16.1.3 POJA-L7059+7061 Osteoclast 2
16.1.3 POJA-L7059+7061 Osteoclast 2
Title: Osteoclast 2
Description:
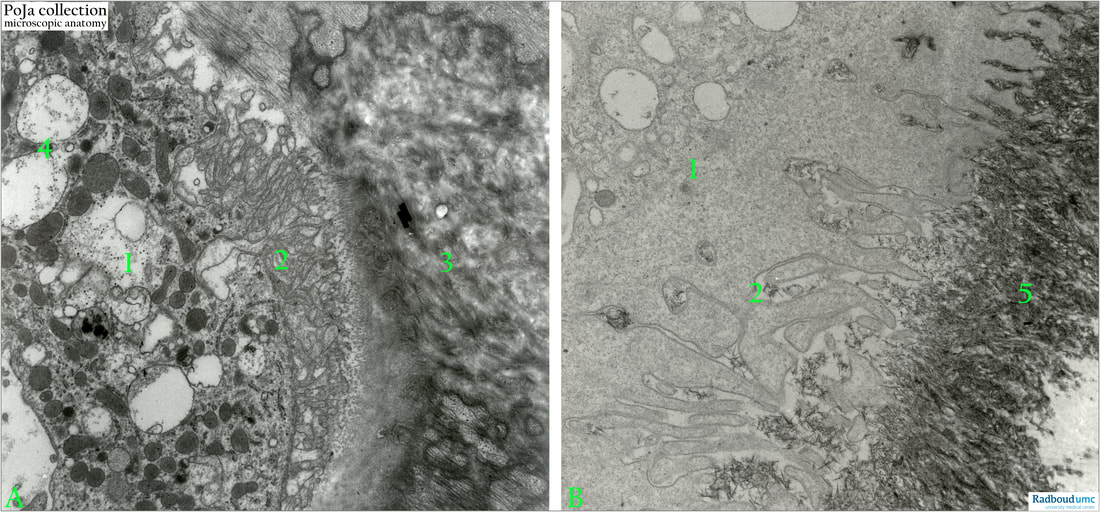
(A+B): Electron micrographs of osteoclast in desmal ossification, rabbit. (A): Survey of the osteoclast (left side). (B): Detail of the osteoclast.
(1): Osteoclast. (In A: left half of the picture).
(2): Area of ruffled border (podosomes).
(3): Bone matrix.
(4): Lysosomal structures.
(5): Hydroxyapatite.
Background:
Note in the right image (B) that between the podosomes are located small hydroxyapatite aggregations in the process of endocytosis. The direct contact zone of osteoclast with bone tissue is called the ruffled border (2). At the opposite side of the ruffled border the basolateral region of the cytoplasm is involved the exocytosis of digested material. Excess bicarbonate is eliminated by passive exchange with chloride ions via chloride-carbonate protein exchangers located at these basolateral membranes. In the acidic microenvironment the degradation and dissolution of hydroxyapatites progress into calcium ions, soluble inorganic phosphates and water. Nowadays it is clear that osteoclasts are not merely bone resorbing cells, they also regulate osteoblast functions and mediate the exodus of haematopoietic stem cells from the marrow into the blood.
See Reference:
(Weivoda, M.M., Chew, C.K., Monroe, D.G. et al. Identification of osteoclast-osteoblast coupling factors in humans reveals links between bone and energy metabolism. Nat Commun 11, 87 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14003-6).
See also:
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, bone, desmal ossification, osteoclast, ruffled border, endocytosis, lysosome, hydroyapatite, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Osteoclast 2
Description:
(A+B): Electron micrographs of osteoclast in desmal ossification, rabbit. (A): Survey of the osteoclast (left side). (B): Detail of the osteoclast.
(1): Osteoclast. (In A: left half of the picture).
(2): Area of ruffled border (podosomes).
(3): Bone matrix.
(4): Lysosomal structures.
(5): Hydroxyapatite.
Background:
Note in the right image (B) that between the podosomes are located small hydroxyapatite aggregations in the process of endocytosis. The direct contact zone of osteoclast with bone tissue is called the ruffled border (2). At the opposite side of the ruffled border the basolateral region of the cytoplasm is involved the exocytosis of digested material. Excess bicarbonate is eliminated by passive exchange with chloride ions via chloride-carbonate protein exchangers located at these basolateral membranes. In the acidic microenvironment the degradation and dissolution of hydroxyapatites progress into calcium ions, soluble inorganic phosphates and water. Nowadays it is clear that osteoclasts are not merely bone resorbing cells, they also regulate osteoblast functions and mediate the exodus of haematopoietic stem cells from the marrow into the blood.
See Reference:
(Weivoda, M.M., Chew, C.K., Monroe, D.G. et al. Identification of osteoclast-osteoblast coupling factors in humans reveals links between bone and energy metabolism. Nat Commun 11, 87 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-14003-6).
See also:
Keywords/Mesh: locomotor system, bone, desmal ossification, osteoclast, ruffled border, endocytosis, lysosome, hydroyapatite, electron microscopy, POJA collection