11.3 POJA-L3121+3151+3149+3150+3152+3153+3154
Title: Spinal cord with ependymal cells
Description:
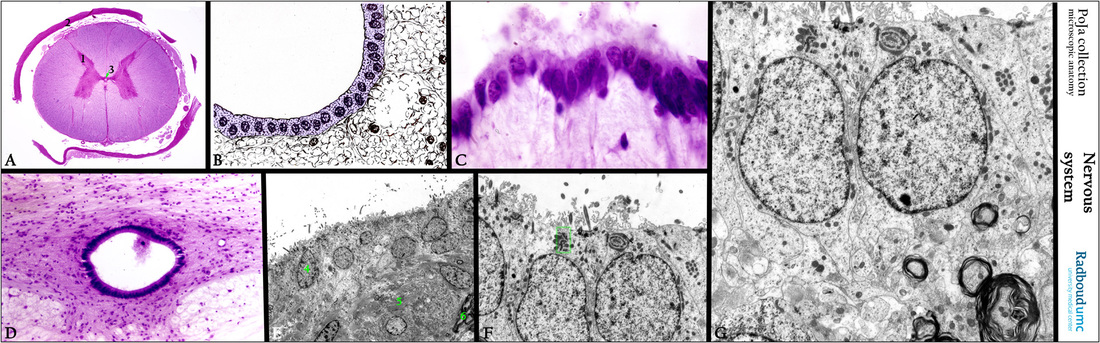
(A): Modified silver stain, bovine, thoracic segment (pars thoracia), showing a relative small butterfly pattern of the gray matter as well as
a small cornu dorsalis (A, 1). Part of the dura is present (A, 2). (A, 3) Central canal filled with cerebrospinal liquor.
(B): Scheme of the central canal that is lined with ependym cells (painted pink, human) and detailed in (G).
(C): Stain hematoxylin-eosin, bovine embryo. These embryonal ependymal cells or ependymocytes are anchoraged in the substantia gelatinosa centralis with deep extensions. The encircling band of substantia gelatinosa centralis is composed
of mainly neuroglia cells and is traversed by the long slender basal processes of the columnar ciliated ependym cells.
(D): Stain hematoxylin-eosin, bovine, showing the canalis centralis encircled by substantia gelatinosa (gray commissure).
The canal is covered with the lining ependymal cells studded with long kinocilia en villi in the embryonic phase (as in C).
(E, F): Electron micrograph of ependymal cells (rabbit). In adulthood these cells (E, 4 and F) are studded with short kinocilia and microvilli and the apical cytoplasm contains many dark-stained mitochondria. The cells (see green rectangle in F) do have zonulae adhaerentes, nexus (F), but not zonulae occludentes thus facilitating a direct exchange of liquor cerebrospinalis with the extracellular space.
(E, 5) Area of the substantia gelatinosa with numerous conspicuous bundles of longitudinal and cross-sectioned neurofilaments in the axons. (E, 6) Myelinated nerve fibers.
(G): Detail of (F). Note in (G) that a basal lamina below the ependymal cells is lacking.
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, spinal cord, central canal, ependymal cell, kinocilium, adherens junction, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Spinal cord with ependymal cells
Description:
(A): Modified silver stain, bovine, thoracic segment (pars thoracia), showing a relative small butterfly pattern of the gray matter as well as
a small cornu dorsalis (A, 1). Part of the dura is present (A, 2). (A, 3) Central canal filled with cerebrospinal liquor.
(B): Scheme of the central canal that is lined with ependym cells (painted pink, human) and detailed in (G).
(C): Stain hematoxylin-eosin, bovine embryo. These embryonal ependymal cells or ependymocytes are anchoraged in the substantia gelatinosa centralis with deep extensions. The encircling band of substantia gelatinosa centralis is composed
of mainly neuroglia cells and is traversed by the long slender basal processes of the columnar ciliated ependym cells.
(D): Stain hematoxylin-eosin, bovine, showing the canalis centralis encircled by substantia gelatinosa (gray commissure).
The canal is covered with the lining ependymal cells studded with long kinocilia en villi in the embryonic phase (as in C).
(E, F): Electron micrograph of ependymal cells (rabbit). In adulthood these cells (E, 4 and F) are studded with short kinocilia and microvilli and the apical cytoplasm contains many dark-stained mitochondria. The cells (see green rectangle in F) do have zonulae adhaerentes, nexus (F), but not zonulae occludentes thus facilitating a direct exchange of liquor cerebrospinalis with the extracellular space.
(E, 5) Area of the substantia gelatinosa with numerous conspicuous bundles of longitudinal and cross-sectioned neurofilaments in the axons. (E, 6) Myelinated nerve fibers.
(G): Detail of (F). Note in (G) that a basal lamina below the ependymal cells is lacking.
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, spinal cord, central canal, ependymal cell, kinocilium, adherens junction, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection