1.1 POJA-L661
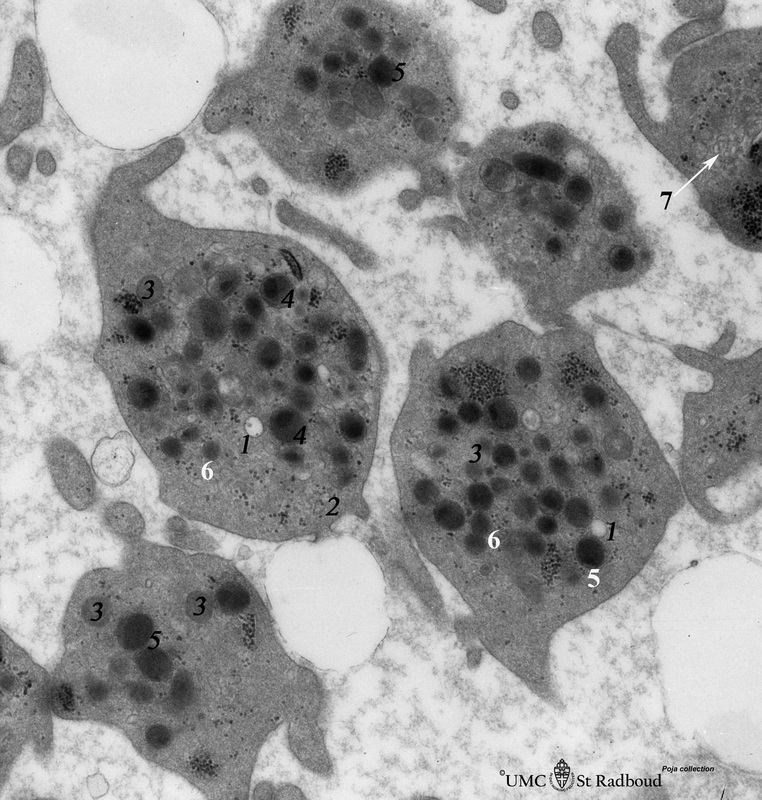
Title: Platelets (peripheral blood, human)
Description: Electron microscopy.
These disc-shaped cells (2-4 mm) without nucleus, are derived from cytoplasmic fragments of the megakaryocyte. Free floating in the peripheral blood they develop thin extensions. They contain among others few mitochondria, smooth tubular systems, marginal localized microtubules, glycogen and different types of granula.
The open canalicular system (OCS) is observed as light vacuoles (1) in between the granules.
(2): Peripheral bundle of microtubules.
(5): Homogeneous electron-dense d granules (5) contain plasma-absorbed serotonin, calcium ions, ADP and ATP etc., while the homogeneous electron-grey ones (l) represents lysosomes (6).
(3): Mitochondria.
(7, ↓ arrow): Dense tubular system.
On the other hand the electron-grey granules with a dark centre (4) (a-granula) are variable in size and shape and contain among others platelet-derived growth factor, factor VIII (von Willebrand), thrombospondin, fibronectin, fibrinogen.
Background: In a clotting process due to adherence to collagen exposed receptors for factor VIII platelets change their shape becoming spherical and develop numerous long thin cytoplasmic processes that interlinked with other platelets. The granular contents are released via the open canalicular system and the clotting cascade is activated due to adhesion of other platelets under the influence of ADP, calcium ions etc.
Keywords/Mesh: blood, bone marrow, platelet, megakaryocyte, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Platelets (peripheral blood, human)
Description: Electron microscopy.
These disc-shaped cells (2-4 mm) without nucleus, are derived from cytoplasmic fragments of the megakaryocyte. Free floating in the peripheral blood they develop thin extensions. They contain among others few mitochondria, smooth tubular systems, marginal localized microtubules, glycogen and different types of granula.
The open canalicular system (OCS) is observed as light vacuoles (1) in between the granules.
(2): Peripheral bundle of microtubules.
(5): Homogeneous electron-dense d granules (5) contain plasma-absorbed serotonin, calcium ions, ADP and ATP etc., while the homogeneous electron-grey ones (l) represents lysosomes (6).
(3): Mitochondria.
(7, ↓ arrow): Dense tubular system.
On the other hand the electron-grey granules with a dark centre (4) (a-granula) are variable in size and shape and contain among others platelet-derived growth factor, factor VIII (von Willebrand), thrombospondin, fibronectin, fibrinogen.
Background: In a clotting process due to adherence to collagen exposed receptors for factor VIII platelets change their shape becoming spherical and develop numerous long thin cytoplasmic processes that interlinked with other platelets. The granular contents are released via the open canalicular system and the clotting cascade is activated due to adhesion of other platelets under the influence of ADP, calcium ions etc.
Keywords/Mesh: blood, bone marrow, platelet, megakaryocyte, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection