10.2 POJA-L2525+2136+2137+2253+2254
Title: Stratum granulosum of the epidermis
Description:
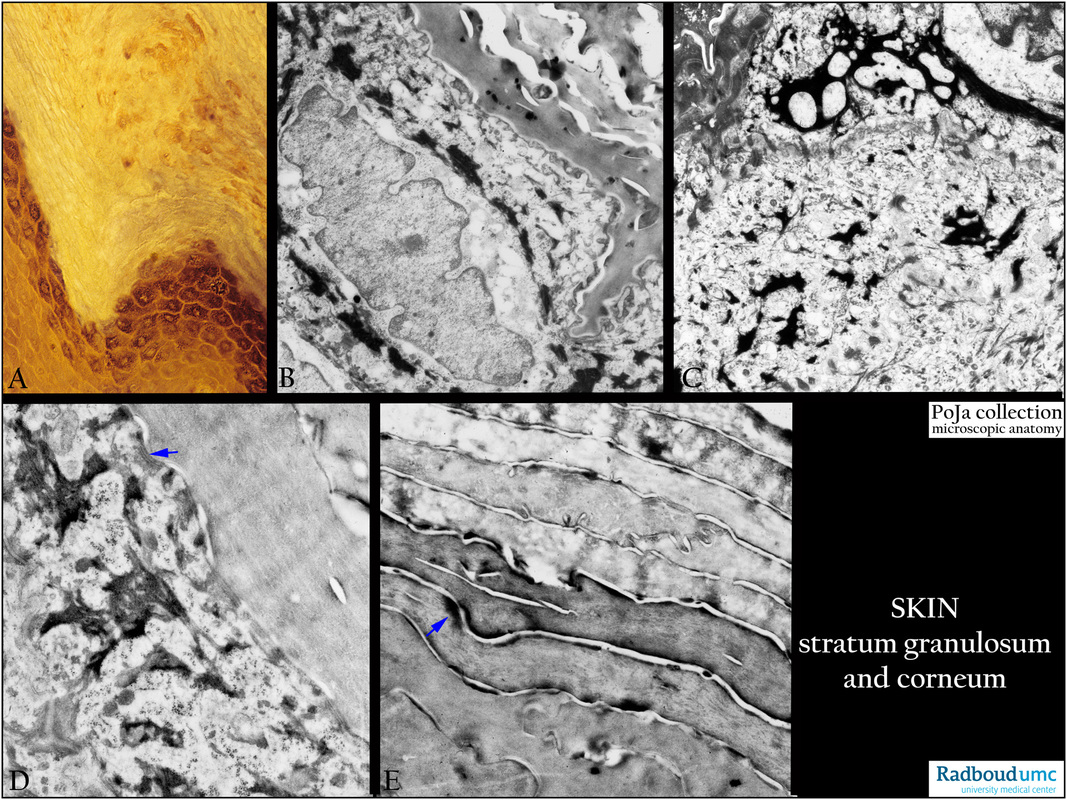
(A): Fingertip, stain hematoxylin-eosin, human. The dark granulated layer of cells represents the stratum granulosum (granular layer),
and upwards they are converted in to the completely keratinized corneum.
(B-E): Fingertip, electron micrographs of stratum corneum and stratum granulosum, human.
The details in (B, C) show the electron-dense keratohyalin aggregates. These aggregates are reduced into electron-dense small
plaques in the corneum layers completely stuffed with dispersed filamentous material shown in (D, E).
Remnants of desmosomal remnants are present at (arrows).
Background: The major protein of the granulosum cells is the protein filaggrin that induces aggregation of keratins into
a keratin-filaggrin complex adjacent to the cell membrane (cell envelope).
At the outside of the cell the released content of the Odland bodies (lamellar granules) cross links the cell envelope and the complex.
This combined material makes the cells water impermeable. Other substances as involucrin, SPR’s (small proline-rich proteins) and
loricrin and claudin-1 are also involved in the aggregation process.
Keywords/Mesh: skin, epidermis, stratum granulosum, granular layer, stratum corneum, corneocyte, keratohyalin, histology,
electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Stratum granulosum of the epidermis
Description:
(A): Fingertip, stain hematoxylin-eosin, human. The dark granulated layer of cells represents the stratum granulosum (granular layer),
and upwards they are converted in to the completely keratinized corneum.
(B-E): Fingertip, electron micrographs of stratum corneum and stratum granulosum, human.
The details in (B, C) show the electron-dense keratohyalin aggregates. These aggregates are reduced into electron-dense small
plaques in the corneum layers completely stuffed with dispersed filamentous material shown in (D, E).
Remnants of desmosomal remnants are present at (arrows).
Background: The major protein of the granulosum cells is the protein filaggrin that induces aggregation of keratins into
a keratin-filaggrin complex adjacent to the cell membrane (cell envelope).
At the outside of the cell the released content of the Odland bodies (lamellar granules) cross links the cell envelope and the complex.
This combined material makes the cells water impermeable. Other substances as involucrin, SPR’s (small proline-rich proteins) and
loricrin and claudin-1 are also involved in the aggregation process.
Keywords/Mesh: skin, epidermis, stratum granulosum, granular layer, stratum corneum, corneocyte, keratohyalin, histology,
electron microscopy, POJA collection