9.5 POJA-La-0227+L2872
Title: Adrenal gland (glandula suprarenalis) (II)
Description:
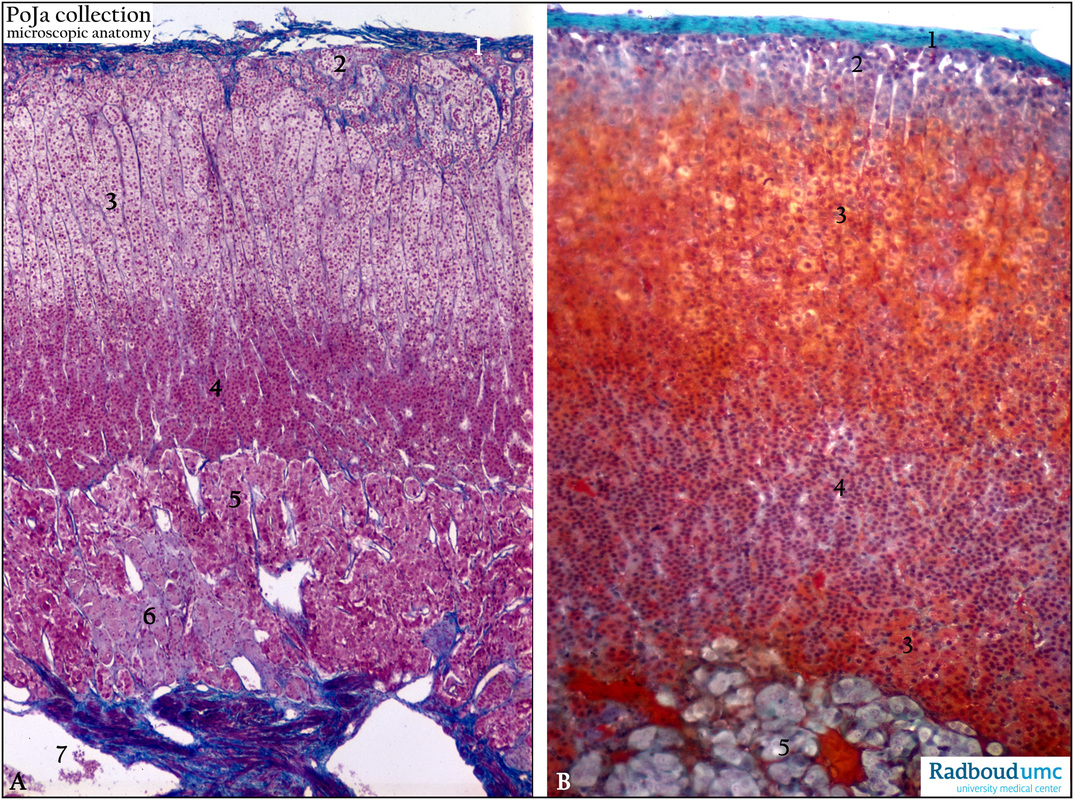
Adrenal gland, stain Azan, human (A) and stain trichrome Mallory, rat (B).
The adrenal gland is surrounded with a capsule of connective tissue (1), containing fat cells and subcapsular network of blood vessels.
(2) Zona glomerulosa being the outer layer of the cortex, having the appearance of round clusters of cells. This layer produces mineralocorticosteroids, such as aldosterone that promotes the back resorption of Na+ in the kidney.
The glomerulosa cells are stimulated by angiotensin II and to some extent by ACTH (hypophysis).
(3) Zona fasciculata with cells that are involved in the production of glucocorticoids, such as cortisol or hydrocortisone.
Their cells are stimulated by ACTH (hypophysis). The fasciculata cells are arranged radial-like long slender gland crypts.
(4) The zona reticularis produces androgens, also stimulated by ACTH.
The medulla (5) contains many chromaffin cells arranged in cords around capillaries. Their membrane-bound secretory granules contain the catecholamine such as adrenalin and noradrenalin. In the medullary area numerous ganglion cells are present (6) that regulate the release of the adrenalin/noradrenalin.
(7) Medullar vein with well-developed smooth muscle bundles.
Keywords/Mesh: adrenal gland, cortex, medulla, adrenalin, catecholamine, histology, POJA collection
Title: Adrenal gland (glandula suprarenalis) (II)
Description:
Adrenal gland, stain Azan, human (A) and stain trichrome Mallory, rat (B).
The adrenal gland is surrounded with a capsule of connective tissue (1), containing fat cells and subcapsular network of blood vessels.
(2) Zona glomerulosa being the outer layer of the cortex, having the appearance of round clusters of cells. This layer produces mineralocorticosteroids, such as aldosterone that promotes the back resorption of Na+ in the kidney.
The glomerulosa cells are stimulated by angiotensin II and to some extent by ACTH (hypophysis).
(3) Zona fasciculata with cells that are involved in the production of glucocorticoids, such as cortisol or hydrocortisone.
Their cells are stimulated by ACTH (hypophysis). The fasciculata cells are arranged radial-like long slender gland crypts.
(4) The zona reticularis produces androgens, also stimulated by ACTH.
The medulla (5) contains many chromaffin cells arranged in cords around capillaries. Their membrane-bound secretory granules contain the catecholamine such as adrenalin and noradrenalin. In the medullary area numerous ganglion cells are present (6) that regulate the release of the adrenalin/noradrenalin.
(7) Medullar vein with well-developed smooth muscle bundles.
Keywords/Mesh: adrenal gland, cortex, medulla, adrenalin, catecholamine, histology, POJA collection