5.6 POJA-L5013+5011+La0073+La0074+2422+2423
Title: Ureter 2
Description:
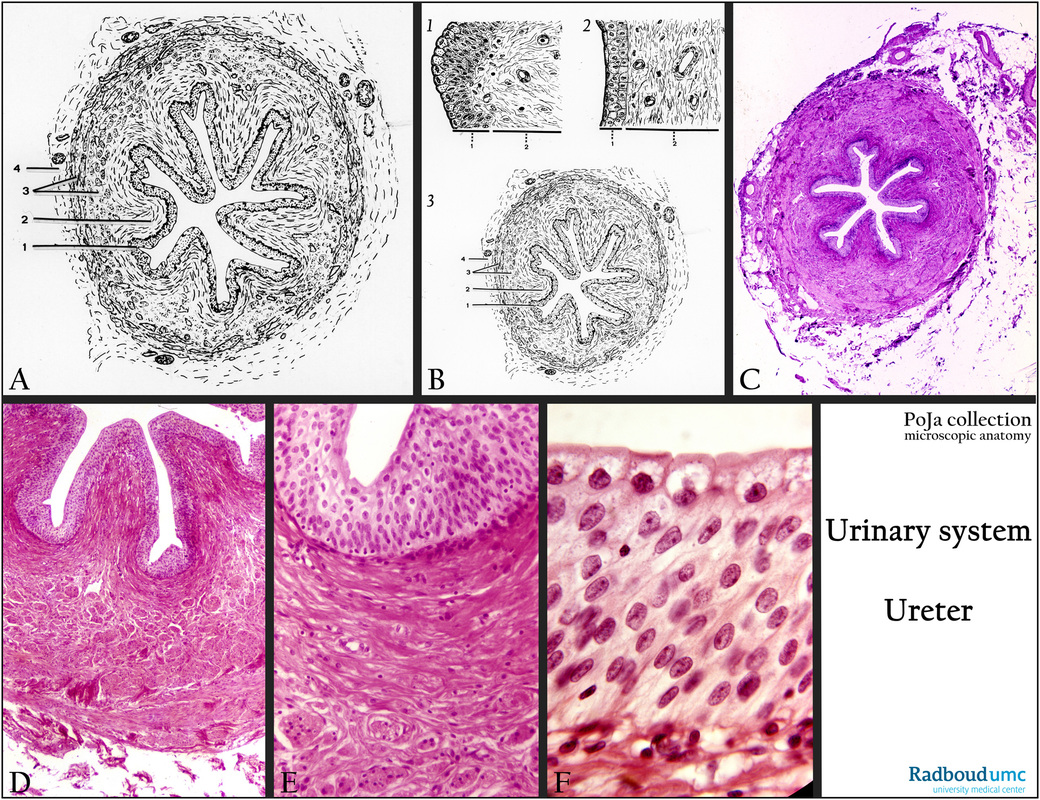
(A, B): Scheme of ureter, human.
The ureter collects and transports the urine from the pelvis of the kidney towards the urinary bladder.
The lumen is constricted in several folds due to the contractional state of the tunica muscularis (3) comprising internal longitudinal
muscle bundles and outer circular muscle layers, covered at the outside with a tunica adventitia (connective tissue) (4).
The thick fibroelastic lamina propria (2) is part of the tunica mucosa forming six to eight folds that disappear upon relaxation of
the muscle layers.
The characteristic epithelium or urothelium lines renal pelvis, ureters, the bladder and parts of the urethra enabling
a high degree of plasticity or stretching.
(C, D, E, F): Contracted ureter, Stain Weigert hematoxylin-eosin, human. The epithelium (urothelium) is a so-called transitional epithelium detailed in (E, F), having an appearance sometimes as a multilayered stratified and sometimes pseudostratified epithelium.
(B1) In the relaxed state of the ureter the epithelium displays a pseudostratified look with layers of cuboidal basal cells,
polygonal intermediate cells and columnar surface cells. These surface cells can extend to apical umbrella-like cells
(“Deckzellen”, “facet cells”) covering neighboring cells below them upon distension of the duct.
These surface cells form a barrier to the urine, and are fortified by crustae (protective glycoprotein) and a dense apical network of intermediary and actin filaments. The cells are also rich in lysosomes.
(B2) Note the distended surface cells in the non-relaxed state of the ureter.
(B3) Cross section of the ureter as detailed in (A).
Note that there are no (sub)mucosal glands. The upper two-third of the ureter has an inner longitudinal and an outer circular smooth muscle layer. The lower third has three layers, i.e. inner longitudinal, middle circular, outer circular.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, ureter, urothelium, transitional epithelium, facet cell, umbrella cell, histology, POJA collection
Title: Ureter 2
Description:
(A, B): Scheme of ureter, human.
The ureter collects and transports the urine from the pelvis of the kidney towards the urinary bladder.
The lumen is constricted in several folds due to the contractional state of the tunica muscularis (3) comprising internal longitudinal
muscle bundles and outer circular muscle layers, covered at the outside with a tunica adventitia (connective tissue) (4).
The thick fibroelastic lamina propria (2) is part of the tunica mucosa forming six to eight folds that disappear upon relaxation of
the muscle layers.
The characteristic epithelium or urothelium lines renal pelvis, ureters, the bladder and parts of the urethra enabling
a high degree of plasticity or stretching.
(C, D, E, F): Contracted ureter, Stain Weigert hematoxylin-eosin, human. The epithelium (urothelium) is a so-called transitional epithelium detailed in (E, F), having an appearance sometimes as a multilayered stratified and sometimes pseudostratified epithelium.
(B1) In the relaxed state of the ureter the epithelium displays a pseudostratified look with layers of cuboidal basal cells,
polygonal intermediate cells and columnar surface cells. These surface cells can extend to apical umbrella-like cells
(“Deckzellen”, “facet cells”) covering neighboring cells below them upon distension of the duct.
These surface cells form a barrier to the urine, and are fortified by crustae (protective glycoprotein) and a dense apical network of intermediary and actin filaments. The cells are also rich in lysosomes.
(B2) Note the distended surface cells in the non-relaxed state of the ureter.
(B3) Cross section of the ureter as detailed in (A).
Note that there are no (sub)mucosal glands. The upper two-third of the ureter has an inner longitudinal and an outer circular smooth muscle layer. The lower third has three layers, i.e. inner longitudinal, middle circular, outer circular.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, ureter, urothelium, transitional epithelium, facet cell, umbrella cell, histology, POJA collection