7.4 POJA-L1778+1779
Title: Metastasis of breast carcinoma in lymph node, (human)
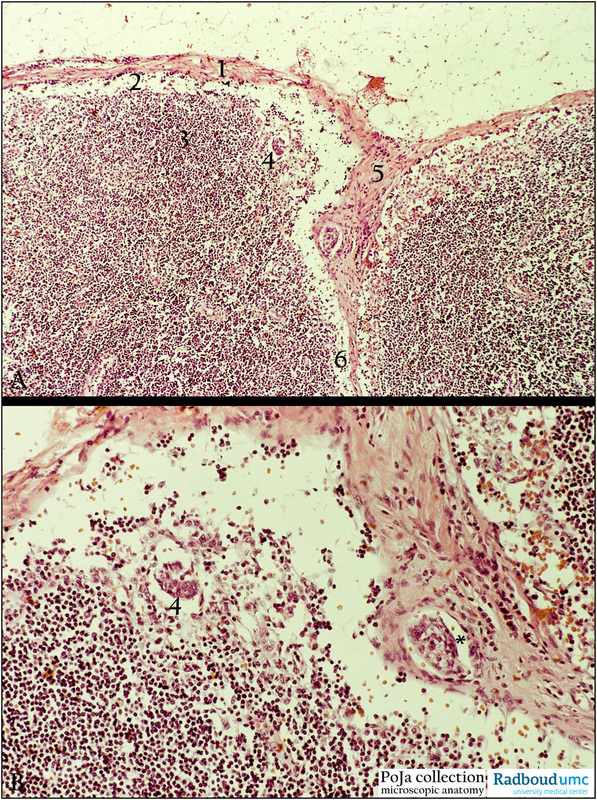
Description: Stain: (A, B) Hematoxylin-eosin.
(A, detail in B): Cortex area of lymph node with capsule (1), subcapsular sinus (2), outer cortex with diffuse lymphatic tissue (3) and epitheloid cluster of entrapped metastatic breast tumor cells peripherally (4). At (5) trabeculum with paratrabecular sinus (6). Note at (*) in small trabecular blood vessel also metastatic tumor cells. (By courtesy of F. van de Molengraft MD PhD, Department of Pathology, Rijnstate Hospital, Arnhem, The Netherlands).
Background: Spread of the tumor eventually occurs through the lymphohematogenous routes. Although the main route for metastasis of breast carcinoma is primary via lymphatic invasion the transport via bloodstream occurs simultaneously. Mostly drainage via the axillary nodes and those along the internal mammary artery is favorable. The more nodes involved and the higher in the axilla the worse the prognosis. Overall about one third of all patients has metastases to lymph nodes at the time of initial diagnosis of breast cancer. The pattern of nodal spread is influenced by the location of the tumor e.g. larger tumor arising in the outer quadrants involve the axillary alone in about 50% of cases, cancers arising in the inner quadrant and center of the breast affect the axilla alone in about 25% of cases.
Keywords/Mesh: breast, mammary glands, breast neoplasms, mammary carcinoma, histology, POJA collection, metastasis, lymph node.
Title: Metastasis of breast carcinoma in lymph node, (human)
Description: Stain: (A, B) Hematoxylin-eosin.
(A, detail in B): Cortex area of lymph node with capsule (1), subcapsular sinus (2), outer cortex with diffuse lymphatic tissue (3) and epitheloid cluster of entrapped metastatic breast tumor cells peripherally (4). At (5) trabeculum with paratrabecular sinus (6). Note at (*) in small trabecular blood vessel also metastatic tumor cells. (By courtesy of F. van de Molengraft MD PhD, Department of Pathology, Rijnstate Hospital, Arnhem, The Netherlands).
Background: Spread of the tumor eventually occurs through the lymphohematogenous routes. Although the main route for metastasis of breast carcinoma is primary via lymphatic invasion the transport via bloodstream occurs simultaneously. Mostly drainage via the axillary nodes and those along the internal mammary artery is favorable. The more nodes involved and the higher in the axilla the worse the prognosis. Overall about one third of all patients has metastases to lymph nodes at the time of initial diagnosis of breast cancer. The pattern of nodal spread is influenced by the location of the tumor e.g. larger tumor arising in the outer quadrants involve the axillary alone in about 50% of cases, cancers arising in the inner quadrant and center of the breast affect the axilla alone in about 25% of cases.
Keywords/Mesh: breast, mammary glands, breast neoplasms, mammary carcinoma, histology, POJA collection, metastasis, lymph node.