|
3.5 POJA-L168
Title: Presecretory ameloblasts in tooth development (bell stage) Description: Electron microscopy, gerbil postnatal. Well-arranged epithelial formation of presecretory ameloblasts (active nuclei) with their distal secretion sides towards the thin grey basal lamina. Predentin at the bottom close to the basal lamina and comprises collagen fibers, odontoblastic extensions and dispersed calcified matrix vesicles (with crystallites of hydroxyapatite). |
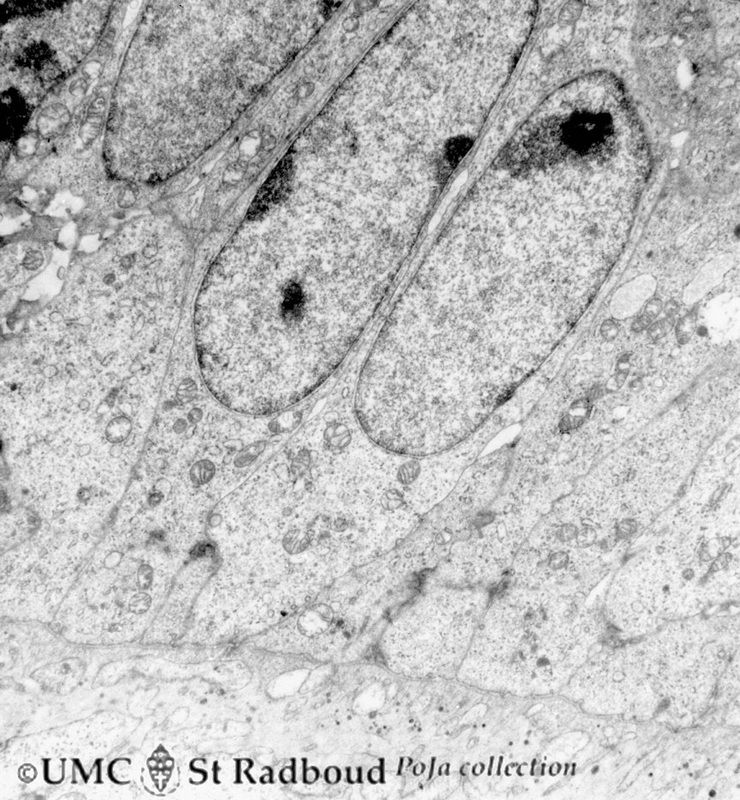
3.5 POJA-L169
Title: Secretory ameloblasts in tooth development (bell stage) Description: Electron microscopy, gerbil postnatal. Cross-sectioned distal sides of ameloblasts (secretion areas or Tomes’processes) with numerous organelles. The dark stained vesicles represent secretory granules contain among others amelogenin. At the right bottom corner intercellular spaces are filled with dark-stained organic matrix of enamel (e.g. amelogenin). The dark stained extracellular space is called the area of interrod growth region with mineralized enamel prisms (longitudinally oriented crystallites). |
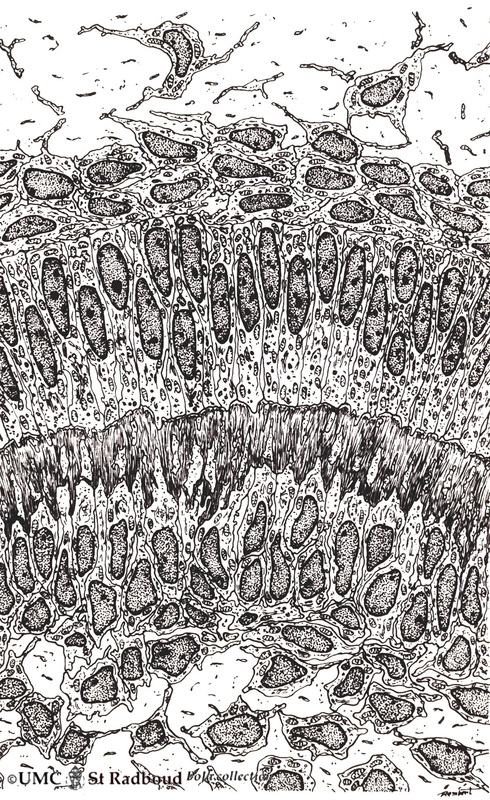
3.5 POJA-L153
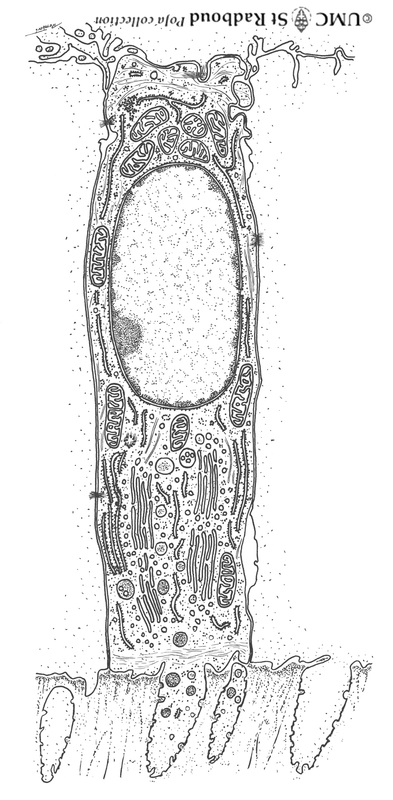
Title: Ameloblasts and odontoblasts in tooth development (advanced bell stage) Description: Scheme electronmicroscopy, human embryo. From top to bottom: - Stellate reticulum consisting of a non- vascularized network of ectoderm- derived cells continuous with the cell layers of the stratum intermedium. - Columnar presecretory ameloblasts with their upper side (nuclear area) in close contact with the stratum intermedium, and at the distal side (secretion area) their basal lamina close to the predentin. - Epithelioid arranged odontoblasts with irregular extensions into the predentin (collagen fibers type I in extracellular matrix). - In close contact with the odontoblasts (basal nuclei) the network of fibroblast- like cells (so-called pulpal cells) producing collagen of the dental papilla (future pulp). 3.5 POJA-L83 Title: Presecretory ameloblast in tooth development Description: Scheme electron microscopy, human embryo. The ectodermal-derived cell appears as tall columnar with fingerlike extensions (dependent on the development stages) at their distal side (secreting area=’functional base’). These extensions are formed as the cell withdraws during the production of initial enamel. The supranuclear area is well developed with a large Golgi area and secretion granules. |
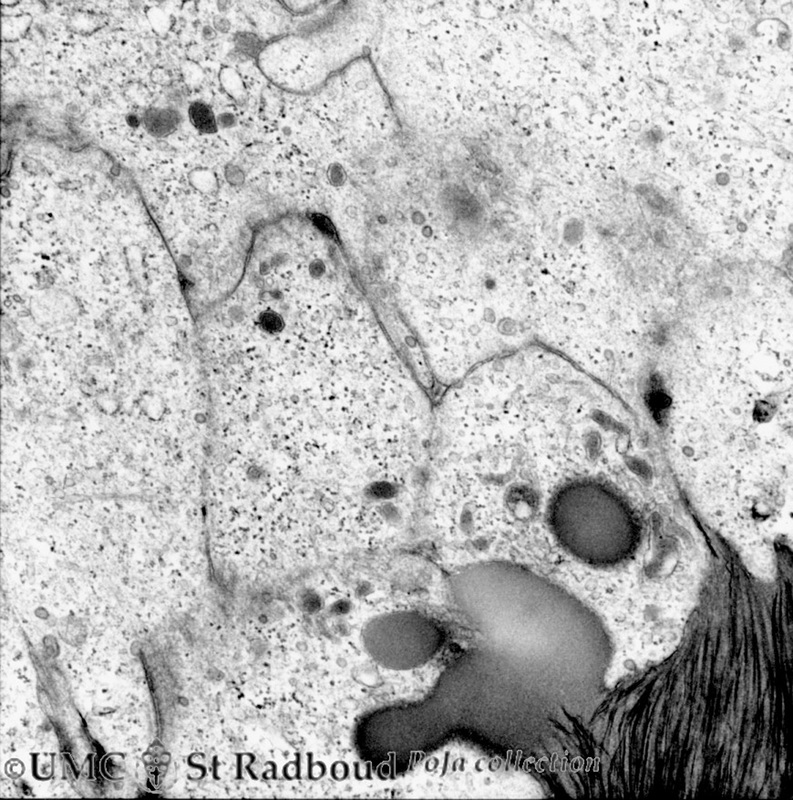
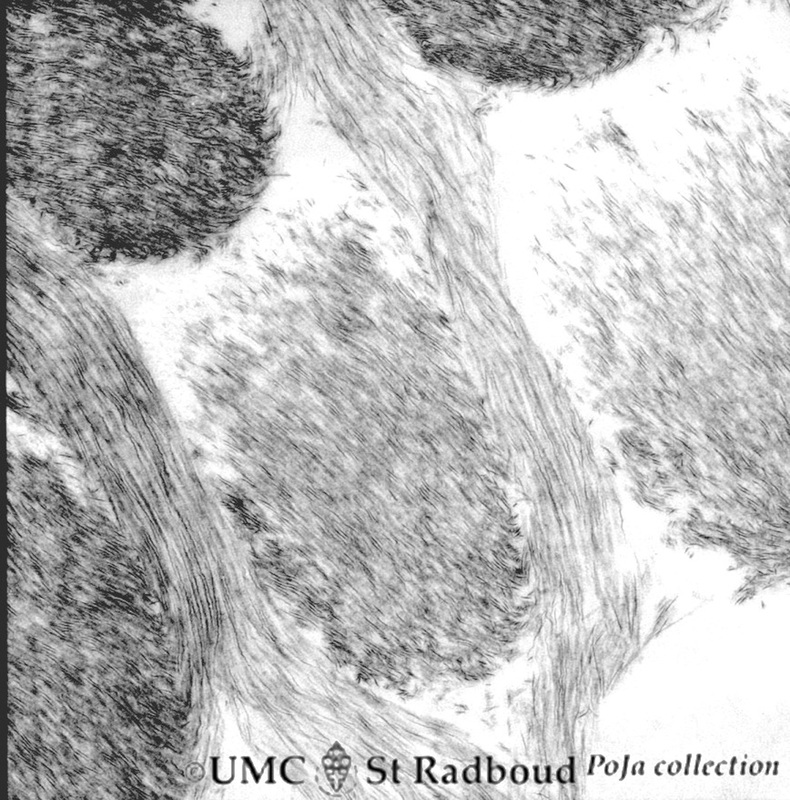
3.5 POJA-L170
Title: Enamel rods (prisms) in tooth development
Description:
Electron microscopy of cross-sectioned rods (prisms), gerbil postnatal. The rods are presented by round aggregates with hydroxyapatite crystals. Between the round rods the interprismatic substance with crystals orientated in a different course.
Note that twisting of the crystallites can be seen in the longitudinal bundles where grey ribbons turn into sharp dark lines and subsequently again into grey ribbons.
Keywords/Mesh: oral cavity, mouth, tooth, tooth development, ameloblast, matrix vesicle, hydroxyapatite crystal, enamel prism, odontoblast, predentin, histology, embryology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Enamel rods (prisms) in tooth development
Description:
Electron microscopy of cross-sectioned rods (prisms), gerbil postnatal. The rods are presented by round aggregates with hydroxyapatite crystals. Between the round rods the interprismatic substance with crystals orientated in a different course.
Note that twisting of the crystallites can be seen in the longitudinal bundles where grey ribbons turn into sharp dark lines and subsequently again into grey ribbons.
Keywords/Mesh: oral cavity, mouth, tooth, tooth development, ameloblast, matrix vesicle, hydroxyapatite crystal, enamel prism, odontoblast, predentin, histology, embryology, electron microscopy, POJA collection