2.1 POJA-L928-II
Title: Thymus after cyclophosphamide treatment (rat)
Description: Stain: H&E.
A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP) (70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution, i.e. inhibition of the cell proliferation and maturation.
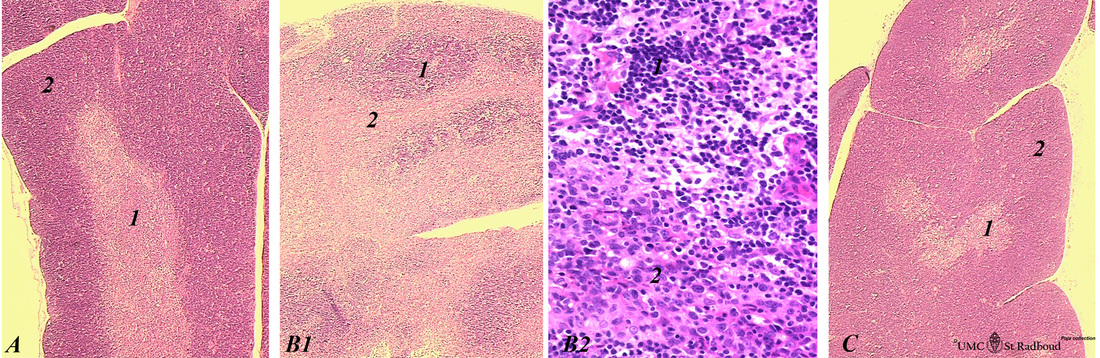
(A): Normal thymus with medulla (1) and cortex (2).
(B1): Inversion of thymic cortex and medulla 4 to 8 days after CP treatment, i.e. the cortex is lightly stained due to exit of T cells to the medulla without a concomitant supply of new T cells in the cortex. The medulla is stained darkly.
(B2): detail of B1 showing a majority of blast-like cells in the cortex and nearly none small T-cells, while the medulla (1) contains predominantly small, darkly staining lymphocytes.
(C): Recovery of the normal situation two weeks later.
The cyclophosphamide treatment induces transiently an immunosupression of the antibody response.
Keywords/Mesh: lymphatic organ, , thymus, cyclophosphamide, toxicology, histology, POJA collection
Title: Thymus after cyclophosphamide treatment (rat)
Description: Stain: H&E.
A single injection with cyclophosphamide (CP) (70 mg/ml) induces a transient cortical involution, i.e. inhibition of the cell proliferation and maturation.
(A): Normal thymus with medulla (1) and cortex (2).
(B1): Inversion of thymic cortex and medulla 4 to 8 days after CP treatment, i.e. the cortex is lightly stained due to exit of T cells to the medulla without a concomitant supply of new T cells in the cortex. The medulla is stained darkly.
(B2): detail of B1 showing a majority of blast-like cells in the cortex and nearly none small T-cells, while the medulla (1) contains predominantly small, darkly staining lymphocytes.
(C): Recovery of the normal situation two weeks later.
The cyclophosphamide treatment induces transiently an immunosupression of the antibody response.
Keywords/Mesh: lymphatic organ, , thymus, cyclophosphamide, toxicology, histology, POJA collection