue recognized as trabeculae (endochondral). Osteoblasts around the periochondrium built a sleeve of perichondral bone in the area of the diaphysis.
Background:
Epiphysis: the region between the growth plate and the extended end of the future bone, covered by articular cartilage.
Metaphysis: region between the growth plate and diaphysis with abundant trabecular bone. Compared to the diaphysis the cortical bone is here thinner.
Diaphysis (shaft): region between the upper and lower metaphyses, and is mainly composed of compact cortical bone.
Reference:
(Borys, D. Anatomy-bone. PathologyOutlines.comwebsite. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bonenormalanatomy.html)
See also:
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, endochondral ossification, foetus, bone, cartilage, chondrocyte, epiphysis, diaphysis, bone marrow, histology, POJA collection
Title: Endochondral ossification in foetus 1
Description:
(A): Immunoperoxidase stain of collagen IV in rat (1 day postnatally).
(1): Epiphysis.
(2): Diaphysis.
(3): Connective tissue with positive basal membrane staining of blood vessels. Collagen IV is characteristic for basal membrane collagen.
(B): Immunoperoxidase stain of keratan sulphate in rat (1 day postnatally).
(1): Cartilage, epiphysis.
(4): Distended hypertrophied cartilage cells.
(5): Formation site of spiculae.
(6): Mesenchyme-fibroblast cells around the chondral bone shape. The unstained space (medullary cavities) between the future trabeculae is the site where bone marrow with haematopoietic cells is formed.
Keratan sulphate is part of the matrix in the cartilage and is produced by the chondrocytes.
(C): Human foetus.
(7): Cartilage epiphyse.
(8): Cartilage diaphyse, area of hypertrophic chondrocytes.
(9): Ossification zone, where cartilage is gradually replaced by bone represented as trabeculae.
(10): Bone marrow.
(11): Site where the periosteum is going to be formed from mesenchymal cells. There is a small opening where blood vessels (medullary or nutrient artery) can enter (future nutrient foramen).
(12): Thick perichondral layer of cells.
The endochondral ossification requires an existing scaffold of hyaline cartilage. The cartilage is degraded and replaced by bone tissue recognized as trabeculae (endochondral). Osteoblasts around the periochondrium built a sleeve of perichondral bone in the area of the diaphysis.
Background:
Epiphysis: the region between the growth plate and the extended end of the future bone, covered by articular cartilage.
Metaphysis: region between the growth plate and diaphysis with abundant trabecular bone. Compared to the diaphysis the cortical bone is here thinner.
Diaphysis (shaft): region between the upper and lower metaphyses, and is mainly composed of compact cortical bone.
Reference:
(Borys, D. Anatomy-bone. PathologyOutlines.comwebsite. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bonenormalanatomy.html)
See also:
- 16.1.3 POJA-L7104+7105+7100 Endochondral ossification in foetus 2
- 16.1.3 POJA-L7134 Endochondral ossification in foetus 3a
- 16.1.3 POJA-L3813 Endochondral ossification in foetus 3
- 16.1.3 POJA-L7109+7108+7101+7097 Endochondral ossification in foetus 4
- 16.1.3 POJA-L7102+7103+7106+7107 Endochondral ossification in foetus 5
- 16.1.3 POJA-L7147+7111+7110 Endochondral ossification in foetus 6
- 16.1.3 POJA-L7116+7115+7123 Endochondral ossification in foetus 7
- 16.1.3 POJA-L7145+7099 Endochondral ossification in foetus 8
- 16.0.5 POJA-L7205 Bone: Introduction Bone formation-5 Long bones
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, endochondral ossification, foetus, bone, cartilage, chondrocyte, epiphysis, diaphysis, bone marrow, histology, POJA collection