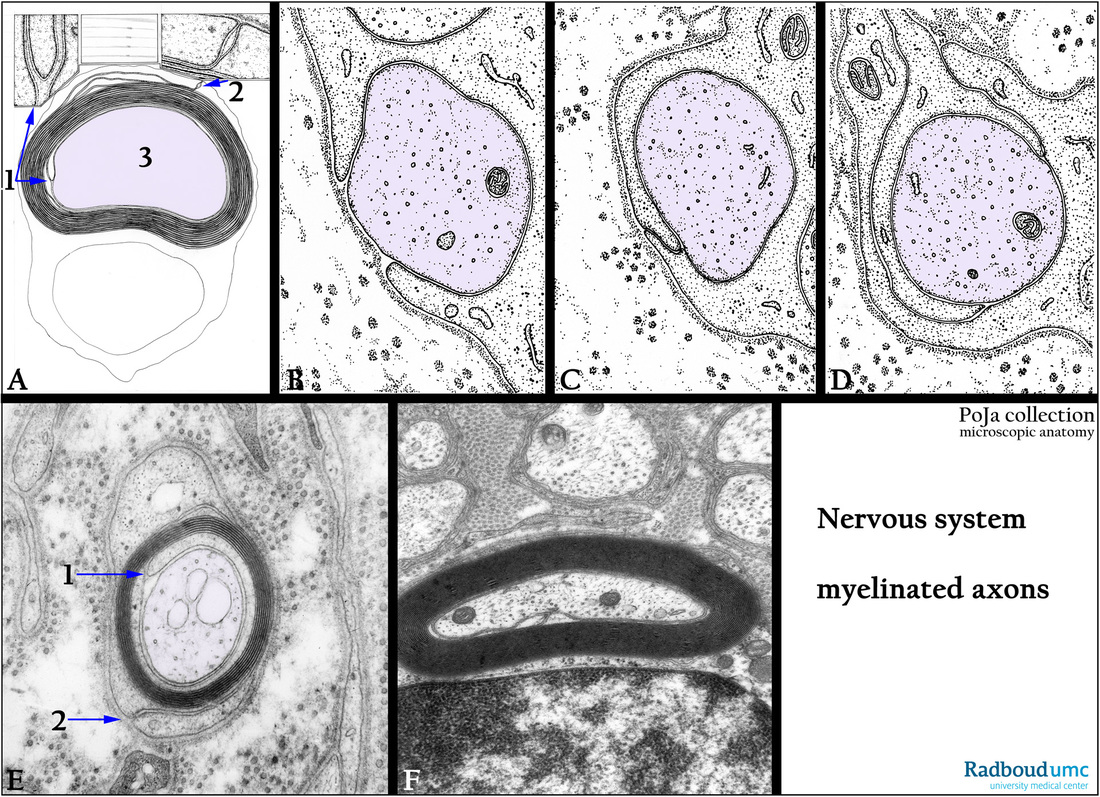
11.2 POJA-L2937+3266+3270+3271+3272+3461
Title: Development of myelin sheath around axons 1
Description:
(A-D): Electron microscopy scheme of the myelination of axons, human. (1) Inner mesaxon. (2) Outer mesaxon. (3) Axon.
(E): Electron micrograph peripheral nerve, rat. Shows the earlier process of wrapping and the first layered myelin lamellae with a distinct inner and outer mesaxon versus the advanced stage of myelination in (F). Note the basal lamina (or external lamina) as well as cross-sectioned collagen fibrils of the endoneurium in (E).
(F): Electron micrograph myelinated nerve near a principal bronchus, golden hamster.
The myelin sheath is formed from Schwann cell processes. The nerve fiber is encircled or wrapped in by the plasmalemma of the Schwann cell. Thus the folded membranes (containing lipoproteins) create lamellae concentrically around the axon. Note also the neurotubuli and the neurofilaments within the axons.
Background: The inner leaflets of the trilaminar cell membranes fuse and form a 3 nm thick membrane.
The distance between inner fused leaflets is ca. 15 nm, the so-called major period (or major dense line).
In the middle of the major period the juxtaposed outer leaflets of apposed cell membranes form a less dark
2 nm thick membrane that bisects the major period (major dense line) and is termed intraperiod line (or minor dense line).
Due to the high content of membrane lipids-proteins the membranes are stained densely with osmium tetroxide.
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, axon, peripheral nerve fiber, myelinated nerve fiber, myelin, mesaxon, Schwann cell, endoneurium, histologie, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Development of myelin sheath around axons 1
Description:
(A-D): Electron microscopy scheme of the myelination of axons, human. (1) Inner mesaxon. (2) Outer mesaxon. (3) Axon.
(E): Electron micrograph peripheral nerve, rat. Shows the earlier process of wrapping and the first layered myelin lamellae with a distinct inner and outer mesaxon versus the advanced stage of myelination in (F). Note the basal lamina (or external lamina) as well as cross-sectioned collagen fibrils of the endoneurium in (E).
(F): Electron micrograph myelinated nerve near a principal bronchus, golden hamster.
The myelin sheath is formed from Schwann cell processes. The nerve fiber is encircled or wrapped in by the plasmalemma of the Schwann cell. Thus the folded membranes (containing lipoproteins) create lamellae concentrically around the axon. Note also the neurotubuli and the neurofilaments within the axons.
Background: The inner leaflets of the trilaminar cell membranes fuse and form a 3 nm thick membrane.
The distance between inner fused leaflets is ca. 15 nm, the so-called major period (or major dense line).
In the middle of the major period the juxtaposed outer leaflets of apposed cell membranes form a less dark
2 nm thick membrane that bisects the major period (major dense line) and is termed intraperiod line (or minor dense line).
Due to the high content of membrane lipids-proteins the membranes are stained densely with osmium tetroxide.
Keywords/Mesh: nervous tissue, axon, peripheral nerve fiber, myelinated nerve fiber, myelin, mesaxon, Schwann cell, endoneurium, histologie, electron microscopy, POJA collection