12.2.4.1 POJA-La0114+L3539+3602+3603+3604
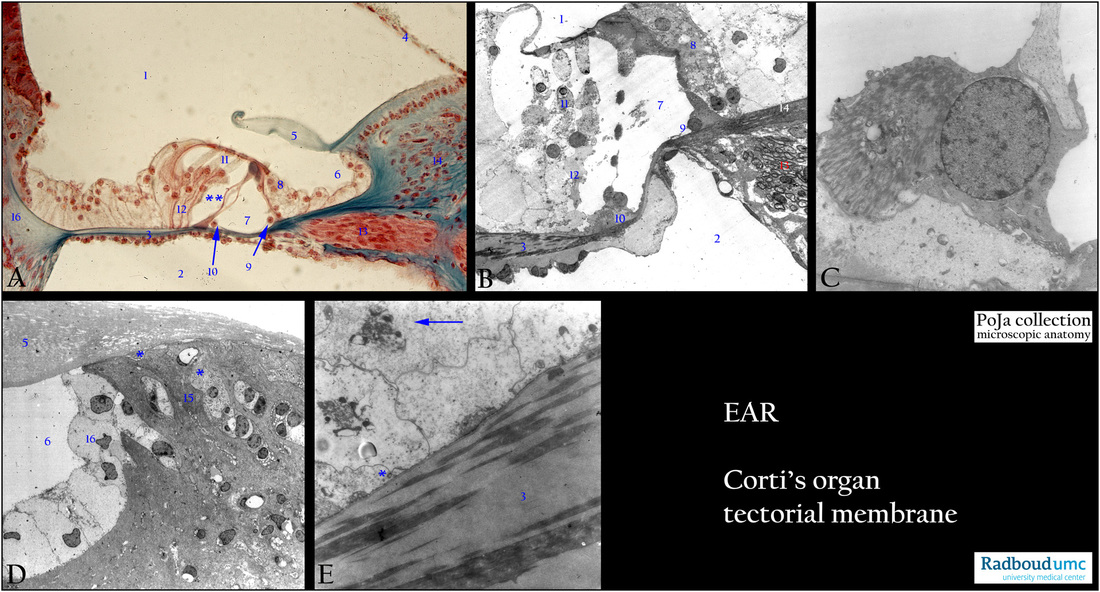
Title: Organ of Corti in the inner ear
Description:
(A) Organ of Corti, stain Azan, human.
(B-E) Electron micrographs, rat.
(1) Scala media or cochlear duct or the spiral membranous labyrinth.
(2) Scala tympani.
(3) Lamina basilaris in (A, B, E). The spiral ligament (A, 16) (connective tissue) is connected to the basilar membrane.
(4) Part of Reissner’s membrane.
(5) Centrally the organ of Corti with the jelly-like tectorial membrane in (A, B).
(6) Inner spiral tunnel (or sulcus) with the border cells (A, D).
(7) Inner tunnel (tunnel of Corti) (A, B).
(8) Inner hair cell close to the inner pillar cell (A, C).
(9) Inner pillar cell.
(10) Outer pillar cell.
(11) Three rows of outer hair cells (OHCs) associated with their phalangeal cells (12) (A, B).
(12) Phalangeal cells (Deiters cells). (A, **) Space of Nuel separates OHCs + Deiters cells from outer pillar cells, at their left the light stained cells of Hensen.
(13) Cochlear nerve.
(14) Osseous spiral membrane.
The basilar membrane (A, 3; B, 3; E, 3): All cells contributing to the organ of Corti lie on a normal basal lamina separating them
from the basilar membrane including the vas spirale (or the outer spiral vessel). The spiral vessel (present in man and guinea pig)
feeds the cells in the organ of Corti. The real basilar lamina is composed of centrally a thick amorphous layer embedding bundles
of microfibrils of collagen (filaments of auditory strings) apposed to the basal lamina at the cellular side (in B, E).
Tectorial membrane (A, 5; D, 5): The spiral limbus is a protrusion of a thickened endosteum over the osseus spiral membrane at
the apex of the cochlear duct. Capillaries (in D) and fibroblasts are present in the spiral limbus.
The vestibular lip (in D) delimits the limbus area (15) from the inner spiral sulcus (D, 6) with inner border cells (D, 16).
The lip contains parallel arranged collagen fibres with electron-light interdental cells (D, **)
These interdental cells secrete proteoglycans as part of the lower side of the tectorial membrane (otogelin).
In the core of the tectorial membrane collagen types II, V, IX and XI are detected as well as three types of non-collagenous proteins (totally50 %) that consists of alpha-tectorin, beta-tectorin and otogelin.
Otogelin is a specific protein synthesized by non-sensory cells located underneath the acellular membranes such as
tectorial membrane (in maturing stages otogelin labels in thick and spaced radial fibre-like structures).
Bundles of 20 nm collagen fibrils are found embedded in a tectorin-based matrix sheet with characteristic striation.
(E): Arrow points to accumulation of remnants of degenerated organelles in the Hensen cells (due to technical procedures).
Keywords/Mesh: inner ear, organ of Corti, hair cell, pillar cell, basilar membrane, interdental cell, tectorial membrane, histology,
electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Organ of Corti in the inner ear
Description:
(A) Organ of Corti, stain Azan, human.
(B-E) Electron micrographs, rat.
(1) Scala media or cochlear duct or the spiral membranous labyrinth.
(2) Scala tympani.
(3) Lamina basilaris in (A, B, E). The spiral ligament (A, 16) (connective tissue) is connected to the basilar membrane.
(4) Part of Reissner’s membrane.
(5) Centrally the organ of Corti with the jelly-like tectorial membrane in (A, B).
(6) Inner spiral tunnel (or sulcus) with the border cells (A, D).
(7) Inner tunnel (tunnel of Corti) (A, B).
(8) Inner hair cell close to the inner pillar cell (A, C).
(9) Inner pillar cell.
(10) Outer pillar cell.
(11) Three rows of outer hair cells (OHCs) associated with their phalangeal cells (12) (A, B).
(12) Phalangeal cells (Deiters cells). (A, **) Space of Nuel separates OHCs + Deiters cells from outer pillar cells, at their left the light stained cells of Hensen.
(13) Cochlear nerve.
(14) Osseous spiral membrane.
The basilar membrane (A, 3; B, 3; E, 3): All cells contributing to the organ of Corti lie on a normal basal lamina separating them
from the basilar membrane including the vas spirale (or the outer spiral vessel). The spiral vessel (present in man and guinea pig)
feeds the cells in the organ of Corti. The real basilar lamina is composed of centrally a thick amorphous layer embedding bundles
of microfibrils of collagen (filaments of auditory strings) apposed to the basal lamina at the cellular side (in B, E).
Tectorial membrane (A, 5; D, 5): The spiral limbus is a protrusion of a thickened endosteum over the osseus spiral membrane at
the apex of the cochlear duct. Capillaries (in D) and fibroblasts are present in the spiral limbus.
The vestibular lip (in D) delimits the limbus area (15) from the inner spiral sulcus (D, 6) with inner border cells (D, 16).
The lip contains parallel arranged collagen fibres with electron-light interdental cells (D, **)
These interdental cells secrete proteoglycans as part of the lower side of the tectorial membrane (otogelin).
In the core of the tectorial membrane collagen types II, V, IX and XI are detected as well as three types of non-collagenous proteins (totally50 %) that consists of alpha-tectorin, beta-tectorin and otogelin.
Otogelin is a specific protein synthesized by non-sensory cells located underneath the acellular membranes such as
tectorial membrane (in maturing stages otogelin labels in thick and spaced radial fibre-like structures).
Bundles of 20 nm collagen fibrils are found embedded in a tectorin-based matrix sheet with characteristic striation.
(E): Arrow points to accumulation of remnants of degenerated organelles in the Hensen cells (due to technical procedures).
Keywords/Mesh: inner ear, organ of Corti, hair cell, pillar cell, basilar membrane, interdental cell, tectorial membrane, histology,
electron microscopy, POJA collection