12.2.3 POJA-L2649+2650+2651+2652
Title: Chorda tympani in the middle ear
Description:
The tympanic cavity (middle ear) is derived from the lumen of the first pharyngeal pouch.
The chorda tympani (nerves from the taste buds on the tongue) enters the temporal bone as part of the facial nerve.
It separates and ascends to the posterior wall of the middle ear space to cross over the cartilaginous (auditory) ossicles e.g. malleus.
Subsequently it joints the lingual nerve that mediates taste sensations from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue.
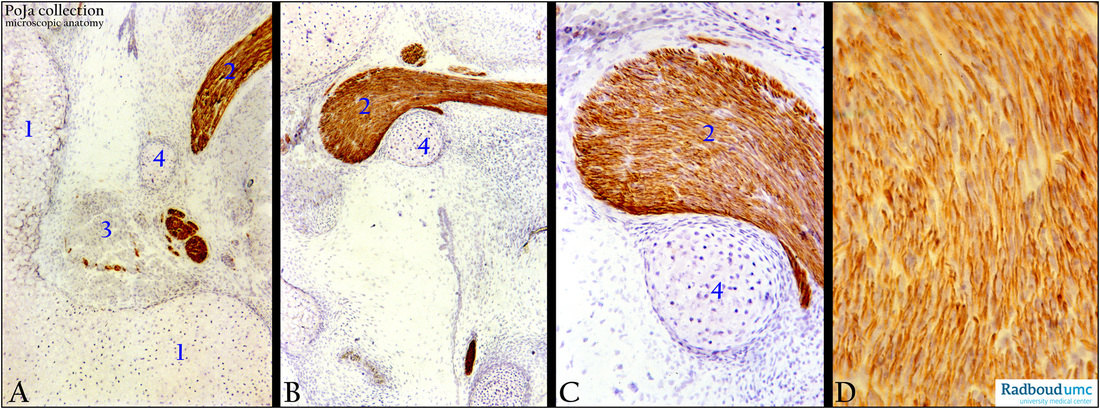
Monoclonal anti-neurofilament antibodies illustrate very clearly the course of the branches (A-C) and the presence in individual nerve fibres (D)
(A-D): Chorda tympani, immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and monoclonal anti-neurofilament antibodies, postnatal rat 4 days.
Cartilaginous part (A, 1) of eustachian tube showing the topographic relation of the chorda tympani (2), tensor tympani (A, 3), cartilaginous manubrium malleus (4).
The tensor tympani is a 25 mm long striated muscle that is attached to the ear drum. Together with the action of the 6 mm long
stapedius muscle attached to the stapes, the amount of sound that enters the inner ear is reduced..
The hyaline cartilaginous structure (C, 4) is surrounded by a thin layer of perichondrial cells that give rise to the chondroblasts.
After division the daughter cells remain together (so-called isogenous cell group). Between the cell groups the interterritorial
matrix is weakly bluish.
Keywords/Mesh: middle ear, chorda tympani, malleus, tensor tympani, neurofilament, histology, POJA collection
Title: Chorda tympani in the middle ear
Description:
The tympanic cavity (middle ear) is derived from the lumen of the first pharyngeal pouch.
The chorda tympani (nerves from the taste buds on the tongue) enters the temporal bone as part of the facial nerve.
It separates and ascends to the posterior wall of the middle ear space to cross over the cartilaginous (auditory) ossicles e.g. malleus.
Subsequently it joints the lingual nerve that mediates taste sensations from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue.
Monoclonal anti-neurofilament antibodies illustrate very clearly the course of the branches (A-C) and the presence in individual nerve fibres (D)
(A-D): Chorda tympani, immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and monoclonal anti-neurofilament antibodies, postnatal rat 4 days.
Cartilaginous part (A, 1) of eustachian tube showing the topographic relation of the chorda tympani (2), tensor tympani (A, 3), cartilaginous manubrium malleus (4).
The tensor tympani is a 25 mm long striated muscle that is attached to the ear drum. Together with the action of the 6 mm long
stapedius muscle attached to the stapes, the amount of sound that enters the inner ear is reduced..
The hyaline cartilaginous structure (C, 4) is surrounded by a thin layer of perichondrial cells that give rise to the chondroblasts.
After division the daughter cells remain together (so-called isogenous cell group). Between the cell groups the interterritorial
matrix is weakly bluish.
Keywords/Mesh: middle ear, chorda tympani, malleus, tensor tympani, neurofilament, histology, POJA collection