12.2.4.1. POJA-L2623+2644+3606+2965+3430+2619+2617+2620
Title: Organ of Corti and innervations in the inner ear
Description:
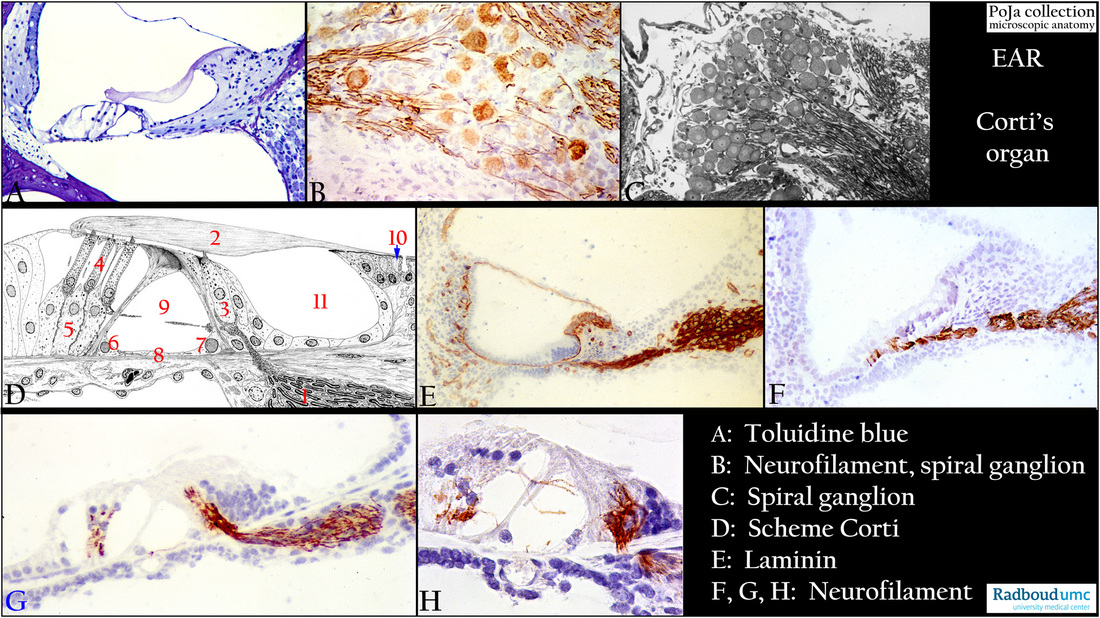
(A): Organ of Corti, stain toluidine blue semi-thin plastic section, guinea pig. Compare with items in (D).
(B): Spiral ganglion (=cochlear ganglion), immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and antibodies against neurofilament, 4 days postnatal rat.
Ganglion cell bodies and the single nerve fibres contrast clearly positively.
(C): Spiral ganglion (=cochlear ganglion), stain toluidine blue semi-thin plastic section (black and white print), adult rat. Note here the dark-stained myelinated nerve fibres.
(D): Organ of Corti, scheme electron microscopy, human. As a mainstay the following items are shown here:
(1) Cochlear nerve. (5) Phalangeal cells (Deiters).
(2) Membrana tectoria. (6) Outer pillar cells
(3) Inner hair cell (IHC). (7) Inner pillar cells.
(4) Three outer hair cells (OHCs) and their supportive Deiters cells. (8) Lamina basilaris.
(9) Inner tunnel or tunnel of Corti with free-traversing nonmyelinated nerve fibres that synapse on the basal poles of IHC and OHCs.
(10) Interdental cells involved in the production of tectorial membrane substance.
(11) Internal spiral tunnel. The striated matrix of the membrana tectoria (2) contains different types of collagen, glycosaminoglycans,
and specific tectorin/otogelin proteins. The membrane is synthesized by interdental cells (10) and extend to the external outer hair cells (OHCs). The tectorial membrane embeds the tips of the tall stereocilia of hair cells and due to perilymph movement in the scala tympani displacement of basilar membrane and organ of Corti results in depolarisation of the HCs.
(E): Organ of Corti, immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and antibodies against laminin, 4 days postnatal rat. All basal lamina-associated structures in the cochlear duct are distinctly positive such as capillaries (stria vascularis), Reissner’s membrane, spiral limbus area,
lamina basilaris and afferent/efferent myelinated nerve fibres.
(F-H): Organ of Corti, immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and antibodies against neurofilament, 4 days postnatal rat.
In (F, G) nerve endings near the supporting cells and on the receptor cells. (H) shows free-traversing unmyelinated nerve fibres
through the inner tunnel and Nuel’s space (beween the outer pillar cells and the OHCs).
Keywords/Mesh: inner ear, organ of Corti, spiral ganglion, cochlear nerve, neurofilament, laminin, histology, electron microscopy,
POJA collection
Title: Organ of Corti and innervations in the inner ear
Description:
(A): Organ of Corti, stain toluidine blue semi-thin plastic section, guinea pig. Compare with items in (D).
(B): Spiral ganglion (=cochlear ganglion), immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and antibodies against neurofilament, 4 days postnatal rat.
Ganglion cell bodies and the single nerve fibres contrast clearly positively.
(C): Spiral ganglion (=cochlear ganglion), stain toluidine blue semi-thin plastic section (black and white print), adult rat. Note here the dark-stained myelinated nerve fibres.
(D): Organ of Corti, scheme electron microscopy, human. As a mainstay the following items are shown here:
(1) Cochlear nerve. (5) Phalangeal cells (Deiters).
(2) Membrana tectoria. (6) Outer pillar cells
(3) Inner hair cell (IHC). (7) Inner pillar cells.
(4) Three outer hair cells (OHCs) and their supportive Deiters cells. (8) Lamina basilaris.
(9) Inner tunnel or tunnel of Corti with free-traversing nonmyelinated nerve fibres that synapse on the basal poles of IHC and OHCs.
(10) Interdental cells involved in the production of tectorial membrane substance.
(11) Internal spiral tunnel. The striated matrix of the membrana tectoria (2) contains different types of collagen, glycosaminoglycans,
and specific tectorin/otogelin proteins. The membrane is synthesized by interdental cells (10) and extend to the external outer hair cells (OHCs). The tectorial membrane embeds the tips of the tall stereocilia of hair cells and due to perilymph movement in the scala tympani displacement of basilar membrane and organ of Corti results in depolarisation of the HCs.
(E): Organ of Corti, immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and antibodies against laminin, 4 days postnatal rat. All basal lamina-associated structures in the cochlear duct are distinctly positive such as capillaries (stria vascularis), Reissner’s membrane, spiral limbus area,
lamina basilaris and afferent/efferent myelinated nerve fibres.
(F-H): Organ of Corti, immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and antibodies against neurofilament, 4 days postnatal rat.
In (F, G) nerve endings near the supporting cells and on the receptor cells. (H) shows free-traversing unmyelinated nerve fibres
through the inner tunnel and Nuel’s space (beween the outer pillar cells and the OHCs).
Keywords/Mesh: inner ear, organ of Corti, spiral ganglion, cochlear nerve, neurofilament, laminin, histology, electron microscopy,
POJA collection