13.1 POJA-L4504+4531+4717+4716
Title: Myocardiocytes
Description:
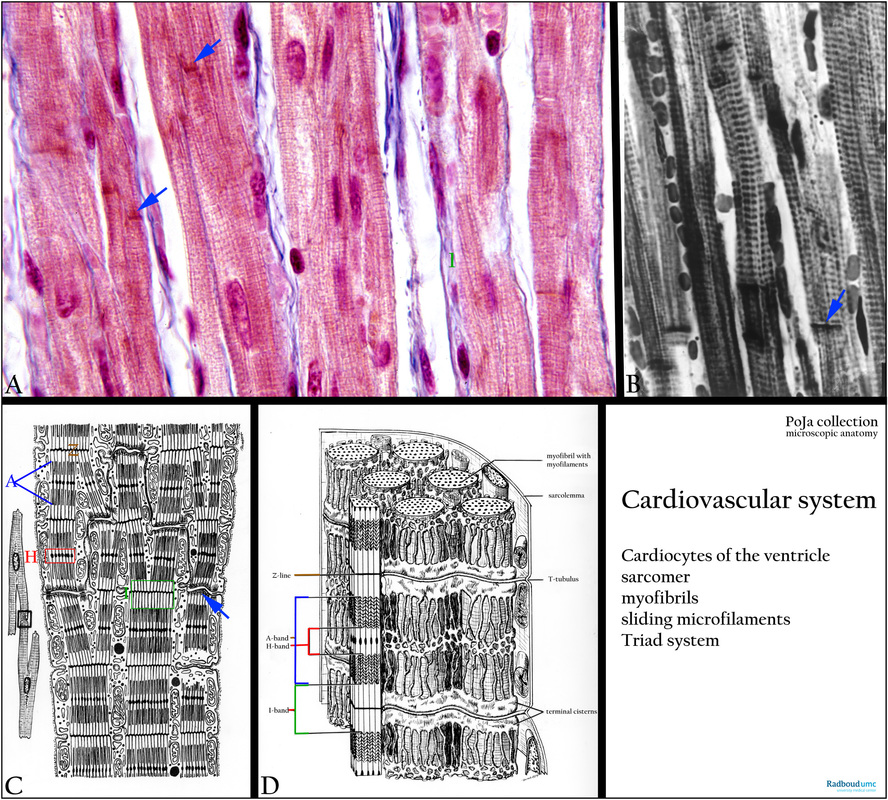
(A): Cardiocytes of ventricle, Azan, human. The anastomosing striated cells are cylindrical and up to 100 micrometers long with a diameter up to 1.5 micrometers , with a single centrally located nucleus. Distinct A-bands alternate with thin Z-lines. Intercalated discs (arrows) join individual cells. A thin endomysium surrounds each cell, it consists of an external lamina (= basal lamina) and a thin network of delicate collagenous fibers (1, green).
(B): Heart ventricle, cardiocytes, black and white, human. Striated cells with dark-stained A-bands. Intercalated discs are indicated by arrows.
(C, D): Electron micrograph schemes of cardiocytes, showing the structural configuration of the myofibrils in the cardiocyte, i.e. the sarcomere with A-, I- and H- band and the Z-line. The blue arrow points to the intercalating discs as anchoring places between branching cardiocytes.
In (D) the configuration of the cisterns of sarcoplasmic reticulum around the myofibrils in a skeletal muscle cell (= fibre) is shown (frog). A transverse tubular system (or T-tubules) extends from the muscle cell surface into the interior of the cells surrounding each myofibril for conveying the excitatory nerve signal to the muscle cell. In cardiocytes the T-tubules are found at the level of the Z-disc and are distinctly larger than those in skeletal muscle cell localised at the A-I junction (in mammals). In mammals, however, the T-tubule is found at the A-I junction where it is also associated with terminal cisterns of the sarcoplasmic reticulum forming a so-called triad. The terminal cisternae contain high concentrations of Ca2+ ions and are provided with Ca2+ channels. Upon excitation of the T tubule system these ion channels are open allowing the Ca2+ ions to flood into the sarcoplasm. Ca-ATPase in the sarcoplasmic reticulum will pump the Ca2+ ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, heart, ventricle, myocardiocyte, cardiocyte, myofibril, myofilament, sarcomere,, intercalated disc, sarcoplasmic reticulum, T-tubule, triad, histology, POJA collection
Title: Myocardiocytes
Description:
(A): Cardiocytes of ventricle, Azan, human. The anastomosing striated cells are cylindrical and up to 100 micrometers long with a diameter up to 1.5 micrometers , with a single centrally located nucleus. Distinct A-bands alternate with thin Z-lines. Intercalated discs (arrows) join individual cells. A thin endomysium surrounds each cell, it consists of an external lamina (= basal lamina) and a thin network of delicate collagenous fibers (1, green).
(B): Heart ventricle, cardiocytes, black and white, human. Striated cells with dark-stained A-bands. Intercalated discs are indicated by arrows.
(C, D): Electron micrograph schemes of cardiocytes, showing the structural configuration of the myofibrils in the cardiocyte, i.e. the sarcomere with A-, I- and H- band and the Z-line. The blue arrow points to the intercalating discs as anchoring places between branching cardiocytes.
In (D) the configuration of the cisterns of sarcoplasmic reticulum around the myofibrils in a skeletal muscle cell (= fibre) is shown (frog). A transverse tubular system (or T-tubules) extends from the muscle cell surface into the interior of the cells surrounding each myofibril for conveying the excitatory nerve signal to the muscle cell. In cardiocytes the T-tubules are found at the level of the Z-disc and are distinctly larger than those in skeletal muscle cell localised at the A-I junction (in mammals). In mammals, however, the T-tubule is found at the A-I junction where it is also associated with terminal cisterns of the sarcoplasmic reticulum forming a so-called triad. The terminal cisternae contain high concentrations of Ca2+ ions and are provided with Ca2+ channels. Upon excitation of the T tubule system these ion channels are open allowing the Ca2+ ions to flood into the sarcoplasm. Ca-ATPase in the sarcoplasmic reticulum will pump the Ca2+ ions back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Keywords/Mesh: cardiovascular system, heart, ventricle, myocardiocyte, cardiocyte, myofibril, myofilament, sarcomere,, intercalated disc, sarcoplasmic reticulum, T-tubule, triad, histology, POJA collection