12.1.4 POJA-L3571+4419+2955+2569
Title: Retina III
Description:
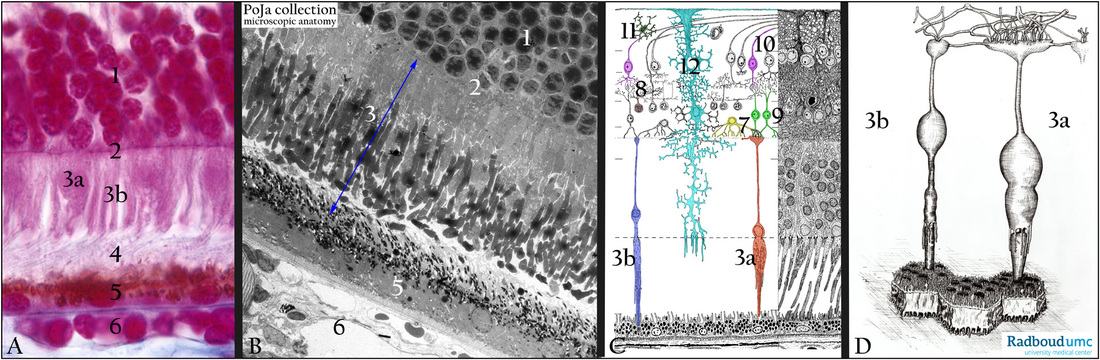
(A): Retina, stain Azan, human.
(1) Outer nuclear layer (stratum granulosum externum).
(2) Outer limiting membrane (membrana limitans externa).
(3a) Cone receptor cell.
(3b) Rod receptor cell.
(4) Layer with the outer segments of the rods and cones.
(5) Pigmented epithelial cells (RPE).
(6) Lamina choriocapillaris.
(B): Retina, electron micrograph, gerbil. Identical layers as in (A).
(3) Inner and outer segment of the receptor cells.
(C): Retina, electron microscopy scheme, human.
(3a) Cones
(3b) Rods
(7) Horizontal cell (yellow);
(8) Amacrine cell (brown).
(9) Bipolar ganglion cell (green).
(10) Multipolar ganglion cell (pink).
(11) Astrocyte.
(12) Müller cell, supporting neuroglia cell (turquoise).
Müller cells belong to the major type of glia cells. They are responsible for homeostatic and metabolic support of retinal neurons.
They control the composition of extracellular space fluid, regulate the BRB (blood-retina-barrier), and provide trophic and
anti-oxidative support of cones & rods and other neurons.
Müller cells also involve in the regulation of synaptic activities in the inner retina and release neuroactive signalling molecules
that modulate neuronal activity.
(D): Retina, electron microscopy schematic 3D-drawing of rod and cone cells with their outer segments dipped between the microvilli of the pigmented epithelium (RPE). In the outer plexiform layer synaptic contacts of the axons of cones and rods with dendrites of different neurons.
(3a) Cone pedicle with numerous penetrating processes of bipolar and horizontal cells.
(3b) Rod spherule also with penetrating extensions of bipolar and horizontal cells.
Keywords/Mesh: eye, retina, rod, cone, pigmented epithelium, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection
Title: Retina III
Description:
(A): Retina, stain Azan, human.
(1) Outer nuclear layer (stratum granulosum externum).
(2) Outer limiting membrane (membrana limitans externa).
(3a) Cone receptor cell.
(3b) Rod receptor cell.
(4) Layer with the outer segments of the rods and cones.
(5) Pigmented epithelial cells (RPE).
(6) Lamina choriocapillaris.
(B): Retina, electron micrograph, gerbil. Identical layers as in (A).
(3) Inner and outer segment of the receptor cells.
(C): Retina, electron microscopy scheme, human.
(3a) Cones
(3b) Rods
(7) Horizontal cell (yellow);
(8) Amacrine cell (brown).
(9) Bipolar ganglion cell (green).
(10) Multipolar ganglion cell (pink).
(11) Astrocyte.
(12) Müller cell, supporting neuroglia cell (turquoise).
Müller cells belong to the major type of glia cells. They are responsible for homeostatic and metabolic support of retinal neurons.
They control the composition of extracellular space fluid, regulate the BRB (blood-retina-barrier), and provide trophic and
anti-oxidative support of cones & rods and other neurons.
Müller cells also involve in the regulation of synaptic activities in the inner retina and release neuroactive signalling molecules
that modulate neuronal activity.
(D): Retina, electron microscopy schematic 3D-drawing of rod and cone cells with their outer segments dipped between the microvilli of the pigmented epithelium (RPE). In the outer plexiform layer synaptic contacts of the axons of cones and rods with dendrites of different neurons.
(3a) Cone pedicle with numerous penetrating processes of bipolar and horizontal cells.
(3b) Rod spherule also with penetrating extensions of bipolar and horizontal cells.
Keywords/Mesh: eye, retina, rod, cone, pigmented epithelium, histology, electron microscopy, POJA collection