14.3 POJA-L6129 Electron micrograph of smooth muscles (rat)
14.3 POJA-L6129 Electron micrograph of smooth muscles (rat)
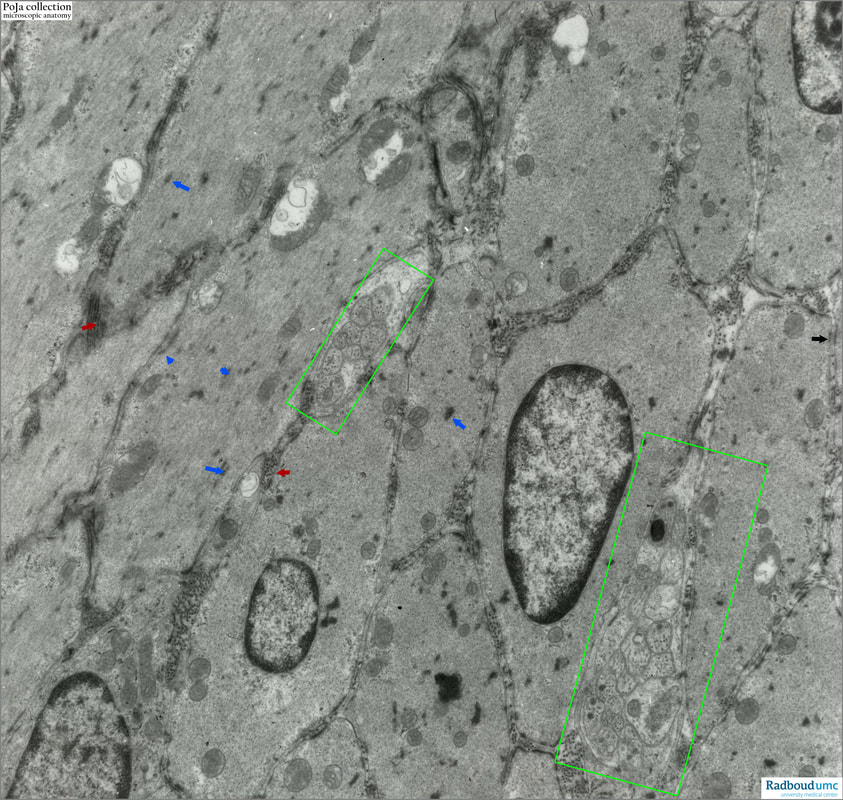
.Title: Electron micrograph of smooth muscles (rat)
Description:
In cross sections nuclei of smooth muscle cells or myocytes (colon) are characteristically located centrally in the cytoplasm.
The myocytes contain many small, irregularly distributed denser areas, dense spots or dense plaques or focal densities in the cytoplasm (blue arrows). These plaques, rich in a-actinin, mediate the anchoring of myofilaments. The cells are connected via nexus connections.
The endomysium contains ECM with collagen IV (basal lamina) and type III collagen (red arrows).
Two green rectangles show non-myelinated axons between the myocytes and in close contact.
The cell membrane (or sarcolemma) of the myocytes presents many caveolae or so-called pinocytotic vesicles and together with some sparse profile of endoplasmic reticulum (SER) they function analogous to the triad system in skeletal muscle to deliver calcium to the cytoplasm. Few myocytic mitochondria are swollen and partly damaged.
Background:
Cytoplasmic densities as well as plasma membrane densities (attachment plaques) are intracellular analogues of the Z-lines in skeletal muscle myofibres. These densities contain a-actinin as actin-binding proteins. An increase in the Ca2+ level concentration within the cytosol is necessary to initiate smooth muscle contraction. This increase is achieved either by initial depolarisation of the cell membrane or hormonal stimulation of cell surface receptors. Calcium binding to calmodulin activates phosphorylation of the myosin light chain kinase. The actin-binding on the myosin head is activated and attach to actin filaments. In the presence of ATP, the myosin head bends producing contraction that shortens the cell and produces the corkscrew shape of the nucleus, especially observed in light microscopy (adapted from Ross and Pawlina in Histology A Text and Atlas 2016).
See also:
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, smooth muscle, dense plaque, caveola, SER, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Description:
In cross sections nuclei of smooth muscle cells or myocytes (colon) are characteristically located centrally in the cytoplasm.
The myocytes contain many small, irregularly distributed denser areas, dense spots or dense plaques or focal densities in the cytoplasm (blue arrows). These plaques, rich in a-actinin, mediate the anchoring of myofilaments. The cells are connected via nexus connections.
The endomysium contains ECM with collagen IV (basal lamina) and type III collagen (red arrows).
Two green rectangles show non-myelinated axons between the myocytes and in close contact.
The cell membrane (or sarcolemma) of the myocytes presents many caveolae or so-called pinocytotic vesicles and together with some sparse profile of endoplasmic reticulum (SER) they function analogous to the triad system in skeletal muscle to deliver calcium to the cytoplasm. Few myocytic mitochondria are swollen and partly damaged.
Background:
Cytoplasmic densities as well as plasma membrane densities (attachment plaques) are intracellular analogues of the Z-lines in skeletal muscle myofibres. These densities contain a-actinin as actin-binding proteins. An increase in the Ca2+ level concentration within the cytosol is necessary to initiate smooth muscle contraction. This increase is achieved either by initial depolarisation of the cell membrane or hormonal stimulation of cell surface receptors. Calcium binding to calmodulin activates phosphorylation of the myosin light chain kinase. The actin-binding on the myosin head is activated and attach to actin filaments. In the presence of ATP, the myosin head bends producing contraction that shortens the cell and produces the corkscrew shape of the nucleus, especially observed in light microscopy (adapted from Ross and Pawlina in Histology A Text and Atlas 2016).
See also:
- 14.3 POJA-L6011+6033 Electron micrograph of rat smooth muscle cell
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, smooth muscle, dense plaque, caveola, SER, electron microscopy, POJA collection