11.2 POJA-L3252+3250+3251+3233+3235
Title: Myelinated peripheral nerve fibers 5
Description:
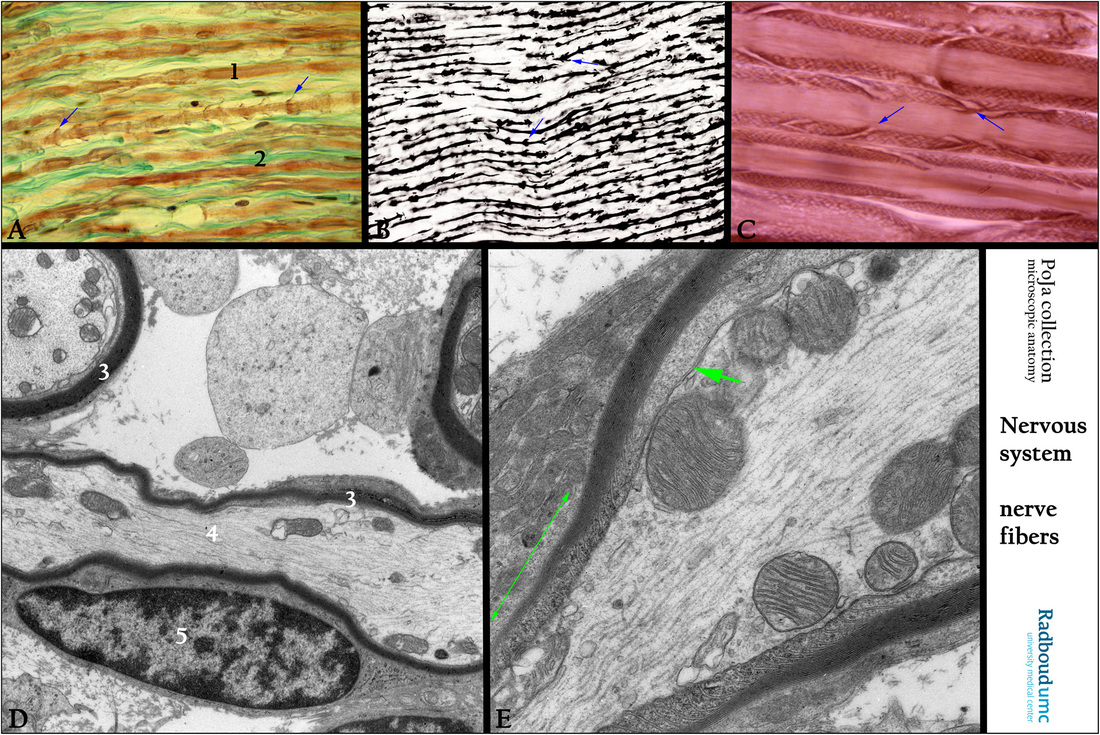
(A): Stain trichrome Goldner, human. Myelinated nerve fibers (1). Endoneurium (2). Golgi funnel (arrows).
(B): Stain iron hematoxylin, black-white picture, human. Black axons and Golgi funnels (arrows).
(C): Osmium impregnation, human. Oblique clefts are the Schmidt-Lanterman incisures (arrows).
(D): Electron micrograph, rat. Longitudinal section through a myelinated nerve. (3) Myelin lamellae. (4) Axon with neurofilaments and neurotubuli. (5) Nucleus of Schwann cell.
(E): Electron micrograph, rat. Myelin in the intermodal region is separated from the axon by a gap of periaxonal space (short green arrow).The lateral edge of myelin sheath that spirals around the axon is the paranodal region (long green arrow), just before the node of Ranvier. The Ranvier nodes “facilitate” a saltatory conduction over the axon. Note that the wrapping of lamellae around the axon gets less in the paranodal area and ends in the Ranvier node area. This local differentiation of myelinated axons is tightly regulated by the Schwann cells. The distinct domains in the area of the Ranvier nodes contain unique sets of ion channels, cell adhesion molecules and cytoplasmic adaptor proteins.
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, axon, neurofilament, neurotubule, peripheral nerve fiber, myelinated nerve,
Ranvier node, Schmidt-Lanterman incisure, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Myelinated peripheral nerve fibers 5
Description:
(A): Stain trichrome Goldner, human. Myelinated nerve fibers (1). Endoneurium (2). Golgi funnel (arrows).
(B): Stain iron hematoxylin, black-white picture, human. Black axons and Golgi funnels (arrows).
(C): Osmium impregnation, human. Oblique clefts are the Schmidt-Lanterman incisures (arrows).
(D): Electron micrograph, rat. Longitudinal section through a myelinated nerve. (3) Myelin lamellae. (4) Axon with neurofilaments and neurotubuli. (5) Nucleus of Schwann cell.
(E): Electron micrograph, rat. Myelin in the intermodal region is separated from the axon by a gap of periaxonal space (short green arrow).The lateral edge of myelin sheath that spirals around the axon is the paranodal region (long green arrow), just before the node of Ranvier. The Ranvier nodes “facilitate” a saltatory conduction over the axon. Note that the wrapping of lamellae around the axon gets less in the paranodal area and ends in the Ranvier node area. This local differentiation of myelinated axons is tightly regulated by the Schwann cells. The distinct domains in the area of the Ranvier nodes contain unique sets of ion channels, cell adhesion molecules and cytoplasmic adaptor proteins.
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, axon, neurofilament, neurotubule, peripheral nerve fiber, myelinated nerve,
Ranvier node, Schmidt-Lanterman incisure, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection