12.2.3 POJA-L2608+2607+2609+2988
Title: Eustachian tube in the middle ear
Description:
Generally the 1.5 cm osseus part (within the petrous part of the temporal bone) of the human eustachian tube has a simple
tunica mucosa with simple ciliary epithelium and a thin proper lamina closely attached to the bone periosteum.
In contrast, the longer pharyngeal cartilaginous part (2.5 cm) of the tube shows a nasopharyngeal mucosa with well-developed
proper lamina, seromucous tubal glands, nerve bundles and lymph nodules.
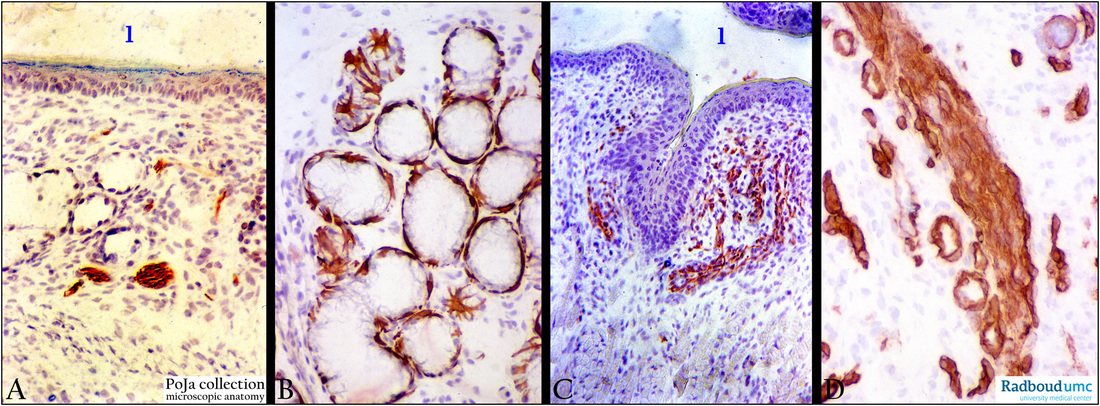
(A, C): Eustachian tube, immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and anti-neurofilament antibodies, postnatal rat, 4 days.
Lumen (1) of the tube. In the proper lamina neurofilament-positive single nerve fibres are present (branches from the maxillary
nerve as principal sensory supply), located between small tubal glands (in A) and thin skeletal muscle fibres (in C).
(B): Eustachian tube, immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and antikeratin-14 antibodies (RCK107), postnatal rat, 1 day.
Cytokeratin 14 stains strongly for the spider-like myoepithelial cells of the tubal glands (glandula tubaria).
(D): Eustachian tube, immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and antibodies against collagen IV, postnatal rat, 1 day.
Staining for collagen IV is strong in capillary basement membranes as well as between individual nerve fibres in the bundle.
Keywords/Mesh: middle ear, eustachian tube, auditory tube, seromucous gland, myoepithelial cell, cytokeratin, neurofilament, collagen IV, histology, POJA collection
Title: Eustachian tube in the middle ear
Description:
Generally the 1.5 cm osseus part (within the petrous part of the temporal bone) of the human eustachian tube has a simple
tunica mucosa with simple ciliary epithelium and a thin proper lamina closely attached to the bone periosteum.
In contrast, the longer pharyngeal cartilaginous part (2.5 cm) of the tube shows a nasopharyngeal mucosa with well-developed
proper lamina, seromucous tubal glands, nerve bundles and lymph nodules.
(A, C): Eustachian tube, immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and anti-neurofilament antibodies, postnatal rat, 4 days.
Lumen (1) of the tube. In the proper lamina neurofilament-positive single nerve fibres are present (branches from the maxillary
nerve as principal sensory supply), located between small tubal glands (in A) and thin skeletal muscle fibres (in C).
(B): Eustachian tube, immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and antikeratin-14 antibodies (RCK107), postnatal rat, 1 day.
Cytokeratin 14 stains strongly for the spider-like myoepithelial cells of the tubal glands (glandula tubaria).
(D): Eustachian tube, immunoperoxidase staining with AEC and antibodies against collagen IV, postnatal rat, 1 day.
Staining for collagen IV is strong in capillary basement membranes as well as between individual nerve fibres in the bundle.
Keywords/Mesh: middle ear, eustachian tube, auditory tube, seromucous gland, myoepithelial cell, cytokeratin, neurofilament, collagen IV, histology, POJA collection