15.1 POJA-L7016+7019 Electron micrograph of hyaline cartilage with chondrocytes
15.1 POJA-L7016+7019 Electron micrograph of hyaline cartilage with chondrocytes
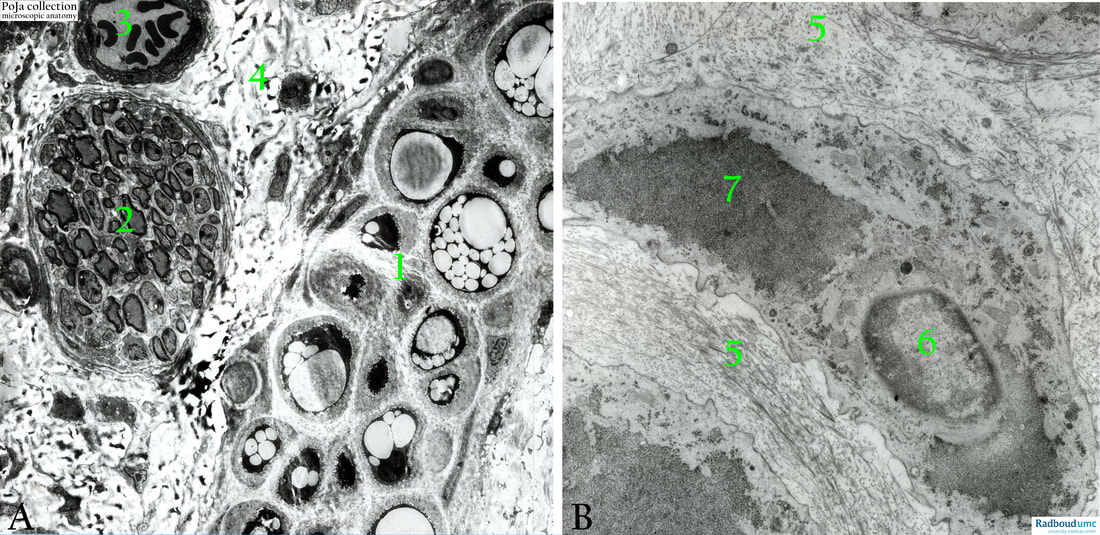
Title: Electron micrograph of hyaline cartilage with chondrocytes
Description:
Electron micrographs of hyaline cartilage (mouse).
(A): Survey.
(1): Chondrocytes show varying amount of lipid loaded vacuoles.
(2): Myelinated nerve fibres.
(3): Arteriole with erythrocytes.
(4): Connective tissue. Note that the nerve fibres and the blood vessels are not located within the cartilage, but in the surrounding connective tissue close to the perichondrium (1).
(B): Nose septum, rat. Lacunar chondrocytes.
(5): Matrix.
(6): Nucleus.
(7): Glycogen, note microvillar projections of the cytoplasms within the lacunae.
Background:
Vacuoles are found in varying amounts in the chondrocyte cytoplasm. The presence depends on the type of species, age, cartilage, localisation, dietary and seaonal influences.
In human chondrocytes proteins are present for fatty acid metabolism and cholesterol biosynthesis, such as acetyl-coenzyme A acetyltransferase 1 (ACAT1), cytochrome P450 oxidase. Additionally, lipids in joint fluid can also penetrate into the cartilage. Therefore, lipids may be available for chondrocytes directly from synovial fluid or by de novo synthesis. Chondrocytes can synthesize these molecules such as phospholipids, cholesterol and fatty acids, however, dietary lipids may also reach the cartilage, modify its composition and be incorporated in chondrocyte metabolism and structures.
Reference:
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, cartilage, hyaline, matrix, nerve fibre, chondrocyte, glycogen,electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Electron micrograph of hyaline cartilage with chondrocytes
Description:
Electron micrographs of hyaline cartilage (mouse).
(A): Survey.
(1): Chondrocytes show varying amount of lipid loaded vacuoles.
(2): Myelinated nerve fibres.
(3): Arteriole with erythrocytes.
(4): Connective tissue. Note that the nerve fibres and the blood vessels are not located within the cartilage, but in the surrounding connective tissue close to the perichondrium (1).
(B): Nose septum, rat. Lacunar chondrocytes.
(5): Matrix.
(6): Nucleus.
(7): Glycogen, note microvillar projections of the cytoplasms within the lacunae.
Background:
Vacuoles are found in varying amounts in the chondrocyte cytoplasm. The presence depends on the type of species, age, cartilage, localisation, dietary and seaonal influences.
In human chondrocytes proteins are present for fatty acid metabolism and cholesterol biosynthesis, such as acetyl-coenzyme A acetyltransferase 1 (ACAT1), cytochrome P450 oxidase. Additionally, lipids in joint fluid can also penetrate into the cartilage. Therefore, lipids may be available for chondrocytes directly from synovial fluid or by de novo synthesis. Chondrocytes can synthesize these molecules such as phospholipids, cholesterol and fatty acids, however, dietary lipids may also reach the cartilage, modify its composition and be incorporated in chondrocyte metabolism and structures.
Reference:
- Lipid transport and metabolism in healthy and osteoarthritic cartilage. Amanda Villalvilla, Rodolfo Gómez, Raquel Largo, Gabriel Herrero-Beaumont in Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14(10), 20793-20808; https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141020793
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, cartilage, hyaline, matrix, nerve fibre, chondrocyte, glycogen,electron microscopy, POJA collection