13.1 POJA-L4526+4715+4527
Title: Myocardiocytes
Description:
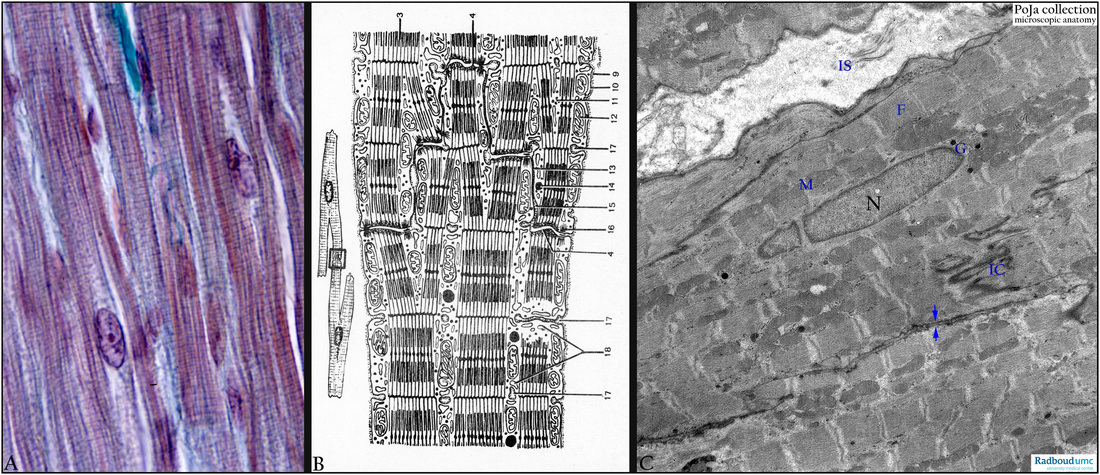
(A): Heart ventricle, cardiocytes, Mallory, human. The striated cells are cylindrical with a single centrally located nucleus, note branching pattern of these cells. There are alternating light and dark bands resulting in fine longitudinal striations. The A-(dark) bands (anisotropic) refer to the thick filament band (mainly myosin) and include a zone where the thin filaments (mainly actin) overlap the thick filaments.
The light I-band (isotropic) include the thin filaments (actin) and the dark Z-line. The unit between two Z-lines is called sarcomere. The Z-line contains α-actinin, filamin, amorphin and Z-protein. A thin endomysium (blue-green) surrounds each cell, ultrastructurally it consists of a basal lamina (= external lamina) and a thin network of thin collagen fibres.
(B): Scheme EM cardiocyte. (3): Myofibrils. (4) Intercalated disc serving as anchoring site for branching muscle cells. (9) Basal lamina. (10) Sarcolemma. (11) Glycogen. (12) Mitochondria. (13) Nexus or gap junction. (14) Fat droplets. (15) Intercellular canal with basal lamina material derived from the sarcolemma. (16) Desmosome. (17) T-tubules invaginating the cell membrane and ending between the sarcoplasmic cisternae (triad). (18) Cross sectioned triad of the terminal cisterns.
(C): Heart ventricle, cardiocytes, EM, rat. Survey of several longitudinal sectioned cardiocytes. Central nucleus (N) and paranuclearly Golgi area (G) with electron-dense granules as well as aggregated mitochondria. (F) actin-myosin myofilaments of the contractile apparatus, (M) mitochondria, (IC) intercalated disc, (IS) interstitium with thin collagen fibres, (arrows) two apposed sarcolemmae.
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, heart, ventricle, myocardiocyte, cardiocyte, myofibril, myofilament, sarcomere, intercalated disc, sarcoplasmic reticulum, T-tubulus, triad, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection
Title: Myocardiocytes
Description:
(A): Heart ventricle, cardiocytes, Mallory, human. The striated cells are cylindrical with a single centrally located nucleus, note branching pattern of these cells. There are alternating light and dark bands resulting in fine longitudinal striations. The A-(dark) bands (anisotropic) refer to the thick filament band (mainly myosin) and include a zone where the thin filaments (mainly actin) overlap the thick filaments.
The light I-band (isotropic) include the thin filaments (actin) and the dark Z-line. The unit between two Z-lines is called sarcomere. The Z-line contains α-actinin, filamin, amorphin and Z-protein. A thin endomysium (blue-green) surrounds each cell, ultrastructurally it consists of a basal lamina (= external lamina) and a thin network of thin collagen fibres.
(B): Scheme EM cardiocyte. (3): Myofibrils. (4) Intercalated disc serving as anchoring site for branching muscle cells. (9) Basal lamina. (10) Sarcolemma. (11) Glycogen. (12) Mitochondria. (13) Nexus or gap junction. (14) Fat droplets. (15) Intercellular canal with basal lamina material derived from the sarcolemma. (16) Desmosome. (17) T-tubules invaginating the cell membrane and ending between the sarcoplasmic cisternae (triad). (18) Cross sectioned triad of the terminal cisterns.
(C): Heart ventricle, cardiocytes, EM, rat. Survey of several longitudinal sectioned cardiocytes. Central nucleus (N) and paranuclearly Golgi area (G) with electron-dense granules as well as aggregated mitochondria. (F) actin-myosin myofilaments of the contractile apparatus, (M) mitochondria, (IC) intercalated disc, (IS) interstitium with thin collagen fibres, (arrows) two apposed sarcolemmae.
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, heart, ventricle, myocardiocyte, cardiocyte, myofibril, myofilament, sarcomere, intercalated disc, sarcoplasmic reticulum, T-tubulus, triad, electron microscopy, histology, POJA collection