5.4.2 POJA-La0050+L2436+2348+2943+2489+2492+2494
Title: Macula densa of the renal glomerulus in kidney II
Description:
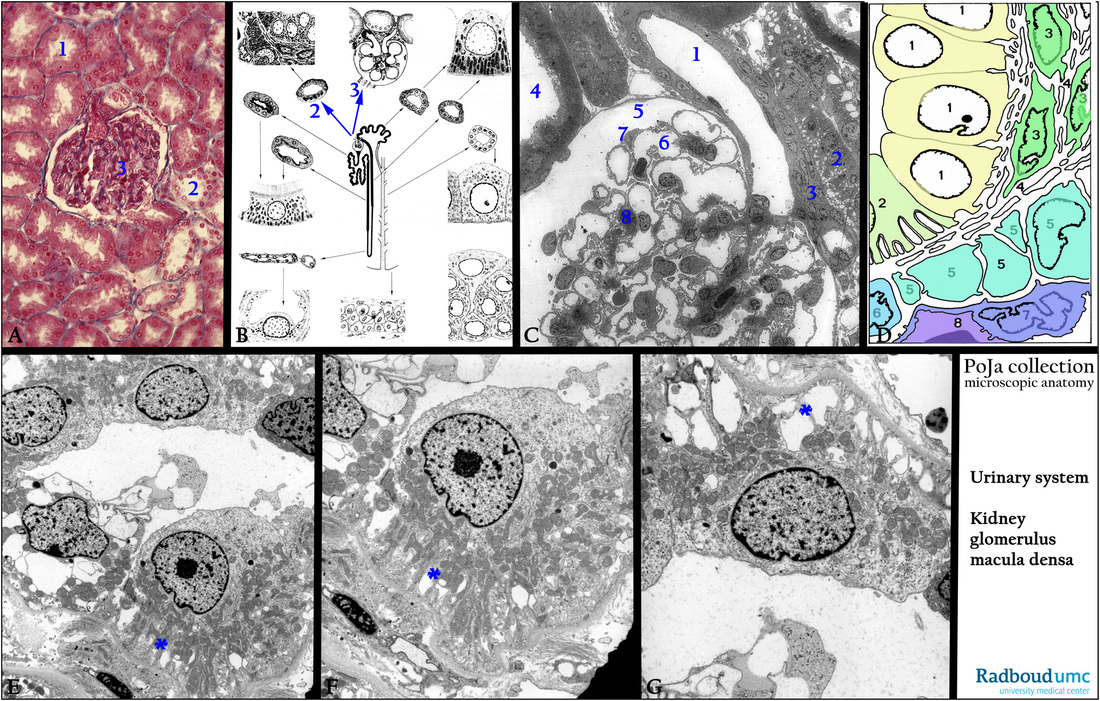
(A): Kidney cortex, stain Azan, human. Glomerulus embedded between the tubules. (1) Proximal tubule. (2) Distal tubule. (3) Glomerulus.
(B): Scheme of the nephron, human, with emphasis on (2) macula densa in distal tubule and (3) glomerulus.
(C): Electron microscopy, glomerulus, rabbit. (1) Afferent arteriole (sectioned without renin granules).
(2) Macula densa.
(3) Lacis cells.
(4) Proximal convoluted tubule with numerous microvilli and mitochondria.
(5) Glomerulus in urinary space encircled with the Bowman’s capsule.
(6) Glomerular capillary.
(7) Podocyte (visceral epithelial cell).
(8) Mesangium cell.
(D): Scheme of the macula densa, human. (1) Macula densa sensory cells.
(2) Regular cell of the distal tubule with basal invaginations
(final part of cortical thick ascending limb).
(3) Lacis cells (or Goormaghtigh cells) or extraglomerular mesangial cells.
(5) JG cells.
(6) Smooth muscle cell.
(7) Endothelial cell of afferent arteriole.
(8) Lumen of vas afferens.
(E - G): Electron microscopy macula densa, human. Note that the specialized macula densa cells are all fixed with feet processes on
the basal lamina of the tubule and exposing the dilated basal labyrinth (***). The cells are devoid of microvilli, but are well equipped
with mitochondria.
The macula densa is a specialized part within the final portion of the cortical thick ascending limb (a subdivision of the distal tubule)
being in close “contact” with the afferent vessel of the glomerulus. These cells monitor the NaCl ions in the liquid in the distal tubules.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, nephron, glomerulus, macula densa, JG cell, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Macula densa of the renal glomerulus in kidney II
Description:
(A): Kidney cortex, stain Azan, human. Glomerulus embedded between the tubules. (1) Proximal tubule. (2) Distal tubule. (3) Glomerulus.
(B): Scheme of the nephron, human, with emphasis on (2) macula densa in distal tubule and (3) glomerulus.
(C): Electron microscopy, glomerulus, rabbit. (1) Afferent arteriole (sectioned without renin granules).
(2) Macula densa.
(3) Lacis cells.
(4) Proximal convoluted tubule with numerous microvilli and mitochondria.
(5) Glomerulus in urinary space encircled with the Bowman’s capsule.
(6) Glomerular capillary.
(7) Podocyte (visceral epithelial cell).
(8) Mesangium cell.
(D): Scheme of the macula densa, human. (1) Macula densa sensory cells.
(2) Regular cell of the distal tubule with basal invaginations
(final part of cortical thick ascending limb).
(3) Lacis cells (or Goormaghtigh cells) or extraglomerular mesangial cells.
(5) JG cells.
(6) Smooth muscle cell.
(7) Endothelial cell of afferent arteriole.
(8) Lumen of vas afferens.
(E - G): Electron microscopy macula densa, human. Note that the specialized macula densa cells are all fixed with feet processes on
the basal lamina of the tubule and exposing the dilated basal labyrinth (***). The cells are devoid of microvilli, but are well equipped
with mitochondria.
The macula densa is a specialized part within the final portion of the cortical thick ascending limb (a subdivision of the distal tubule)
being in close “contact” with the afferent vessel of the glomerulus. These cells monitor the NaCl ions in the liquid in the distal tubules.
Keywords/Mesh: urinary system, kidney, nephron, glomerulus, macula densa, JG cell, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection