4.2.1 POJA-L3793+3794+3795
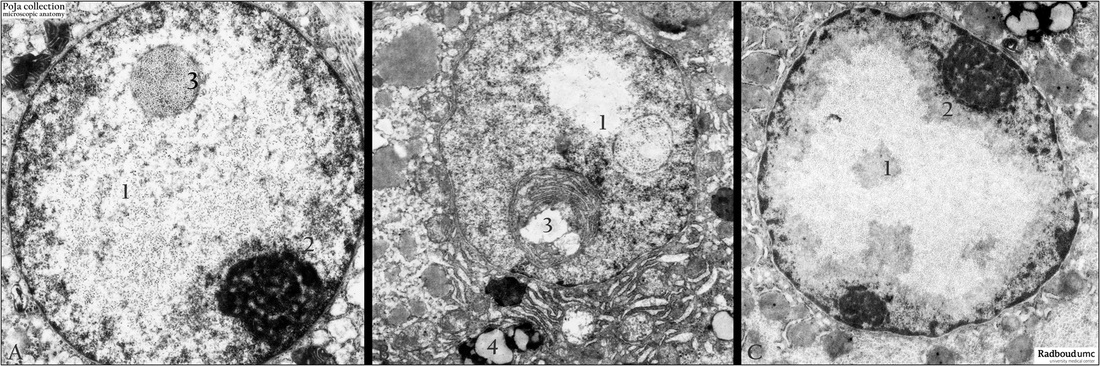
Title: Nuclear abnormalities in cellular pathology of the liver (human)
Description: Electron micrographs of liver cell nuclei.
(A) Alcoholic hepatitis. Cell nuclear inclusions (1) shown as a collection of interchromatin-like granules. The diameter is in the range of monoparticulate α-glycogen, the beaded string-like granules and its electron-density suggest a viral component. (2) Nucleolus. (3) Appears as a focal inclusion that consist of close packed -glycogen particles often referred as glycogen body, that could also be observed in normal tissues.
(B) Cell nuclear abnormalities in obstetric liver atrophy. (1) Resembles free lipid accumulation between the interchromatin and perichromatin granules. However (3) is a sectioned invagination of RER, fat and (4) a glycogen body with aggregation of - glycogen particles.
(C) Alcoholic hepatitis. Nuclear inclusion consisting of fine-dispersed -glycogen throughout the nucleus. (1) Chromatin. (2) Nucleolus. Nuclear deviations usually occur at viral hepatitis and many other chronical liver diseases (alcoholic hepatitis).
Keywords/Mesh: liver, liver disease, nucleus, nuclear inclusion, glycogen body, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Nuclear abnormalities in cellular pathology of the liver (human)
Description: Electron micrographs of liver cell nuclei.
(A) Alcoholic hepatitis. Cell nuclear inclusions (1) shown as a collection of interchromatin-like granules. The diameter is in the range of monoparticulate α-glycogen, the beaded string-like granules and its electron-density suggest a viral component. (2) Nucleolus. (3) Appears as a focal inclusion that consist of close packed -glycogen particles often referred as glycogen body, that could also be observed in normal tissues.
(B) Cell nuclear abnormalities in obstetric liver atrophy. (1) Resembles free lipid accumulation between the interchromatin and perichromatin granules. However (3) is a sectioned invagination of RER, fat and (4) a glycogen body with aggregation of - glycogen particles.
(C) Alcoholic hepatitis. Nuclear inclusion consisting of fine-dispersed -glycogen throughout the nucleus. (1) Chromatin. (2) Nucleolus. Nuclear deviations usually occur at viral hepatitis and many other chronical liver diseases (alcoholic hepatitis).
Keywords/Mesh: liver, liver disease, nucleus, nuclear inclusion, glycogen body, electron microscopy, POJA collection