2.1 POJA-L951
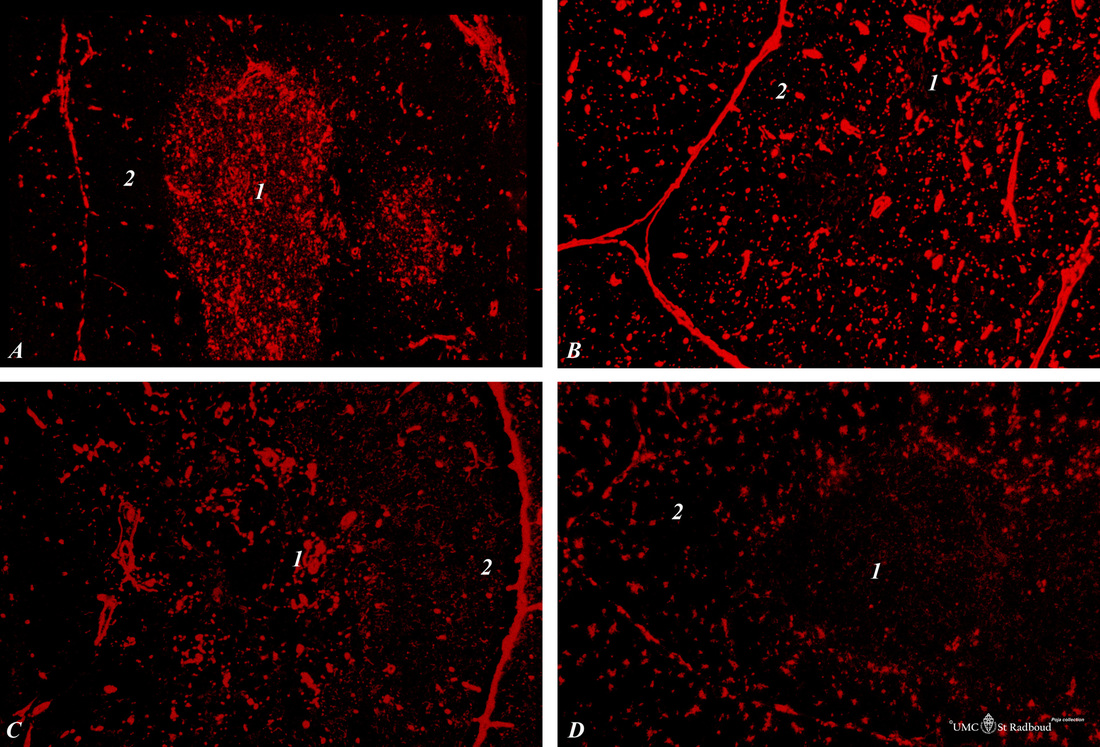
Title: Immunohistochemistry of thymus (rat)
Description: Stain: Alexa-594 red immunofluorescence.
(1): Medulla.
(2): Cortex of the thymus.
(A): Staining with monoclonal antibody against vimentin illustrates that vimentin is localised in the stromal cells of the connective tissue of the capsule, of the septae or trabeculae that invade the cortex (1) and overwhelmingly in cells of the richly vascularised medullary meshwork (1).
(B): The reticulin fibres present in the medulla and in the perivascular space contain laminin (and type IV collagen, not shown). Laminin-5 promotes human mature thymocyte migration in vitro and probably also in vivo in the medulla via a multimolecular mechanism involving laminin-5 integrin receptors, metalloproteinase-14 and CD44. Laminin can be part of the thymic emigration process. Laminin is also involved in the migration of immature thymocytes within thymic nurse cell (TNC-) complexes.
(C): Fibronectin (FN) is found as stromal component of the capsule, the vascularisation in the medulla (1), but also as part of the cortical reticular meshwork (2).
Cross-talk between immature thymocyte and thymic epithelium and stromal cells through cell-to-cell adhesion mediated by fibronectin/VLA/receptor interaction plays a central role in driving T cell development and maturation.
(D): ED2 reacts with a membrane antigen CD163 (175, 160 and 95kDa) on resident rat macrophages. The macrophage type that is present in the cortex, transitional zone between cortex (more) and medulla (less).
Keywords/Mesh: lymphatic organs, thymus, immunohistochemistry, vimentin, laminin, fibronectin, ED2, rat, toxicology, histology, POJA collection
Title: Immunohistochemistry of thymus (rat)
Description: Stain: Alexa-594 red immunofluorescence.
(1): Medulla.
(2): Cortex of the thymus.
(A): Staining with monoclonal antibody against vimentin illustrates that vimentin is localised in the stromal cells of the connective tissue of the capsule, of the septae or trabeculae that invade the cortex (1) and overwhelmingly in cells of the richly vascularised medullary meshwork (1).
(B): The reticulin fibres present in the medulla and in the perivascular space contain laminin (and type IV collagen, not shown). Laminin-5 promotes human mature thymocyte migration in vitro and probably also in vivo in the medulla via a multimolecular mechanism involving laminin-5 integrin receptors, metalloproteinase-14 and CD44. Laminin can be part of the thymic emigration process. Laminin is also involved in the migration of immature thymocytes within thymic nurse cell (TNC-) complexes.
(C): Fibronectin (FN) is found as stromal component of the capsule, the vascularisation in the medulla (1), but also as part of the cortical reticular meshwork (2).
Cross-talk between immature thymocyte and thymic epithelium and stromal cells through cell-to-cell adhesion mediated by fibronectin/VLA/receptor interaction plays a central role in driving T cell development and maturation.
(D): ED2 reacts with a membrane antigen CD163 (175, 160 and 95kDa) on resident rat macrophages. The macrophage type that is present in the cortex, transitional zone between cortex (more) and medulla (less).
Keywords/Mesh: lymphatic organs, thymus, immunohistochemistry, vimentin, laminin, fibronectin, ED2, rat, toxicology, histology, POJA collection